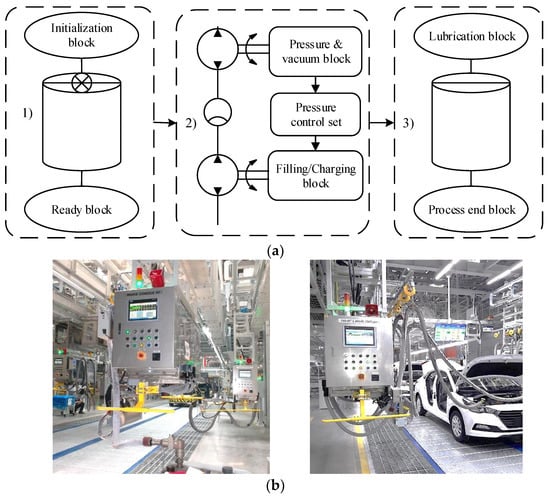
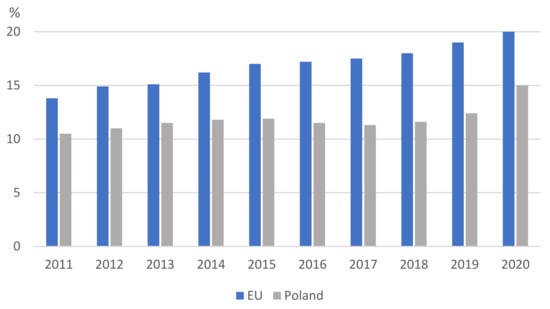
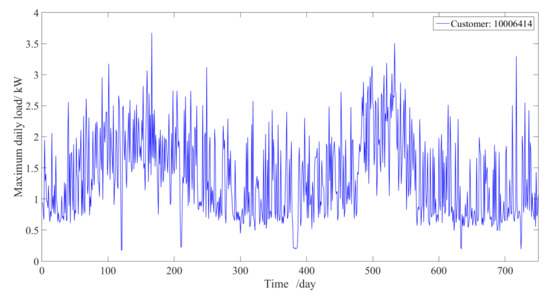
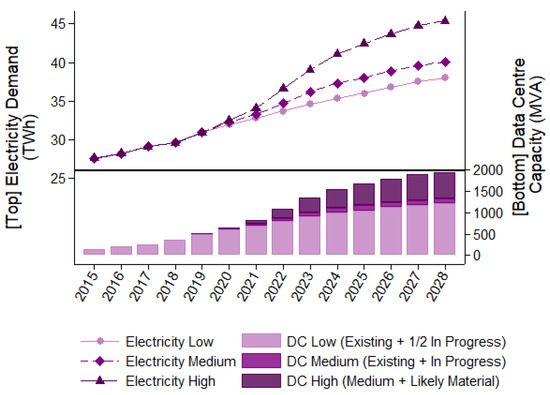
Energies 2021, 14(22), 7569; https://doi.org/10.3390/en14227569 - 12 Nov 2021
Cited by 28 | Viewed by 4717
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Multiple microgrids (MGs) close to each other can be interconnected to construct a cluster to enhance reliability and flexibility. This paper presents a comprehensive and comparative review of recent studies on DC MG clusters’ control strategies. Different schemes regarding the two significant control
[...] Read more.
Multiple microgrids (MGs) close to each other can be interconnected to construct a cluster to enhance reliability and flexibility. This paper presents a comprehensive and comparative review of recent studies on DC MG clusters’ control strategies. Different schemes regarding the two significant control aspects of networked DC MGs, namely DC-link voltage control and power flow control between MGs, are investigated. A discussion about the architecture configuration of DC MG clusters is also provided. All advantages and limitations of various control strategies of recent studies are discussed in this paper. Furthermore, this paper discusses three types of consensus protocol with different time boundaries, including linear, finite, and fixed. Based on the main findings from the reviewed studies, future research recommendations are proposed.
Full article