Electronics 2023, 12(7), 1516; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12071516 - 23 Mar 2023
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 2211
Abstract
Gliomas, primary brain tumors arising from glial cells, can be effectively identified using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), a widely employed diagnostic tool in clinical settings. Accurate glioma segmentation, which is crucial for diagnosis and surgical intervention, can be achieved by integrating multiple MRI
[...] Read more.
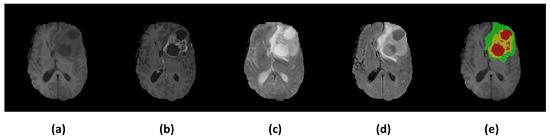
Gliomas, primary brain tumors arising from glial cells, can be effectively identified using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), a widely employed diagnostic tool in clinical settings. Accurate glioma segmentation, which is crucial for diagnosis and surgical intervention, can be achieved by integrating multiple MRI modalities that offer complementary information. However, limited access to multiple modalities in certain clinical contexts often results in suboptimal performance of glioma segmentation methods. This study introduces a novel generalized knowledge distillation framework designed to transfer multimodal knowledge from a teacher model to a unimodal student model via two distinct distillation strategies: segmentation graph distillation and cascade region attention distillation. The former enables the student to replicate the teacher’s softened output, whereas the latter facilitates extraction and learning of region feature information at various levels within the teacher model. Our evaluation of the proposed distillation strategies using the BraTS 2018 dataset confirms their superior performance in unimodal segmentation contexts compared with existing methods.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Future AI and Robotics: Visual- and Spatial-Based Perception Enhancement and Reasoning)
►
Show Figures