Life 2022, 12(10), 1556; https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101556 - 7 Oct 2022
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 3244
Abstract
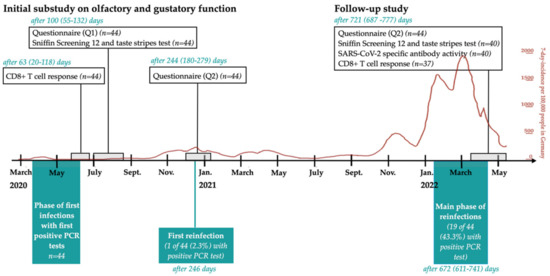
Persistent chemosensory dysfunction (PCD) is a common symptom of long-COVID. Chemosensory dysfunction (CD) as well as SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody levels and CD8+ T-cell immunity were investigated in a cohort of 44 healthcare workers up to a median of 721 days after a positive
[...] Read more.
Persistent chemosensory dysfunction (PCD) is a common symptom of long-COVID. Chemosensory dysfunction (CD) as well as SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody levels and CD8+ T-cell immunity were investigated in a cohort of 44 healthcare workers up to a median of 721 days after a positive PCR test. CD was assessed using questionnaires and psychophysical screening tests. After 721 days, 11 of 44 (25%) participants reported PCD, with five describing an impaired quality of life. One participant reported hyperosmia (increased sense of smell). The risk of PCD at 721 days was higher for participants reporting qualitative changes (parosmia (altered smell), dysgeusia (altered taste), or phantosmia (hallucination of smell)) during initial infection than in those with isolated quantitative losses during the first COVID-19 infection (62.5% vs. 7.1%). The main recovery rate occurred within the first 100 days and did not continue until follow-up at 2 years. No correlation was found between antibody levels and CD, but we observed a trend of a higher percentage of T-cell responders in participants with CD. In conclusion, a significant proportion of patients suffer from PCD and impaired quality of life 2 years after initial infection. Qualitative changes in smell or taste during COVID-19 pose a higher risk for PCD.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Olfactory and Gustatory Dysfunctions in COVID‐19 Patients)
►
Show Figures