Journal Description
Mining
Mining
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on mining science and engineering published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, GeoRef, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 19.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Geology)
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Mining is a companion journal of Minerals.
- Journal Cluster of Geotechnical Engineering and Geology: Minerals, GeoHazards, Mining, Geotechnics, Glacies.
Latest Articles
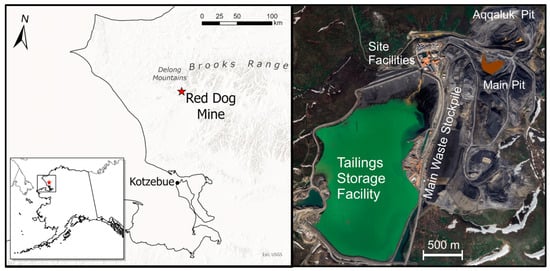
Influence of Phased Cover Placement on the Acid-Generating Main Waste Stockpile at the Red Dog Mine, Alaska, USA
Mining 2025, 5(4), 74; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040074 - 7 Nov 2025
Abstract
With the weathering of iron sulfide minerals, acid rock drainage (ARD) emanates from the 60-millon tonne Main Waste Stockpile (MWS) at the Red Dog Mine. Following completion of the stockpile, a collection trench was constructed in 2012–2013 to capture and treat a portion
[...] Read more.
With the weathering of iron sulfide minerals, acid rock drainage (ARD) emanates from the 60-millon tonne Main Waste Stockpile (MWS) at the Red Dog Mine. Following completion of the stockpile, a collection trench was constructed in 2012–2013 to capture and treat a portion of the ARD, and a cover system was emplaced from 2021 to 2025 to cover 90% of the stockpile. Select wells in the collection trench are associated with the different cover phases. Analysis of the water chemistry of samples collected at the wells indicates increased pH and decreased dissolved solids with each phase of the cover along with significant changes in flow and solutes such as aluminum, iron, sulfate, and zinc. Although the cover should continue to decrease ARD volume, acidity, and solute concentrations, an evaluation of historical acid production and iron sulfide consumption in the stockpile indicates a likely majority of the iron sulfide content remains available for weathering and acid production. Continued MWS ARD monitoring is necessary to evaluate the multi-year effect of the cover because of the variability of the pre-cover ARD, identification of seasonal and multi-year precipitation influences on ARD generation, and a yet to be determined influence of the cover on the volume of infiltrating precipitation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Sustainable Mining Engineering)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Geomechanical Modeling of the Northern Katpar Deposit (Kazakhstan): Assessing the Impact of Rock Mass Disturbance on Stability Safety Factor
by
Denis Akhmatnurov, Nail Zamaliyev, Ravil Mussin, Vladimir Demin, Baurzhan Tolovkhan, Nikita Ganyukov, Krzysztof Skrzypkowski, Waldemar Korzeniowski, Jerzy Stasica and Zbigniew Rak
Mining 2025, 5(4), 73; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040073 - 7 Nov 2025
Abstract
The development of a geomechanical model is aimed at enhancing the safety of mining operations through the determination of optimal slope angles and the probabilistic assessment of pit wall stability. For the conditions of open-pit mining, three-dimensional geomechanical models were constructed based on
[...] Read more.
The development of a geomechanical model is aimed at enhancing the safety of mining operations through the determination of optimal slope angles and the probabilistic assessment of pit wall stability. For the conditions of open-pit mining, three-dimensional geomechanical models were constructed based on the calculation of the slope stability factor using the Rocscience Slide2/Slide3 (v.9.027, 2023) software package. The stress–strain state of the rock mass at the final stage of extraction was evaluated using the finite element method. Strength reduction factors (SRF) were determined considering the physico-mechanical properties of the rocks forming the near-contour zone of the massif. The stability of the pit slopes was assessed along individual geological cross-sections in accordance with the design contours of the Northern Katpar open pit. Calculations performed using several methods confirmed the overall stability of the pit walls. The final design parameters of the projected open pit were determined. For the first time, it was established that in the southern and southwestern sectors of the Northern Katpar pit, within the elevation range of +700 to +400 m, a reduction in the SFR (from 1.18 to 1.41) occurs due to the predominance of siltstones and the presence of tectonic disturbances. The generalized results of numerical slope stability analyses for the design pit contour, together with the developed geological–structural model of the deposit, provide a basis for ensuring the safe conduct of mining operations at the site.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Application of Empirical, Analytical, and Numerical Approaches in Mining Geomechanics, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Society and Mining: Reimagining Legitimacy in Times of Crisis—The Case of Panama
by
Chafika Eddine
Mining 2025, 5(4), 72; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040072 - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
This study examines Panama’s 2023 mining restrictions to illuminate persistent legitimacy crises in extractive governance. Employing a qualitative case study, it draws on 25 semi-structured interviews with government officials, industry representatives, Indigenous leaders, local communities, mining critics and other civil society actors, alongside
[...] Read more.
