- Article
Light-YOLO-Pepper: A Lightweight Model for Detecting Missing Seedlings
- Qiang Shi,
- Yongzhong Zhang and
- Yafei Wang
- + 1 author
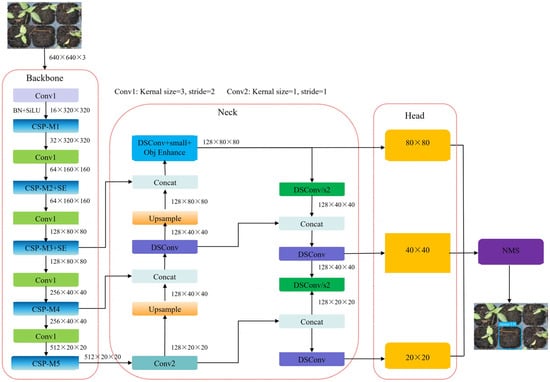
The aim of this study was to accurately meet the demand of real-time detection of seedling shortage in large-scale seedling production and solve the problems of low precision of traditional models and insufficient adaptability of mainstream lightweight models. This study proposed a Light-YOLO-Pepper seedling shortage detection model based on the improvement of YOLOv8n. This model was based on YOLOv8n. The SE (Squeeze-and-Excitation) attention module was introduced to dynamically suppress the interference of the nutrient soil background and enhance the features of the seedling shortage area. Depth-separable convolution (DSConv) was used to replace the traditional convolution, which can reduce computational redundancy while retaining core features. Based on K- means clustering, customized anchor boxes were generated to adapt to the hole sizes of 72-unit (large size) and 128-unit (small size and high-density) seedling trays. The results show that the overall mAP@0.5, accuracy and recall rate of Light-YOLO-Pepper model were 93.6 ± 0.5%, 94.6 ± 0.4% and 93.2 ± 0.6%, which were 3.3%, 3.1%, and 3.4% higher than YOLOv8n model, respectively. The parameter size of the Light-YOLO-Pepper model was only 1.82 M, the calculation cost was 3.2 G FLOPs, and the reasoning speeds with regard to the GPU and CPU were 168.4 FPS and 28.9 FPS, respectively. The Light-YOLO-Pepper model was superior to the mainstream model in terms of its lightweight and real-time performance. The precision difference between the two seedlings was only 1.2%, and the precision retention rate in high-density scenes was 98.73%. This model achieves the best balance of detection accuracy, lightweight performance, and scene adaptability, and can efficiently meet the needs of embedded equipment and real-time detection in large-scale seedling production, providing technical support for replanting automation.
15 January 2026