AI in Knowledge-Based Information and Decision Support Systems
A special issue of Electronics (ISSN 2079-9292). This special issue belongs to the section "Computer Science & Engineering".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (15 October 2023) | Viewed by 16859
Special Issue Editors
Interests: intelligent systems; intelligent information processing
Interests: artificial intelligence; intelligent systems
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
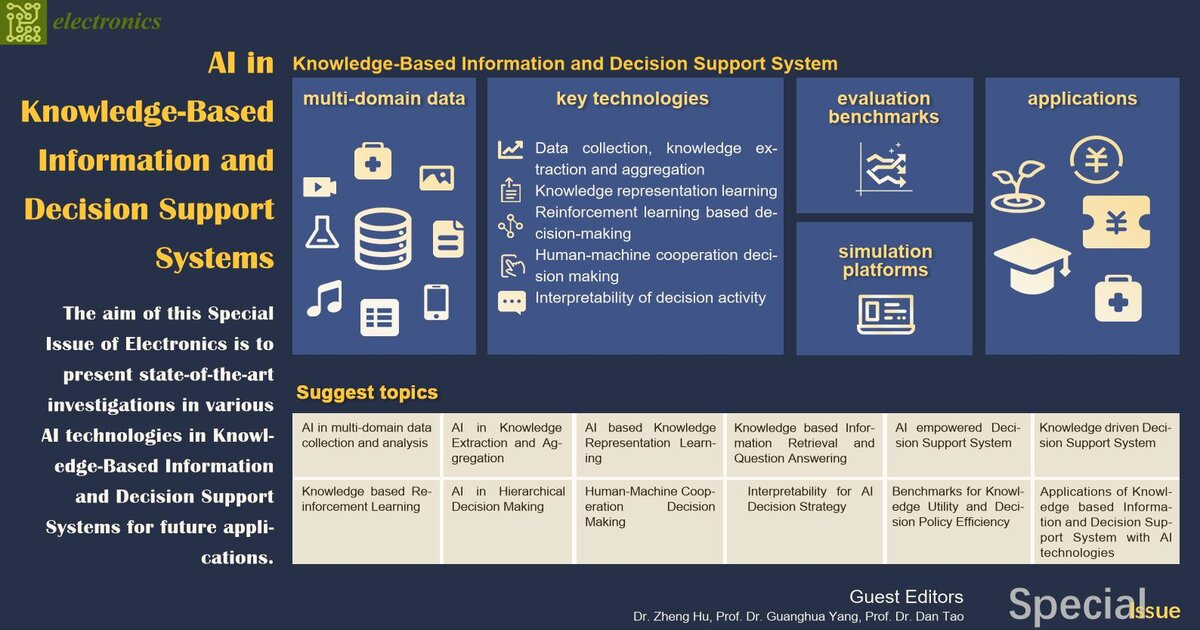
Artificial intelligence (AI) has achieved significant success in many applications, such as visual perception, language translation, speech recognition, and robot manipulation. As the goal of AI is to possess human-level intelligence in problem solving, one promising avenue of research for AI is to explore its potential role in knowledge-based information and decision support systems, which has numerous applications related to finance, marketing, agriculture, education, and medicine. Such systems aid an organization or business in decision-making activities by comprehensive reasoning using accumulated knowledge learning from a huge volume of multi-domain data. The potential key technologies of this frontier include data collection and analysis, knowledge extraction and aggregation, knowledge representation learning, semantic information understanding and retrieval, reinforcement learning-based decision making, human–machine cooperation decision making, and the interpretability of decision activity. In addition, the evaluation benchmarks for knowledge utility and simulation platforms for decision-making strategies are also important to the development of such systems.
The purpose of this Special Issue of Electronics is to collect high-quality articles that present and discuss new problems, solutions, and technologies in the fields of knowledge-based information, decision support systems, and related areas of artificial intelligence.
We invite researchers to contribute original and unique articles, as well as sophisticated review articles. Topics include, but are not limited to, the following areas:
- AI in multi-domain data collection and analysis;
- AI in knowledge extraction and aggregation;
- AI-based knowledge representation learning;
- Knowledge-based information retrieval and question answering;
- AI-empowered decision support systems;
- Knowledge-driven decision support systems;
- Knowledge-based reinforcement learning;
- AI in hierarchical decision making;
- Human–machine cooperation decision making;
- Interpretability for AI decision strategy;
- Benchmarks for knowledge utility and decision policy efficiency;
- Applications of knowledge-based information and decision support systems with AI technologies.
We look forward to receiving your contributions.
Dr. Zheng Hu
Prof. Dr. Guanghua Yang
Prof. Dr. Dan Tao
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Electronics is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- artificial intelligence
- knowledge-based systems
- decision support systems







