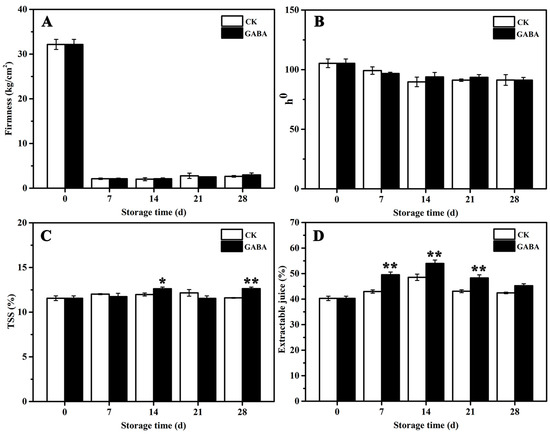
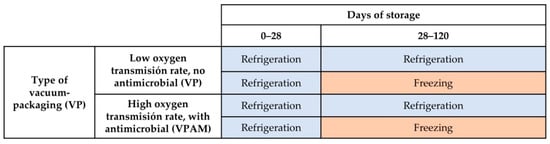
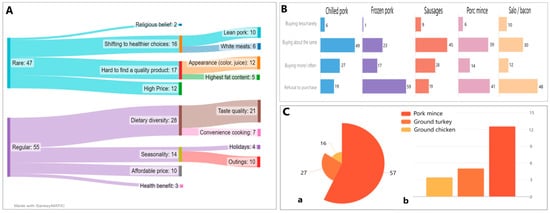
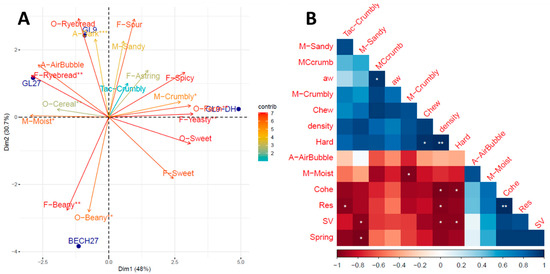
Foods 2023, 12(4), 697; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040697 - 6 Feb 2023
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 2838
Abstract
There is a need to comprehensively evaluate the rice quality of different rice varieties under different nitrogen treatments. Therefore, in this study, we used twenty-one hybrid indica rice varieties and twenty-three inbred japonica rice varieties with three nitrogen fertilizer levels to investigate differences
[...] Read more.
There is a need to comprehensively evaluate the rice quality of different rice varieties under different nitrogen treatments. Therefore, in this study, we used twenty-one hybrid indica rice varieties and twenty-three inbred japonica rice varieties with three nitrogen fertilizer levels to investigate differences in rice qualities. As compared with hybrid indica rice, inbred japonica rice had lower coefficient of variation values for grain shape, mild rice percentage, and head rice percentage, but relatively higher coefficient of variation values for chalkiness traits, appearance, and taste value of cooked rice. A principal component analysis and membership function method were used to comprehensively evaluate the qualities of rice. The overall eating quality value by sensory evaluation and head rice percentage explained 61.3% and 67.9% of the variations in comprehensive quality of hybrid indica rice and inbred japonica rice across different nitrogen levels, respectively. We also found that rice comprehensive quality was better under low nitrogen levels for hybrid indica rice, while for inbred japonica rice, properly increasing nitrogen application could improve the comprehensive quality.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Plant Foods)
►
Show Figures