Cancers 2023, 15(1), 190; https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15010190 - 28 Dec 2022
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2235
Abstract
Human gut microbiota physiologically and actively participates as a symbiont to a wide number of fundamental biological processes, such as absorption and metabolism of nutrients, regulation of immune response and inflammation; gut microbiota plays also an antitumor role. However, dysbiosis, resulting from a
[...] Read more.
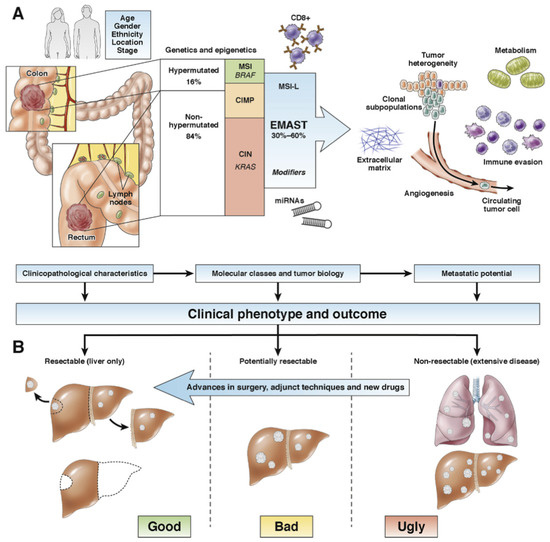
Human gut microbiota physiologically and actively participates as a symbiont to a wide number of fundamental biological processes, such as absorption and metabolism of nutrients, regulation of immune response and inflammation; gut microbiota plays also an antitumor role. However, dysbiosis, resulting from a number of different situations—dysmicrobism, infections, drug intake, age, diet—as well as from their multiple combinations, may lead to tumorigenesis and is associated with approximately 20% of all cancers. In a diagnostic, prognostic, therapeutic, and epidemiological perspective, it is clear that the bifaceted role of microbiota needs to be thoroughly studied and better understood. Here, we discuss the anti- and pro-tumorigenic potential of gut and other microbiota districts along with the causes that may change commensal bacteria from friend to foes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Non Herbal Nutraceutical, Probiotic, Vitamins and Fatty Acids in Cancer)
►
Show Figures