This study examines Panama’s 2023 mining restrictions to illuminate persistent legitimacy crises in extractive governance. Employing a qualitative case study, it draws on 25 semi-structured interviews with government officials, industry representatives, Indigenous leaders, local communities, mining critics and other civil society actors, alongside policy and document analysis. Findings suggest that legitimacy reconstruction relies on four interdependent conditions: procedural justice, institutional trust, epistemic legitimacy, and relational governance. Stakeholders consistently emphasized transparency, capacity building, and inclusive engagement as essential for future mining activity, underscoring that technical standards alone are insufficient without credible institutions. Building on—but extending beyond—frameworks such as Social License to Operate (SLO) and Free, Prior and Informed Consent (FPIC), this paper offers Social Legitimacy for Mining (SLM) as a provisional, co-produced framework. Developed through literature synthesis and refined by diverse stakeholder perspectives, SLM is applied in Panama as an illustrative proof of concept that may inform further research and practice, while recognizing the need for additional adaptation across jurisdictions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Envisioning the Future of Mining, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Underground Pumped Hydroelectric Energy Storage in Salt Caverns in Southern Ontario, Canada: Impact of Operating Temperature on Cavern Stability and Interlayer Leakage
by
Jingyu Huang, Yutong Chai, Jennifer Williams and Shunde Yin
Mining 2025, 5(4), 71; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040071 - 3 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Underground pumped hydro storage (UPHS) in solution-mined salt caverns offers a promising approach to address the intermittency of renewable energy in flat geological regions such as Southern Ontario, Canada. This work presents the first fully coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) numerical model of a two-cavern
[...] Read more.
Underground pumped hydro storage (UPHS) in solution-mined salt caverns offers a promising approach to address the intermittency of renewable energy in flat geological regions such as Southern Ontario, Canada. This work presents the first fully coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) numerical model of a two-cavern UPHS system in Southern Ontario, providing a foundational assessment of long-term cavern stability and brine leakage behavior under cyclic operation. The model captures the key interactions among deformation, leakage, and temperature effects governing cavern stability, evaluating cyclic brine injection–withdrawal at operating temperatures of 10 °C, 15 °C, and 20 °C over a five-year period. Results show that plastic deformation is constrained to localized zones at cavern–shale interfaces, with negligible risk of tensile failure. Creep deformation accelerates with temperature, yielding maximum strains of 2.6–3.2% and cumulative cavern closure of 1.8–2.6%, all within engineering safety thresholds. Leakage predominantly migrates through limestone interlayers, while shale contributes only local discharge pathways. Elevated temperature enhances leakage due to reduced brine viscosity, but cumulative volumes remain very low, confirming the sealing capacity of bedded salt. Overall, lower operating temperatures minimize both convergence and leakage, ensuring greater stability margins, indicating that UPHS operation should preferentially adopt lower brine temperatures to balance storage efficiency with long-term cavern stability. These findings highlight the feasibility of UPHS in Ontario’s salt formations and provide design guidance for balancing storage performance with geomechanical safety.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Key Strategies and Future Prospects for Raw Material Diversification in Global Aluminum Production: A Case Study of UC RUSAL
by
Tatiana Ponomarenko, Konstantin Spivakov and Natalia Romasheva
Mining 2025, 5(4), 70; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040070 - 29 Oct 2025
Abstract
Aluminum’s unique properties have led to its widespread use across multiple industries, including transportation, aviation, power generation, construction, and food packaging. In recent years, global aluminum consumption has risen significantly, with China experiencing particularly sharp growth in both production and demand. In Russia,
[...] Read more.
Aluminum’s unique properties have led to its widespread use across multiple industries, including transportation, aviation, power generation, construction, and food packaging. In recent years, global aluminum consumption has risen significantly, with China experiencing particularly sharp growth in both production and demand. In Russia, the aluminum industry is dominated by UC RUSAL, which consolidates all Russian aluminum and alumina production facilities, along with several international operations and mining assets. Despite its global presence, the company remains heavily reliant on imported raw materials (approximately 50%) for alumina production, resulting in reduced operational efficiency and declining output. This dependency has necessitated the exploration of strategies to diversify raw material sources across different stages of the aluminum production value chain. This study identifies and classifies key diversification options for global aluminum companies, focusing on secondary aluminum production, primary aluminum production, and alumina extraction from mined minerals, industrial waste, and by-products. The options were evaluated based on predefined criteria (feasibility, cost per Mg of alumina, logistics, alumina output, and economic security), and two options were selected. The research substantiates the feasibility of diversifying production through nepheline utilization. For the medium term, an economic efficiency assessment was conducted for a proposed 30% capacity expansion at the Pikalevo Alumina Refinery. Additionally, long-term opportunities for increasing aluminum output were identified, including leveraging foreign assets while accounting for associated risks.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Mining Technology and Equipment: Innovations and Case Studies)
►▼
Show Figures
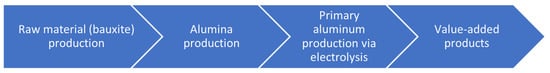
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Urban Mining of Bivalve Shell Waste as a Sustainable Alternative to Limestone Exploitation: A Review on Alkali-Activated Cements and Mortars
by
Arthur Paim Cescon, Giovani Jordi Bruschi and Eduardo Pavan Korf
Mining 2025, 5(4), 69; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040069 - 29 Oct 2025
Abstract
The concept of urban mining refers to the recovery and valorization of valuable resources from urban and industrial waste, contributing to circular economy principles. Within this framework, the present study provides a critical review of alkali-activated binders incorporating bivalve mollusk shells as alternative
[...] Read more.
