Healthcare 2020, 8(4), 415; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8040415 - 21 Oct 2020
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2133
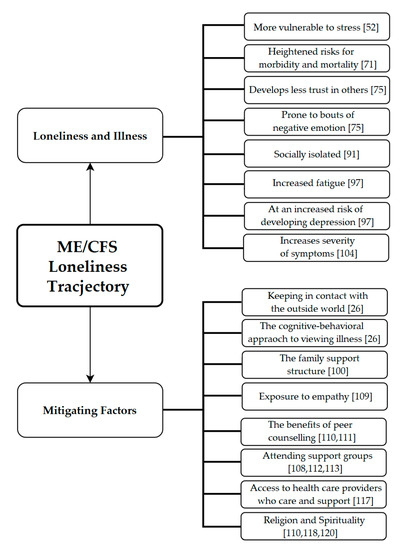
Abstract
Introduction: The purposes of this study were to explore the resemblance in the weight status within couples with different family contextual factors and analyze the influence of the level of overweight or obesity of a spouse on that of the other spouse. Methods:
[...] Read more.
Introduction: The purposes of this study were to explore the resemblance in the weight status within couples with different family contextual factors and analyze the influence of the level of overweight or obesity of a spouse on that of the other spouse. Methods: The data were from the sixth National Health Service Survey of Henan Province in 2018. After screening, 7432 eligible couples were finally included. Socioeconomic and demographic factors were compared by the χ2 test or nonparametric test. The difference in the body mass index (BMI) of spouses was assessed by a t-test. The Pearson correlation coefficient and kappa value were used as indicators of consistency in weight status. A logistic regression analysis was used to further explore the effect of a spouse’s level of overweight/obesity on that of the other spouse. Results: The results show that the prevalence of overweight/obesity in couples aged 20 or older is 33.76%. The Pearson correlation coefficient of the BMI within couples was 0.102 (95% CI: 0.076–0.120). The kappa coefficients suggested a low resemblance in the weight status within couples (k = 0.049, 95% CI: 0.031–0.069). Besides, the influence of the overweight/obesity status of the wives on that of the husbands (odds ratio (OR) = 1.411, 95% CI: 1.309–1.521) was slightly higher than that of the husbands on that of the wives (OR = 1.404, 95% CI: 1.302–1.514). Conclusions: We found that there was a moderate but significant resemblance in the body weight status between spouses, especially elderly couples with a low education level in rural areas. Health education activities for couple interventions can have a good effect of intervention.
Full article