Agronomy 2022, 12(12), 3005; https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123005 - 29 Nov 2022
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 6026
Abstract
Although there are many new types of environmentally friendly fertilizers that can improve maize yield, chemical fertilizers are the most widespread type of fertilizer used in the agricultural sector of China due to their low cost and ease of application. However, the misuse
[...] Read more.
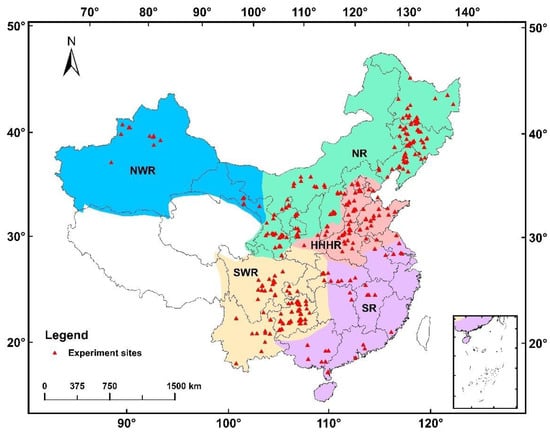
Although there are many new types of environmentally friendly fertilizers that can improve maize yield, chemical fertilizers are the most widespread type of fertilizer used in the agricultural sector of China due to their low cost and ease of application. However, the misuse of chemical fertilizers could lead to environmental problems, such as the massive emission of greenhouse gases (GHG). Therefore, it is important to determine how fertilizer-use efficiency (FUE) could be improved to stabilize or increase maize yield while reducing GHG emissions. In this study, we collected 6618 date records which include three datasets (for N, P, and K) from five maize-growing regions in China from 2005 to 2018, and performed a meta-analysis on the effects of N, K, and P fertilization levels on maize yield, partial factor productivity (PFP), agronomic efficiency (AE), and the carbon footprint of maize production. Additionally, scenario analyses were performed to estimate optimal fertilizer application rates for stabilizing or increasing maize yield while reducing GHG emissions. It was shown that FUE and maize yield responses to fertilization level varied in different regions. Compared to the past, the maize production of China has improved significantly in terms of FUE and its carbon footprint in recent years. Because of improvements in maize cultivars and cultivation technologies, it is possible to decrease N, P, and K application rates and reduce per unit area carbon footprint of maize, without compromising yield. In the future, N fertilization should be reduced by 10% from current levels, and the application of P and K fertilizers should be increased or decreased depending on the conditions of each maize-growing region. Thus, it should be possible to stabilize or even increase yields and reduce GHG emissions of maize production, thereby achieving green and efficient development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Crop Yield Formation and Fertilization Management)
►
Show Figures