1
School of Spatial Planning and Design, Hangzhou City University, Hangzhou 310015, China
2
School of Media Engineering, Communication University of Zhejiang, Hangzhou 310018, China
3
School of Public Administration, Zhejiang University of Finance & Economics, Hangzhou 310018, China
4
School of Information Management and Artificial Intelligence, Zhejiang University of Finance & Economics, Hangzhou 310018, China
Buildings 2023, 13(3), 676; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13030676 - 3 Mar 2023
Viewed by 3096
Abstract
With the transformation of industry in China, and industrial production changes from an incremental economy to a stock economy, a massive renovation of industrial buildings and intensification of renovation conflicts coexist. Industrial building renovation conflict seriously affects industrial building renovation. Based on the
[...] Read more.
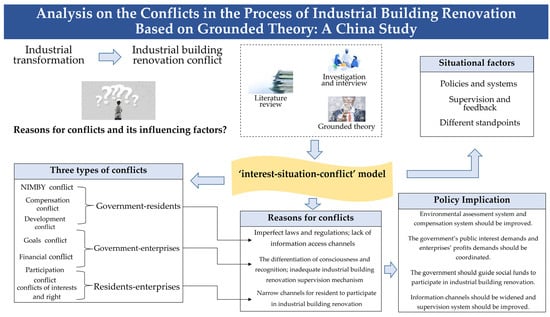
With the transformation of industry in China, and industrial production changes from an incremental economy to a stock economy, a massive renovation of industrial buildings and intensification of renovation conflicts coexist. Industrial building renovation conflict seriously affects industrial building renovation. Based on the Grounded Theory, this paper selects Ningbo City as the research area and builds the “interest–situation–conflict” model through investigation and interview, exploring the reasons for conflicts and the influencing factors of industrial building renovation. Situational factors for three types of conflicts, namely, government–residents, government–enterprises, and residents–enterprises, are greatly affected by policies and systems, supervision and feedback, and different standpoints, respectively. Based on the “interest-situation-conflict” model, this paper analyzes the reasons for the conflicts among government, enterprises, and residents and puts forward countermeasures to solve nimby (not in my back yard) conflict, compensation conflict, development conflict, goals conflict, financial conflict, participation conflict, and conflict of interests and rights, so as to promote the renovation of industrial buildings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Strategies for Sustainable Urban Development)
▼
Show Figures