The concept of urban mining refers to the recovery and valorization of valuable resources from urban and industrial waste, contributing to circular economy principles. Within this framework, the present study provides a critical review of alkali-activated binders incorporating bivalve mollusk shells as alternative calcium sources. Shells from oysters, scallops, mussels, clams, cockles, and periwinkles were examined, either in their natural or calcined forms, for use as calcium sources, alkaline activators, or fillers in low-carbon binders. The review evaluates key processing parameters, including precursor composition, type and concentration of alkaline activators, curing conditions, and calcination temperatures, and compares the resulting mechanical, chemical, and microstructural properties. In addition, several studies report applications of these binders in soil stabilization and heavy metal immobilization, demonstrating performances comparable to Portland cement. The findings confirm the technical potential of mollusk shell residues and their contribution to the circular economy by diverting aquaculture waste from landfills and marine environments. Nonetheless, significant knowledge gaps persist, including the limited investigation of non-oyster species, the absence of field-scale studies, and the lack of resource mapping, life cycle, or economic assessments. This synthesis highlights preliminary insights, such as optimal calcination temperatures between 700 and 900 °C and effective combinations with silica and alumina-rich residues. Overall, it outlines a pathway toward transforming an underutilized waste stream into sustainable and technically viable construction materials.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Envisioning the Future of Mining, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Real-Time Drilling Control for Hanging-Wall Stability: SCADA-Based Mitigation of Overbreak and Dilution in Long-Hole Stoping
by
Eustina Gurumani, Tawanda Zvarivadza, Lawrence Ndhlovu, Rejoice Moyo, Richard Masethe, Mbalenhle Mpanza and Moshood Onifade
Mining 2025, 5(4), 68; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040068 - 22 Oct 2025
Abstract
Study develops and field-validates a SCADA-based real-time monitoring system to reduce unplanned dilution and hanging-wall over-break in underground long-hole stoping at a Zimbabwean gold mine. The objectives were to detect and constrain drilling deviation in real time, quantify the impact on stope stability
[...] Read more.
Study develops and field-validates a SCADA-based real-time monitoring system to reduce unplanned dilution and hanging-wall over-break in underground long-hole stoping at a Zimbabwean gold mine. The objectives were to detect and constrain drilling deviation in real time, quantify the impact on stope stability and dilution, and evaluate operational and economic effects. The system integrates IMU inclinometers (hole angle), rotary encoders (depth), and LiDAR (collar spacing) with a Siemens S7 PLC (RS Americas, Fort Worth, TX, USA) and AVEVA™ InTouch HMI 2023 R2. Field trials across three production stopes (12L, 14L, 15L) compared baseline manual monitoring to SCADA control. Mean angular deviation fell from 0.8–1.6° to 0.2–0.3°, length deviation from 0.8–1.1 m to 0.05–0.08 m, and positional error from 0.25–0.32 m to 0.04–0.06 m; major collapses were eliminated, and ELOS dropped (e.g., 0.20 m to 0.05 m). Dilution decreased from 25% (typical 21–26%) to 16–18%, with mill feed grade rising from 1.90 to 2.25 g/t; production rates were maintained, with brief auto-stops in 5% of holes and rapid operator correction. Real-time drilling control materially reduces unplanned dilution and improves wall stability without productivity penalties, yielding compelling economics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mine Automation and New Technologies, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Methodological Approach in Selecting Sustainable Indicators (IPREGS) and Creating an Aggregated Composite Index (AKI) for Assessing the Sustainability of Mineral Resource Management: A Case Study of Varaždin County
by
Melita Srpak, Darko Pavlović, Karolina Novak Mavar and Ivan Zelenika
Mining 2025, 5(4), 67; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040067 - 20 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Varaždin County is rich in mineral resources, attracting considerable investor interest in opening new exploration areas and expanding existing exploitation fields. Since the economic value of mineral resources changes with market conditions, continuous professional assessment is required. Although the proposed methodological framework is
[...] Read more.
