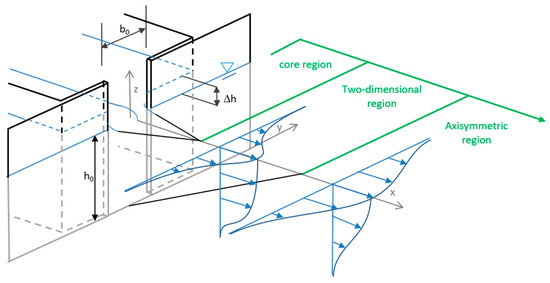
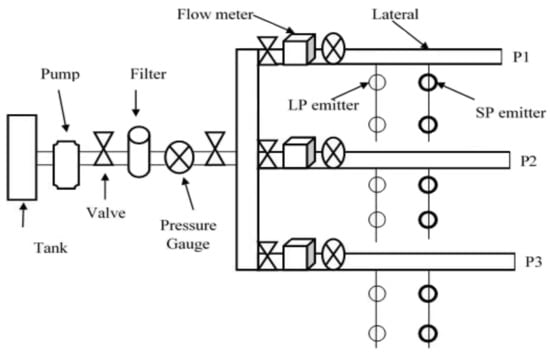
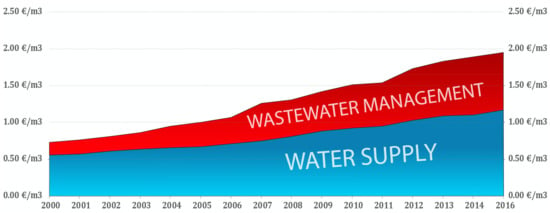
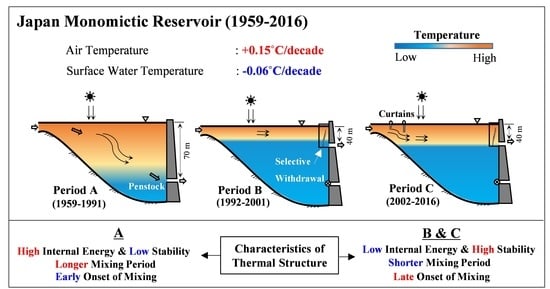
Water 2021, 13(8), 1046; https://doi.org/10.3390/w13081046 - 10 Apr 2021
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2889
Abstract
Multi-objective evolutionary algorithms (MOEAs) are widely used to optimize multi-purpose reservoir operations. Considering that most outcomes of MOEAs are Pareto optimal sets with a large number of incomparable solutions, it is not a trivial task for decision-makers (DMs) to select a compromise solution
[...] Read more.
Multi-objective evolutionary algorithms (MOEAs) are widely used to optimize multi-purpose reservoir operations. Considering that most outcomes of MOEAs are Pareto optimal sets with a large number of incomparable solutions, it is not a trivial task for decision-makers (DMs) to select a compromise solution for application purposes. Due to the increasing popularity of data-driven decision-making, we introduce a clustering-based decision-making method into the multi-objective reservoir operation optimization problem. Traditionally, solution selection has been conducted based on trade-off ranking in objective space, and solution characteristics in decision space have been ignored. In our work, reservoir operation processes were innovatively clustered into groups with unique properties in decision space, and the trade-off surfaces were analyzed via clustering in objective space. To attain a suitable performance, a new similarity measure, referred to as the Mei–Wang fluctuation similarity measure (MWFSM), was tailored to reservoir operation processes. This method describes time series in terms of both their shape and quantitative variation. Then, a compromise solution was selected via the joint use of two clustering results. A case study of the Three Gorges cascade reservoirs system under small and medium floods was investigated to verify the applicability of the proposed method. The results revealed that the MWFSM effectively distinguishes reservoir operation processes. Two more operation patterns with similar positions but different shapes were identified via MWFSM when compared with Euclidean distance and the dynamic time warping method. Furthermore, the proposed method decreased the selection range from the whole Pareto optimal set to a set containing relatively few solutions. Finally, a compromise solution was selected.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Water Resources Management, Policy and Governance)
►
Show Figures