Molecules 2021, 26(6), 1710; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061710 - 19 Mar 2021
Cited by 24 | Viewed by 4542
Abstract
Infections associated with the emergence of multidrug resistance and mosquito-borne diseases have resulted in serious crises associated with high mortality and left behind a huge socioeconomic burden. The chemical investigation of Lavandulacoronopifolia aerial parts extract using HPLC–MS/MS led to the tentative identification
[...] Read more.
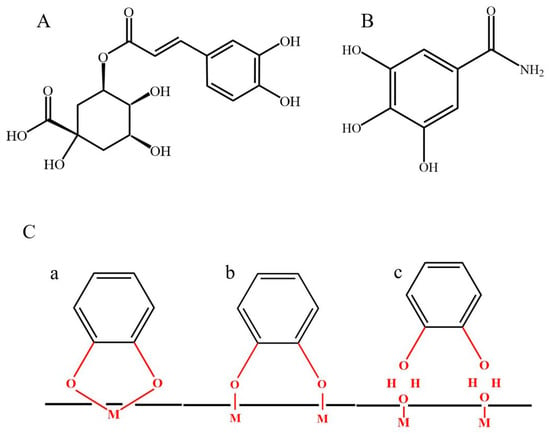
Infections associated with the emergence of multidrug resistance and mosquito-borne diseases have resulted in serious crises associated with high mortality and left behind a huge socioeconomic burden. The chemical investigation of Lavandulacoronopifolia aerial parts extract using HPLC–MS/MS led to the tentative identification of 46 compounds belonging to phenolic acids, flavonoids and their glycosides, and biflavonoids. The extract displayed larvicidal activity against Culex pipiens larvae (LC50 = 29.08 µg/mL at 72 h). It significantly inhibited cytochrome P-450 monooxygenase (CYP450), acetylcholinesterase (AChE), and carboxylesterase (CarE) enzymes with the comparable pattern to the control group, which could explain the mode of larvae toxification. The extract also inhibited the biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by 17–38% at different Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MICs) (0.5–0.125 mg/mL) while the activity was doubled when combined with ciprofloxacin (ratio = 1:1 v:v). In conclusion, the wild plant, L.coronopifolia, can be considered a promising natural source against resistant bacteria and infectious carriers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Bioproducts for Health II)
►
Show Figures