Molecules 2018, 23(1), 113; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010113 - 8 Jan 2018
Cited by 28 | Viewed by 4876
Abstract
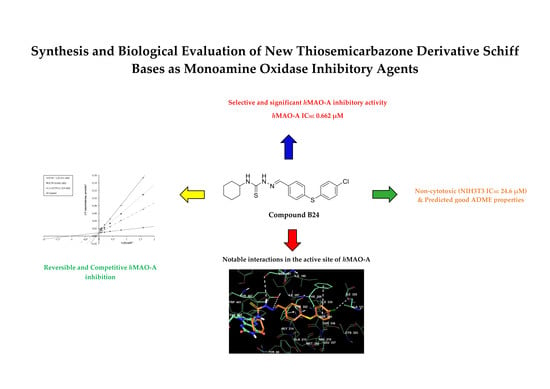
A new series of N-pyridyl-hydrazone derivatives was synthesized by using a simple and efficient method. The final compounds obtained were screened for their inhibitory potency against monoamine oxidase (MAO) A and B. The newly synthesized compounds 2a–2n specifically inhibited monoamine
[...] Read more.
A new series of N-pyridyl-hydrazone derivatives was synthesized by using a simple and efficient method. The final compounds obtained were screened for their inhibitory potency against monoamine oxidase (MAO) A and B. The newly synthesized compounds 2a–2n specifically inhibited monoamine oxidases, displaying notably low IC50 values. Compounds 2i and 2j, with a CF3 and OH group on the 4-position of the phenyl ring, respectively, showed considerable MAO-A and MAO-B inhibitory activities. Compounds 2k, 2l and 2n, with N-methylpyrrole, furan and pyridine moieties instead of the phenyl ring, were the most powerful and specific inhibitors of MAO-A, with IC50 values of 6.12 μM, 10.64 μM and 9.52 μM, respectively. Moreover, these active compounds were found to be non-cytotoxic to NIH/3T3 cells. This study supports future studies aimed at designing MAO inhibitors to obtain more viable medications for neurodegenerative disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Bioorganic Chemistry)
►
Show Figures