Varaždin County is rich in mineral resources, attracting considerable investor interest in opening new exploration areas and expanding existing exploitation fields. Since the economic value of mineral resources changes with market conditions, continuous professional assessment is required. Although the proposed methodological framework is broadly applicable to mineral resource management, this case study focuses on the exploitation of construction sand and gravel deposits in Varaždin County. In this way, it addresses the sustainability challenges characteristic of quarry operations rather than large-scale mining projects. The objective of this study was to develop and test a new method for quantifying sustainability indicators in the mineral resource management (spatial, resource-related, environmental, economic, and social sustainability—IPREGS) and for calculating an aggregated composite index (AKI) using a pilot project for construction sand and gravel. The research establishes a cause–effect relationship between quantified indicators (IPREGS) and the newly established aggregated composite index (AKI). Methodologically, the study applied multivariate analysis to questionnaire data, enabling the selection, weighting, and aggregation of indicators and the design of a conceptual framework for AKI calculation. The resulting methodology provides an instrument for monitoring and improving sustainable mineral resource management, supporting the objectives of the circular economy. The findings highlight the potential of the AKI to reduce systemic inefficiencies, guide policy development, and offer a transparent mechanism for assessing both implementation and effectiveness. This significantly improves the current state and strengthens the basis for evidence-based economic policy-making. The case study in Varaždin County further demonstrated that the AKI not only reproduces administrative decisions with high consistency but also clarifies how applicants should proceed in cases of partial acceptance and how policymakers can interpret conflicting outcomes across different index variants.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Toward Sustainable Mining: Exploring Alternative Mineral Resources and Innovative Extraction Techniques
by
Roohollah Shirani Faradonbeh, Mohammad Imtiaz Shah, Moein Bahadori and Hyoongdoo Jang
Mining 2025, 5(4), 66; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040066 - 18 Oct 2025
Abstract
The relentless pace of industrialisation and globalisation has precipitated the rapid depletion of surface mineral deposits, presenting a formidable challenge to conventional mining operations and exerting a detrimental impact on their profitability. This depletion, coupled with the escalating demand for minerals, has driven
[...] Read more.
The relentless pace of industrialisation and globalisation has precipitated the rapid depletion of surface mineral deposits, presenting a formidable challenge to conventional mining operations and exerting a detrimental impact on their profitability. This depletion, coupled with the escalating demand for minerals, has driven prices to unprecedented highs, thereby inflating operating costs across various industries. Traditional surface and underground mining methods, struggling to meet burgeoning demands, contribute significantly to environmental degradation and substantial energy consumption. In response to these challenges, this study advocates for a paradigm shift from conventional mining methods and mineral resources toward untapped alternatives that hold the potential for enhanced economic viability and sustainability. Utilising environmentally friendly techniques and adopting more economical approaches becomes paramount in addressing the pressing demands of the current era and securing resources for future generations. This short review examines potential alternative mineral resources and the associated mining methods, including fluidised mining, deep-sea mining, brine mining, urban mining, in-situ and heap leaching, and space mining. A meticulous evaluation of the state-of-the-art technologies developed for these unconventional methods is conducted, including an assessment of their respective advantages and disadvantages. Finally, the study deliberates on the prospects of each approach, elucidating their potential contributions to alleviating the global metal crisis. This research provides insights that can inform sustainable mining practices and guide the industry toward a more environmentally responsible and economically viable future. The urgency of such a transition is underscored by the need to address the challenges posed by conventional mining and ensure the availability of mineral resources for generations to come.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mine Automation and New Technologies, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Comprehensive Technical and Economic Analysis of Rubber-Tyred Transport Implementation in Longwall Mining: A Case Study on the V.D. Yalevsky Coal Mine
by
Andrey Sidorenko, Aleksey Kriukov, Anatoliy Meshkov and Sergey Sidorenko
Mining 2025, 5(4), 65; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040065 - 16 Oct 2025
Abstract
This article presents a concept for modernizing the transport system of high-performance coal mines through the transition from traditional monorail to rubber-tyred transport (RTT). The study was conducted based on materials from the V.D. Yalevsky Mine of JSC “SUEK-Kuzbass” with daily longwall output
[...] Read more.
This article presents a concept for modernizing the transport system of high-performance coal mines through the transition from traditional monorail to rubber-tyred transport (RTT). The study was conducted based on materials from the V.D. Yalevsky Mine of JSC “SUEK-Kuzbass” with daily longwall output up to 60,000 tons and production capacity up to 10 million tons per year. Analysis of the existing transport system efficiency revealed low equipment utilization rates (52–70%) and significant time losses during shift changeovers (up to 4.3 h/day in development workings). Technical solutions for phased RTT implementation were developed, including six roadway surface scenarios and a fleet composition of 60 specialized equipment units. The research methodology is based on time study observations using the automated “Granch” system, analysis of equipment utilization coefficients, and economic–mathematical modeling using NPV, MIRR, and payback period. The transition to rubber-tyred transport provides a five-fold increase in travel speed (from 4.5 to 25 km/h), reduction in shift changeover time to zero, increase in operating time by 20% in development and 4.5% in extraction, and a reduction in longwall move duration from 173–209 to 88 days. Additional coal production amounts to 6.5 million tons. Economic justification shows NPV of USD 64.2 million with MIRR of 2.4% and a payback period of 4.5 years.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Mining Technology and Equipment: Innovations and Case Studies)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
From Agro-Industrial Waste to Gold Lixiviant: Evaluating Cassava Wastewater Applications in Artisanal Mining
by
Emiliano Mendonça Silva, Maria do Carmo S. Barreto, Marcello M. Veiga and Giorgio De Tomi
Mining 2025, 5(4), 64; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040064 - 13 Oct 2025
Abstract
Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining (ASGM) is a primary source of global mercury pollution, creating an urgent need for sustainable, low-cost alternatives to amalgamation. This study investigates the use of cassava wastewater (manipueira), a cyanogenic agricultural byproduct, as a lixiviant for
[...] Read more.
