Nutrients 2019, 11(9), 2011; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092011 - 27 Aug 2019
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 4869
Abstract
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is treated with dietary restrictions and sometimes tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4). PKU patients are at risk for developing micronutrient deficiencies, such as vitamin B12 and folic acid, likely due to their diet. Tyrosinemia type 1 (TT1) is similar to PKU in both pathogenesis
[...] Read more.
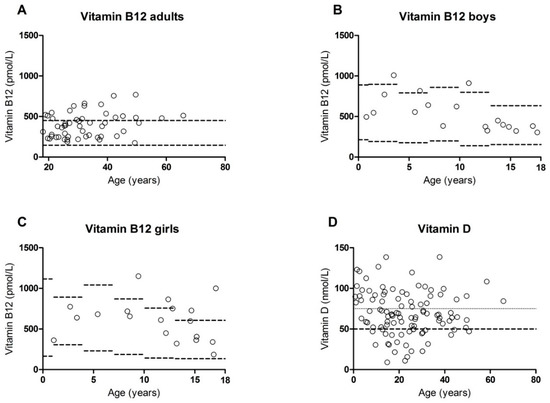
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is treated with dietary restrictions and sometimes tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4). PKU patients are at risk for developing micronutrient deficiencies, such as vitamin B12 and folic acid, likely due to their diet. Tyrosinemia type 1 (TT1) is similar to PKU in both pathogenesis and treatment. TT1 patients follow a similar diet, but nutritional deficiencies have not been investigated yet. In this retrospective study, biomarkers of micronutrients in TT1 and PKU patients were investigated and outcomes were correlated to dietary intake and anthropometric measurements from regular follow-up measurements from patients attending the outpatient clinic. Data was analyzed using Kruskal–Wallis, Fisher’s exact and Spearman correlation tests. Furthermore, descriptive data were used. Overall, similar results for TT1 and PKU patients (with and without BH4) were observed. In all groups high vitamin B12 concentrations were seen rather than B12 deficiencies. Furthermore, all groups showed biochemical evidence of vitamin D deficiency. This study shows that micronutrients in TT1 and PKU patients are similar and often within the normal ranges and that vitamin D concentrations could be optimized.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Dietetics and Nutritional Aspects in Inherited Metabolic Diseases (IMD))
►
Show Figures