Nutrients 2021, 13(9), 2923; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13092923 - 24 Aug 2021
Cited by 21 | Viewed by 5644
Abstract
Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive and highly metastatic breast cancer subtype with limited treatment options. Obesity and insulin resistance are associated with a worse prognosis in those with TNBC. Moringa oleifera (moringa) is a tropical edible plant used for both
[...] Read more.
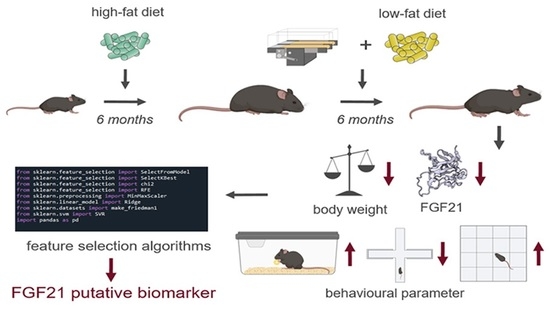
Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive and highly metastatic breast cancer subtype with limited treatment options. Obesity and insulin resistance are associated with a worse prognosis in those with TNBC. Moringa oleifera (moringa) is a tropical edible plant used for both food and medicinal purposes and found to have anti-obesity and anti-cancer effects in vitro and in preclinical models. The anti-cancer effects of moringa seed extract alone and in combination with chemotherapy were evaluated in immunocompromised female mice with diet-induced obesity bearing MDA-MB-231-derived xenograft tumors. Moringa supplementation protected against high-fat diet- and chemotherapy-induced increases in fasting glucose and improved insulin sensitivity. Moringa supplementation alone did not attenuate tumor growth relative to chemotherapy alone, and in combination worsened tumor progression. Moringa supplementation alone reduced angiogenesis, but this effect was abrogated in combination with chemotherapy. Moringa supplementation may be an effective strategy to improve metabolic health in mice with obesity and TNBC and reduce angiogenesis in tumors, but may have a negative interaction when used as a concurrent complementary therapy. Caution should be taken when considering the consumption of moringa seed extracts while receiving chemotherapy for breast cancer treatment. Further investigations of alternative timings of moringa therapy are warranted.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Phytochemicals and Human Health)
►
Show Figures