Artisanal and Small-Scale Gold Mining (ASGM) is a primary source of global mercury pollution, creating an urgent need for sustainable, low-cost alternatives to amalgamation. This study investigates the use of cassava wastewater (manipueira), a cyanogenic agricultural byproduct, as a lixiviant for a gold concentrate (14.30–15.87 ppm Au) from an artisanal mine. Two approaches were evaluated: direct leaching with manipueira in natura (250 ppm CN−) in single and double 8 h and 12 h cycles, and leaching with a cyanide solution concentrated from dilute manipueira (100 ppm CN−) via a simplified air-stripping system. Results were benchmarked against the mine’s amalgamation (44.7% recovery) and 30-day heap leach (75.8% recovery) processes. The most effective method observed was a two-cycle, 8 h leach with manipueira in natura, which achieved a mean gold recovery of
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Sustainable Mining Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Assessment of Dyke-Induced Strength Variations in Coal and Its Surroundings Using a Non-Destructive In Situ Testing Approach
by
Sahendra Ram, Ashok Kumar, Krzysztof Skrzypkowski, Jerzy Stasica, Zbigniew Rak and Maciej Madziarz
Mining 2025, 5(4), 63; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040063 - 8 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In situ uniaxial compressive strength mapping across dykes of different thicknesses within a coal mass and its influence zones at two mines in the Jharia coalfield has been carried out in this study. It provides insight into the manner in which the dyke
[...] Read more.
In situ uniaxial compressive strength mapping across dykes of different thicknesses within a coal mass and its influence zones at two mines in the Jharia coalfield has been carried out in this study. It provides insight into the manner in which the dyke intrusion altered the adjacent coal mass, leading to the formation of jhama and pulverized zones with modified strength properties. A Digital Schmidt Hammer with an impact energy of 2.207 Nm was used to estimate the in situ uniaxial compressive strength of the coal around the seam–dyke interface in different mines selected for the study. At the first mine, the dyke had a thickness of approximately 15 m, with its influence on the surrounding coal mass extending up to 13.5 m on both sides. Unlike the first mine, the dyke in the second mine was merely 1 m thick, with its effect limited to a zone of around 2.1 m. The average uniaxial compressive strength of unaltered (intact) coal at the studied mines ranged from 31.7 to 38.5 MPa. The zones influenced by the dyke at both mines comprised jhama, which exhibited a 15–18% higher uniaxial compressive strength compared to the surrounding intact coal, and pulverized coal zones, which showed a 46–56% reduction in strength relative to the intact coal.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Modernization of Hoisting Operations Through the Design of an Automated Skip Loading System—Enhancing Efficiency and Sustainability
by
Keane Baulen Size, Rejoice Moyo, Richard Masethe, Tawanda Zvarivadza and Moshood Onifade
Mining 2025, 5(4), 62; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040062 - 4 Oct 2025
Abstract
This study presents the design and validation of an automated skip loading system for vertical shaft hoisting operations, aimed at addressing inefficiencies in current manual systems that contribute to consistent underperformance in meeting daily production targets. Initial assessments revealed a task completion rate
[...] Read more.
This study presents the design and validation of an automated skip loading system for vertical shaft hoisting operations, aimed at addressing inefficiencies in current manual systems that contribute to consistent underperformance in meeting daily production targets. Initial assessments revealed a task completion rate of 91.6%, largely due to delays and inaccuracies in manual ore loading and accounting. To resolve these challenges, an automated system was developed using a bin and conveyor mechanism integrated with a suite of industrial automation components, including a programmable logic controller (PLC), stepper motors, hydraulic cylinders, ultrasonic sensors, and limit switches. The system is designed to transport ore from the draw point, halt when one ton is detected, and activate the hoisting process automatically. Digital simulations demonstrated that the automated system reduced loading time by 12% and increased utilization by 16.6%, particularly by taking advantage of the 2 h post-blast idle period. Financial evaluation of the system revealed a positive Net Present Value (NPV) of $1,019,701, a return on investment (ROI) of 69.7% over four years, and a payback period of 2 years and 11 months. The study concludes that the proposed solution significantly improves operational efficiency and recommends further enhancements to the hoisting infrastructure to fully optimize performance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mine Automation and New Technologies, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Beyond Traceability: Leveraging Opportunities and Innovation in Chain of Custody Standards for the Mining Industry
by
Thania Nowaz, Samuel Olmos Betin, Lukas Förster, Paulina Fernandez and Oscar Jaime Restrepo Baena
Mining 2025, 5(4), 61; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040061 - 25 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Organisations are increasingly adopting the Chain of Custody (CoC) standards in the mining industry to enhance the traceability of minerals. It ensures that the minerals they have received are from credible sources and accompanied by verifiable information. However, unlikeother industries such as timber,
[...] Read more.
