Healthcare 2020, 8(4), 550; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8040550 - 10 Dec 2020
Cited by 37 | Viewed by 5637
Abstract
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has caused a global pandemic and exerted a profound physiological and mental impact on the public. Due to anxiety from being bombarded by information from the news and social media, people may constantly read and repost, with a fear
[...] Read more.
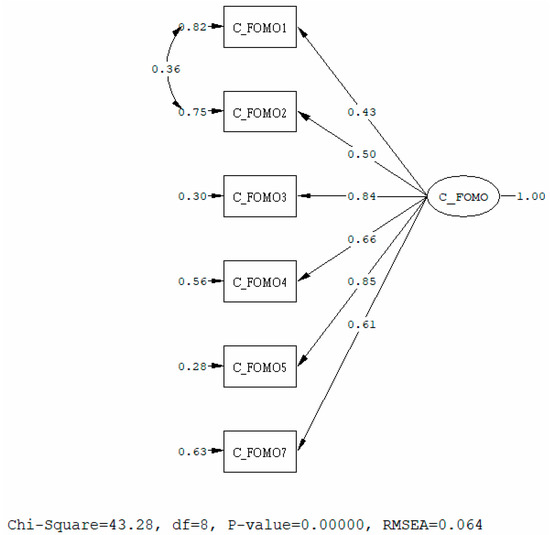
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has caused a global pandemic and exerted a profound physiological and mental impact on the public. Due to anxiety from being bombarded by information from the news and social media, people may constantly read and repost, with a fear of missing out (FOMO), information about COVID-19 on social media. So far, there has been little research on COVID-19 FOMO. We therefore compiled the COVID-19 information fear of missing out scale (CIFS) and administered it to 1178 adults in Taiwan to identify the possible factors influencing CIFS scores. We demonstrated that the CIFS had good reliability, factor validity, and criterion validity. With regard to demographic variables, we found that gender, marital status, travel time to the nearest hospital, and educational background influenced CIFS scores. In contrast, the participant age and whether he or she lived in an urban area did not affect the CIFS scores. With regard to social media usage, social media usage time (r = 0.025) and the numbers of COVID-19-related posts read on social media (r = 0.117) or instant messaging (r = 0.169) were not highly correlated with CIFS scores. Rather, CIFS scores were found to be significantly correlated to the frequency of reposting COVID-19-related information on social media (r = 0.497) and on instant messaging (r = 0.447). These results indicate that CIFS scores are closely associated not with passive browsing on social media but with the frequency at which an individual actively reposts information. In other words, what creates CIF is not an overabundance of information (i.e., an infodemic) but the active reposting and interpretation of information. Individual autonomy for interpretation of the received information and self-determination about reposting are key factors for COVID-19 information FOMO. When facing the COVID-19-related news on social media, it is the active information-related FOMO, not the passive infodemic, that influences our social media usage.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) Outbreak: Epidemiology, Research and Implications for Public Health)
►
Show Figures