Diagnostics 2019, 9(4), 166; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9040166 - 29 Oct 2019
Cited by 20 | Viewed by 4682
Abstract
The ability to accurately measure multiple proteins simultaneously in a single assay has the potential to markedly improve the efficiency of clinical tests composed of multiple biomarkers. We investigated the diagnostic accuracy of the two multiplex protein array platforms for detecting a bladder-cancer-associated
[...] Read more.
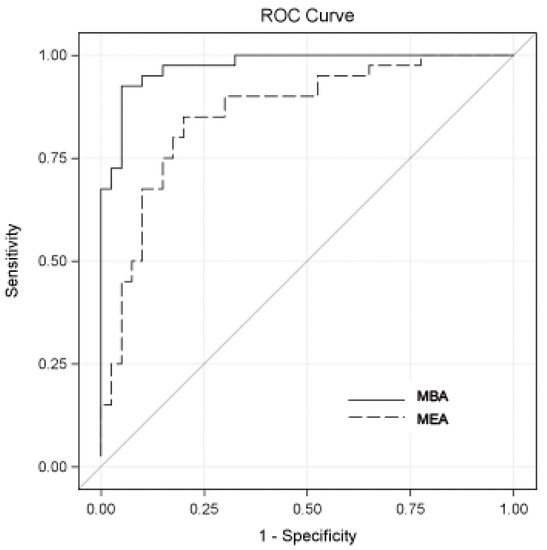
The ability to accurately measure multiple proteins simultaneously in a single assay has the potential to markedly improve the efficiency of clinical tests composed of multiple biomarkers. We investigated the diagnostic accuracy of the two multiplex protein array platforms for detecting a bladder-cancer-associated diagnostic signature in samples from a cohort of 80 subjects (40 with bladder cancer). Banked urine samples collected from Kyoto and Nara Universities were compared to histologically determined bladder cancer. The concentrations of the 10 proteins (A1AT; apolipoprotein E—APOE; angiogenin—ANG; carbonic anhydrase 9—CA9; interleukin 8—IL-8; matrix metalloproteinase 9—MMP-9; matrix metalloproteinase 10—MMP10; plasminogen activator inhibitor 1—PAI-1; syndecan—SDC1; and vascular endothelial growth factor—VEGF) were monitored using two prototype multiplex array platforms and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) according to the manufacturer’s technical specifications. The range for detecting each biomarker was improved in the multiplex assays, even though the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) was typically lower in the commercial ELISA kits. The area under the receiver operating characteristics (AUROC) of the prototype multiplex assays was reported to be 0.97 for the multiplex bead-based immunoassay (MBA) and 0.86 for the multiplex electrochemoluminescent assay (MEA). The sensitivities and specificities for MBA were 0.93 and 0.95, respectively, and for MEA were 0.85 and 0.80, respectively. Accuracy, positive predictive values (PPV), and negative predictive values (NPV) for MBA were 0.94, 0.95, and 0.93, respectively, and for MEA were 0.83, 0.81, and 0.84, respectively. Based on these encouraging preliminary data, we believe that a multiplex protein array is a viable platform that can be utilized as an efficient and highly accurate tool to quantitate multiple proteins within biologic specimens.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Urogenital Cancers: Diagnostic, Predictive, and Prognostic Markers)
►
Show Figures