Organisations are increasingly adopting the Chain of Custody (CoC) standards in the mining industry to enhance the traceability of minerals. It ensures that the minerals they have received are from credible sources and accompanied by verifiable information. However, unlikeother industries such as timber, where the effectiveness and benefits of CoC standards are mainly explored, this study subtly shifts the focus towards identifying strategic opportunities and innovation areas within the CoC standards that could extend beyond traceability. Four CoC standards were selected, and their provisions examined. It was found that implementing these requirements could not only enhance transparency but also support broader sustainability goals across the entire value chain. The study also identifies several challenges that could act as barriers to the CoC system, and these are seen as opportunities for innovative approaches to enhance the effectiveness of the standards. These are labelled as transformative innovation areas, and while they do include blockchains and analytical proof of origin technologies, this study also seeks to advocate for solutions that are more pragmatic and scalable. By identifying opportunities and areas of innovation, the findings will help improve the practical implementation of the standards and suggest areas for future evaluations of effectiveness that could consider aspects beyond traceability, such as sustainability and transparency.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
FLAC3D-IMASS Modelling of Rock Mass Damage in Unsupported Underground Mining Excavations: A Safety Factor-Based Framework
by
Mahdi Saadat, Mattin Khishvand and Andrew Seccombe
Mining 2025, 5(4), 60; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040060 - 24 Sep 2025
Abstract
The implementation and application of a safety factor (SF)-based numerical framework in FLAC3D-IMASS (Itasca Model for Advanced Strain Softening) is presented for the evaluation of the short-term stability of unsupported underground excavations in sedimentary rock masses during pillar recovery in bord-and-pillar mining. The
[...] Read more.
The implementation and application of a safety factor (SF)-based numerical framework in FLAC3D-IMASS (Itasca Model for Advanced Strain Softening) is presented for the evaluation of the short-term stability of unsupported underground excavations in sedimentary rock masses during pillar recovery in bord-and-pillar mining. The stability of underground openings during the initial hours post-excavation must be ensured, as they are not accessed thereafter; therefore, short-term stability assessment is essential. The framework was specifically calibrated to field observations and applied to a case study from an Australian bord-and-pillar mine, focusing on plunge and bellout configurations commonly used during the pillar extraction stage to enhance ore recovery. The modelling approach was integrated with rock mass degradation behavior under static loading conditions and was used to calculate three-dimensional distributions of SF to identify potential failure zones. The results demonstrate that the coal (CO) roof scenario generally maintains structural stability, while the impure coal (Cox) roof scenario is observed to exhibit significant instability, particularly at greater excavation advancement. Among the tested bellout geometries, 8.0 m spans were observed to provide improved performance due to shorter tunnel lengths that enhance confinement and reduce the volume of disturbed rock. Overall, the proposed SF framework effectively captures localized failure mechanisms and is demonstrated as a practical design tool for assessing the short-term stability of unsupported structures during critical stages of underground mining operations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Application of Empirical, Analytical, and Numerical Approaches in Mining Geomechanics, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Empirical–Analytical Model of Mine Water Level Rebound
by
Dmytro Rudakov, Somayeh Sharifi and Sebastian Westermann
Mining 2025, 5(4), 59; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5040059 - 23 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper aims to develop a robust empirical–analytical model using the statistics of mine water level rebound in abandoned mines and the basic physical principles of underground hydraulics. The data collected and treated included the time series of the mine water level for
[...] Read more.
This paper aims to develop a robust empirical–analytical model using the statistics of mine water level rebound in abandoned mines and the basic physical principles of underground hydraulics. The data collected and treated included the time series of the mine water level for 35 closed and flooded mines from four European countries. Within the developed model, mine water level evolution is governed by an ordinary differential equation with one fitting parameter that depends on the floodable cavity volume in a mine and water inflow before flooding begins. The model assumes that rock properties and residual void distribution are homogeneous, and the mines being flooded are almost isolated hydraulically from the neighboring ones. The exponential formula, as the governing equation solution, was found to be the most suitable for fitting the measurements. The calculated exponential curves allow for excellent or very good fitting of the measured water levels for 17 of 35 mines, and acceptable fitting for 11 mines in terms of minimizing mean-square-root deviation. The proposed approach can be applied to preliminary assessments of mine water level rebound in developing and calibrating sophisticated numerical flow models.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Underground Pumped Hydroelectric Energy Storage in Salt Caverns in Southern Ontario, Canada: Layout and Working Pressure Design
by
Jingyu Huang, Yutong Chai, Jennifer Williams and Shunde Yin
Mining 2025, 5(3), 58; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5030058 - 16 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
As the global shift toward renewable energy accelerates, large-scale energy storage is essential to balance intermittent supply and growing demand. While conventional Pumped Hydro Storage remains dominant, Underground Pumped Hydro Storage (UPHS) offers a promising alternative, particularly in flat regions with ample subsurface
[...] Read more.
