Appl. Sci. 2019, 9(7), 1395; https://doi.org/10.3390/app9071395 - 3 Apr 2019
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 3177
Abstract
Most of the molybdenum (Mo) bilayer films are deposited by direct current (DC) magnetron sputtering at the bottom and the top layer (DC/DC). However, the deposition of Mo bilayer film by radio frequency (RF) Mo bottom layer and DC Mo top layer magnetron
[...] Read more.
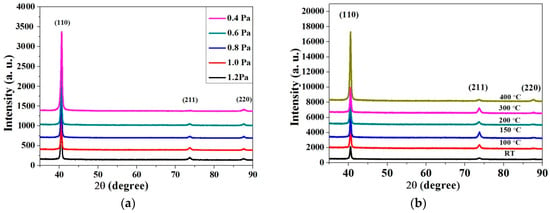
Most of the molybdenum (Mo) bilayer films are deposited by direct current (DC) magnetron sputtering at the bottom and the top layer (DC/DC). However, the deposition of Mo bilayer film by radio frequency (RF) Mo bottom layer and DC Mo top layer magnetron sputtering has been less studied by researchers. In this paper, the bottom layer of Mo bilayer film was deposited by RF magnetron sputtering to maintain its good adhesion and high reflectance, and the top layer was deposited by DC magnetron sputtering to obtain good conductivity (RF/DC). Generally, the bottom layer sputtering pressure is relatively random, in this paper, the effects of the bottom layer RF sputtering pressures on the microstructures and properties of Mo bilayer films were first studied in detail. Next, in order to further improve their properties, the as-prepared Mo bilayer films at 0.4 Pa bottom layer RF sputtering pressure were annealed at different temperatures and then investigated. Specifically, Mo bilayer films were deposited on soda-lime glass substrates by RF/DC magnetron sputtering at different bottom layer RF sputtering pressures in the range of 0.4–1.2 Pa, the powers of bottom layer RF sputtering and top layer DC sputtering were 120 W and 100 W, respectively. Then, Mo bilayer films, prepared at a bottom layer sputtering pressure of 0.4 Pa and top layer sputtering pressure of 0.3 Pa, were annealed for 30 min at various temperatures in the range of 100–400 °C. The effects of bottom layer sputtering pressures and the annealing temperatures on the microstructures, electrical and optical properties of Mo bilayer films were clarified by X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), atomic-force microscopy (AFM), and ultraviolet (UV)-visible spectra, respectively. It is shown that with decreasing bottom layer sputtering pressure from 1.2 to 0.4 Pa and increasing annealing temperature from 100 to 400 °C, the crystallinity, electrical and optical properties of Mo bilayer films were improved correspondingly. The optimized Mo bilayer film was prepared at the top layer sputtering pressure of 0.3 Pa, the bottom layer sputtering pressure of 0.4 Pa and the annealing temperature of 400 °C. The extremely low resistivity of 0.92 × 10−5 Ω.cm was obtained. The photo-conversion efficiency of copper indium gallium selenium (CIGS) solar cell with the optimized Mo bilayer film as electrode was up to as high as 13.5%.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue CIGS Thin Films and Solar Cells)
►
Show Figures