Water 2023, 15(2), 300; https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020300 - 11 Jan 2023
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 2368
Abstract
Potential landslide identification and monitoring are essential to prevent geological disasters. However, in mountainous areas where the surface gradient changes significantly, the leveling effect is not completely removed, affecting the deformation results. In this paper, the SBAS-InSAR and PS-InSAR time-series processing methods were
[...] Read more.
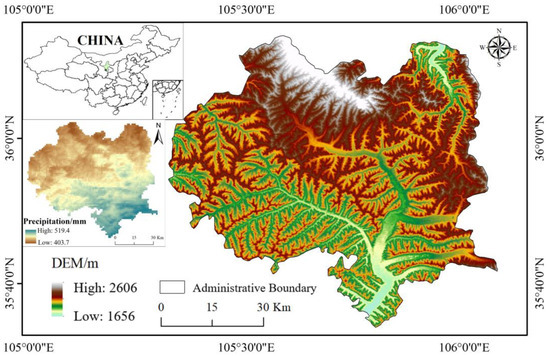
Potential landslide identification and monitoring are essential to prevent geological disasters. However, in mountainous areas where the surface gradient changes significantly, the leveling effect is not completely removed, affecting the deformation results. In this paper, the SBAS-InSAR and PS-InSAR time-series processing methods were combined to interfere with the SAR image data of the ascending orbit in the southern mountainous area of Ningxia and its surrounding regions. Based on the obtained surface deformation monitoring results and optical images, landslide hazard identification was successfully carried out within the coverage area of 3130 km2 in Xiji County. The results show that the whole study area presented a relatively stable state, most of the deformation rates were concentrated in the range of 0 mm/a to −10 mm/a, and the deformation in the southwest area was larger. A total of 11 large potential landslides (which were already registered potential danger points of geological disasters) were identified in the study area, including three historical collapses. The landslide identification results were highly consistent with the field survey results after verification. The timing analysis of the typical landslide point of the Jiaowan landslide was further carried out, which showed that the Jiaowan landslide produced new deformation during the monitoring time, but it was still in a basically stable state. It can do a good job in disaster prevention and reduction while strengthening monitoring. The results of this study have a guiding effect on landslide prevention and mitigation in the mountainous areas of southern Ningxia.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Landslides and Sediment Disasters Prevention)
►
Show Figures