As the global shift toward renewable energy accelerates, large-scale energy storage is essential to balance intermittent supply and growing demand. While conventional Pumped Hydro Storage remains dominant, Underground Pumped Hydro Storage (UPHS) offers a promising alternative, particularly in flat regions with ample subsurface space. Southern Ontario, Canada, underlain by thick salt formations and a history of salt mining, presents favorable conditions for UPHS development, yet relative studies remain limited. This work presents the first UPHS-specific geomechanical feasibility assessment in the Canadian Salina Group, introducing a paired-cavern layout tied to Units B and A2 and explicitly capturing both elasto-plastic and creep behavior. Using COMSOL Multiphysics 6.3, a three-dimensional numerical model was developed featuring two vertically separated cylindrical caverns located in Unit B and the lower part of Unit A2. A 24 h operating cycle was simulated over a 10-year period, incorporating elasto-plastic deformation and salt creep. Minimum working pressures were varied to evaluate long-term cavern stability. The results show that a minimum pressure of 0.3 σv balances structural integrity and operational efficiency, with creep strain and volumetric convergence remaining within engineering limits. Beyond previous salt-cavern studies focused on hydrogen or CAES, this study provides the first coupled elasto-plastic and creep simulation tailored to UPHS operations in bedded salt, establishing a safe operating-pressure guideline and offering site-relevant design insights for modular underground energy storage systems in sedimentary basins.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Technogenic Waste in Backfill Composite Is a Paradigm of Circular Economy
by
Marat M. Khayrutdinov, Alexander V. Aleksakhin, Tatiana N. Kibuk, Lyudmila N. Korshunova, Maria A. Lozinskaya, Olga Yu. Legoshina, Oleg O. Skryabin and Galina V. Kruzhkova
Mining 2025, 5(3), 57; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5030057 - 15 Sep 2025
Abstract
The depletion of shallow coal reserves necessitates a shift from open-pit to underground mining, increasing the need for safe and efficient backfill systems. However, traditional backfill materials—especially cement—are costly and environmentally burdensome. To address this, our study explores a sustainable alternative using industrial
[...] Read more.
The depletion of shallow coal reserves necessitates a shift from open-pit to underground mining, increasing the need for safe and efficient backfill systems. However, traditional backfill materials—especially cement—are costly and environmentally burdensome. To address this, our study explores a sustainable alternative using industrial waste, contributing to the principles of a circular economy. This research presents a novel backfill formulation that achieves full cement replacement through the use of fly ash, supplemented with nanocrystalline silica and glass fiber to enhance strength and setting dynamics. Eighteen sample sets were prepared for each composition, using consistent mixing, curing, and testing protocols. Mechanical strength was evaluated at multiple curing intervals alongside microstructural characterization using SEM and XRD. The results show that mixtures containing nanomodified silica and fiber exhibit significantly improved compressive, shear, and splitting strength—up to 40% higher than fly ash-only compositions. Microstructural analysis revealed accelerated C-S-H gel development, reduced porosity, and more uniform pore structures over time. These findings confirm the mechanical viability and economic potential of waste-based backfill systems. The proposed formulation enables safer underground operations, improved extraction efficiency, and reduced environmental impact—offering a scalable solution for modern coal mining.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Mining Technology and Equipment: Innovations and Case Studies)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Geotechnical Design of Barrier Pillar Between Boxcut and Underground Mining for Shallow Dipping Orebodies: A Case Study
by
Benedict Ncube, Hideki Shimada, Takashi Sasaoka, Akihiro Hamanaka, Koki Kawano and Joan Atieno Onyango
Mining 2025, 5(3), 56; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5030056 - 10 Sep 2025
Abstract
A barrier pillar between the surface and underground mining sections provides a critical buffer zone in the transition from the boxcut highwall to underground sections by isolating stress fields from underground sections and preventing them from affecting the boxcut highwall slope. In this
[...] Read more.
