Agronomy 2022, 12(12), 3155; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123155 - 12 Dec 2022
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 2456
Abstract
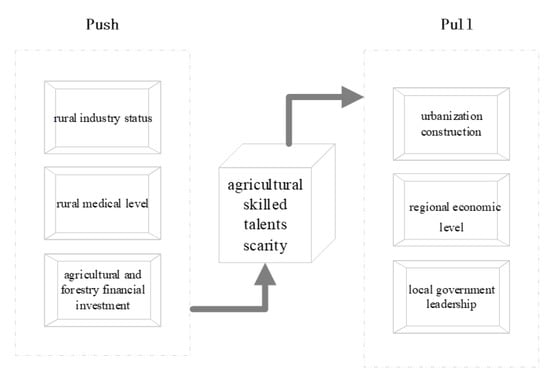
As skilled talent is the core element in optimizing the industrial structure, clarifying the factors that influence the lack of skilled talent in the agricultural industry is essential. The lack of skilled talent in the agricultural industry is a complex problem. The author
[...] Read more.
As skilled talent is the core element in optimizing the industrial structure, clarifying the factors that influence the lack of skilled talent in the agricultural industry is essential. The lack of skilled talent in the agricultural industry is a complex problem. The author based this study on the push–pull theory and used the fuzzy-set qualitative comparative analysis (FSQCA) research method to explore the “joint effect” of the factors that affect the lack of skilled talents in the agricultural industry in 14 cities of Hunan Province. This paper found that indicators such as the rural industry status, rural medical level, agricultural and forestry financial investment, urbanization construction, regional economic development level, and local government officials were all presented under sufficient conditions. These influencing factors have a “combined effect” on the agricultural industry’s lack of skilled talent. The rural industry status indicator was the core condition, appearing in all the configurations. This article’s main marginal contribution is that it defined three conditional configurations for the lack of “present” agricultural skilled talents, and dependent configurations are consistent. Among the three conditional configurations, the “rural industry + economic construction and financial investment” configuration is the most powerful way to retain skilled agricultural talents. In addition, the causal relationship between the lack of “present” agricultural industry skilled talents and the lack of “absent” agricultural industry skilled talents are asymmetric. The primary task is to develop rural industries to solve the problem of the shortage of skilled talent in the agricultural industry. Additionally, then implement the ‘industry+‘ combination policy. So the government must create related policies in the following areas: the supply of essential public services in rural areas, the economic construction of prefectures, the development of county urbanization, and the financial investment in agriculture, forestry, and water conservancy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Novel Studies in Agricultural Economics and Sustainable Farm Management)
(This article belongs to the Section Farming Sustainability)
►
Show Figures
(This article belongs to the Section Farming Sustainability)