1
Cellular Traffic Research Group, Department of Medical Biology, Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières, Trois-Rivières, QC G9A 5H7, Canada
2
Institute of Earth Systems, University of Malta, Msida MSD 2080, Malta
3
Department of Psychiatry and Neuroscience, U. Laval and CHU Research Center, Québec, QC G9A 5H7, Canada
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17(8), 1293; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081293 - 9 Aug 2016
Cited by 56 | Viewed by 11263
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, primarily affecting dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. There is currently no cure for PD and present medications aim to alleviate clinical symptoms, thus prevention remains the ideal strategy to reduce the prevalence of this
[...] Read more.
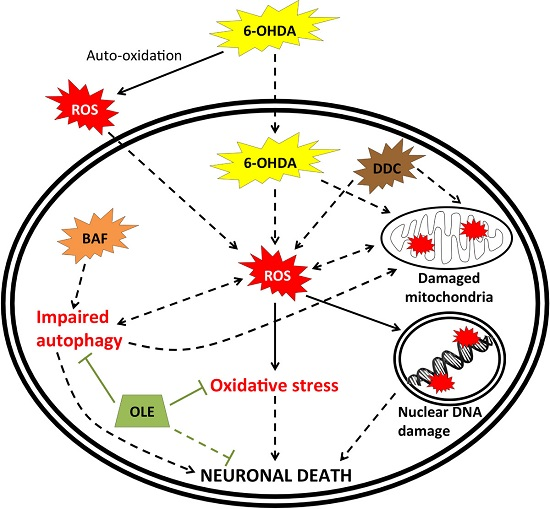
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, primarily affecting dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. There is currently no cure for PD and present medications aim to alleviate clinical symptoms, thus prevention remains the ideal strategy to reduce the prevalence of this disease. The goal of this study was to investigate whether oleuropein (OLE), the major phenolic compound in olive derivatives, may prevent neuronal degeneration in a cellular dopaminergic model of PD, differentiated PC12 cells exposed to the potent parkinsonian toxin 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA). We also investigated OLE’s ability to mitigate mitochondrial oxidative stress and modulate the autophagic flux. Our results obtained by measuring cytotoxicity and apoptotic events demonstrate that OLE significantly decreases neuronal death. OLE could also reduce mitochondrial production of reactive oxygen species resulting from blocking superoxide dismutase activity. Moreover, quantification of autophagic and acidic vesicles in the cytoplasm alongside expression of specific autophagic markers uncovered a regulatory role for OLE against autophagic flux impairment induced by bafilomycin A1. Altogether, our results define OLE as a neuroprotective, anti-oxidative and autophagy-regulating molecule, in a neuronal dopaminergic cellular model.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Mechanism of Action of Food Components in Disease Prevention)
▼
Show Figures