A barrier pillar between the surface and underground mining sections provides a critical buffer zone in the transition from the boxcut highwall to underground sections by isolating stress fields from underground sections and preventing them from affecting the boxcut highwall slope. In this study, an empirical scaled span method and Rocscience RS2 software were used to conduct parametric studies on key parameters for designing barrier pillars and analyzing the room and pillar design for a planned underground mine on the Great Dyke, Zimbabwe. The approach included analyzing the effect of barrier pillar width, assuming a 10° dipping angle of the orebody, with room and pillar dimensions of 7 m and 6 m, respectively. The impact on boxcut slope stability and the roof of the first stope was monitored. The stability of the barrier pillar was analyzed for varying widths (6 m, 10 m, 20 m, 30 m, and 40 m) and orebody dipping angles (0°, 10°, 20°, 30°, and 40°). The effect of deteriorated rock mass conditions, represented by Geological Strength Index (GSI) values from 30 to 50, was assessed. The optimum room and pillar design was evaluated against the planned 6 m pillar sizes. This comprehensive study aims to support the integrity and longevity of the critical structures of the mining operation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Application of Empirical, Analytical, and Numerical Approaches in Mining Geomechanics, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Numerical Investigation of Ultra-Long Gravity Heat Pipe Systems for Geothermal Power Generation at Mount Meager
by
Yutong Chai, Wenwen Cui, Ao Ren, Soheil Asgarpour and Shunde Yin
Mining 2025, 5(3), 55; https://doi.org/10.3390/mining5030055 - 9 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The Super-long Gravity Heat Pipe (SLGHP) is an efficient geothermal energy utilization technology that can transmit thermal energy by fully utilizing natural temperature differences without external energy input. This study focuses on the high-altitude geothermal environment of Mount Meager, Canada, and employs numerical
[...] Read more.
The Super-long Gravity Heat Pipe (SLGHP) is an efficient geothermal energy utilization technology that can transmit thermal energy by fully utilizing natural temperature differences without external energy input. This study focuses on the high-altitude geothermal environment of Mount Meager, Canada, and employs numerical simulations and dynamic thermal analysis to systematically investigate the thermal transport performance of the SLGHP system under both steady-state and dynamic operating conditions. The study also examines the impact of various structural parameters on the system’s performance. Three-dimensional CFD simulations were conducted to analyze the effects of pipe diameter, length, filling ratio, working fluid selection, and pipe material on the heat transfer efficiency and heat flux distribution of the SLGHP. The results indicate that working fluids such as CO2 and NH3 significantly enhance the heat flux density, while increasing pipe diameter may reduce the amount of liquid retained in the condenser section, thereby affecting condensate return and thermal stability. Furthermore, dynamic thermal analysis using a three-node RC network model simulated the effects of diurnal temperature fluctuations and variations in the convective heat transfer coefficient in the condenser section on system thermal stability. The results show that the condenser heat flux can reach a peak of 5246 W/m2 during the day, while maintaining a range of 2200–2600 W/m2 at night, with the system exhibiting good thermal responsiveness and no significant lag or flow interruption. In addition, based on the thermal output of the SLGHP system and the integration with the Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) system, the power generation potential analysis indicates that the system, with 100 heat pipes, can provide stable power generation of 50–60 kW. In contrast to previous SLGHP studies focused on generalized modeling, this work introduces a site-specific CFD–RC framework, quantifies structural sensitivity via heat flux indices, and bridges numerical performance with economic feasibility, offering actionable insights for high-altitude deployment. This system has promising practical applications, particularly for providing stable renewable power in remote and cold regions. Future research will focus on field experiments and system optimization to further improve system efficiency and economic viability.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Crystals, Materials, Minerals, Mining, Toxics
Innovative Strategies to Mitigate the Impact of Mining
Topic Editors: Chongchong Qi, Qiusong Chen, Danial Jahed ArmaghaniDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
Minerals, Mining, Geosciences, Water, Remote Sensing
From Earth to Innovation: Modern Trends in Mining, Geoinformation, and Geoscientific Applications
Topic Editors: Justyna Woźniak, Przemysław Kowalczuk, Artur KrawczykDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topic in
Materials, Mining, Recycling, Resources, Sustainability, Minerals, Geosciences, Environments
Sustainable Recycling and Reuse of Industrial By-Products or Waste from Geo-Resource Exploitation
Topic Editors: Sossio Fabio Graziano, Rossana Bellopede, Giovanna Antonella Dino, Nicola CaredduDeadline: 30 May 2026
Topic in
Metals, Minerals, Mining
Innovations and Sustainable Approaches in Mining, Metallurgy, Technology and Materials Engineering: Insights from IOC 2025
Topic Editors: Markus A. Reuter, Peizhong Feng, Ljubiša BalanovićDeadline: 30 August 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Mining
Mine Management Optimization in the Era of AI and Advanced Analytics
Guest Editors: Pratt Rogers, Muhammet Mustafa Kahraman, Yuan LiDeadline: 20 December 2025
Special Issue in
Mining
Feature Papers in Sustainable Mining Engineering
Guest Editors: Mostafa Benzaazoua, Yassine Ait-KhouiaDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Mining
Advances in Mining Technology and Equipment: Innovations and Case Studies
Guest Editors: Fangwei Xie, Nikita BabyrDeadline: 2 February 2026
Special Issue in
Mining
Application of Empirical, Analytical, and Numerical Approaches in Mining Geomechanics, 2nd Edition
Guest Editors: Mohammad H.B. (Farzine) Nasseri, Bibhu MohantyDeadline: 31 March 2026