Cancers 2023, 15(4), 1062; https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041062 - 7 Feb 2023
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2993
Abstract
Biliary tract cancer (BTC) is a rare gastrointestinal cancer with a dismal prognosis. Biomarkers with clinical utility are needed. In this study, we investigated the association between survival and 89 immuno-oncology-related proteins, with the aim of identifying prognostic biomarkers for BTC. The study
[...] Read more.
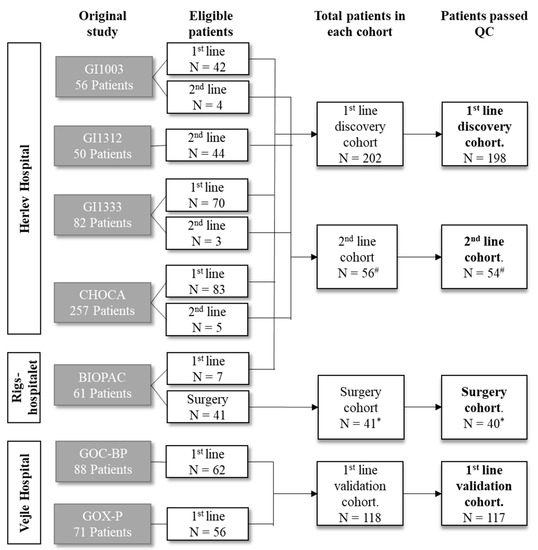
Biliary tract cancer (BTC) is a rare gastrointestinal cancer with a dismal prognosis. Biomarkers with clinical utility are needed. In this study, we investigated the association between survival and 89 immuno-oncology-related proteins, with the aim of identifying prognostic biomarkers for BTC. The study included patients with BTC (n = 394) treated at three Danish hospitals. Patients were divided into four cohorts: the first-line discovery cohort (n = 202), first-line validation cohort (n = 118), second-line cohort (n = 56), and surgery cohort (n = 41). Plasma protein levels were measured using a proximity extension assay (Olink Proteomics). Twenty-seven proteins were associated with overall survival (OS) in a multivariate analysis in the discovery cohort. In the first-line validation cohort, high levels of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-15, mucin 16, hepatocyte growth factor, programmed cell death ligand 1, and placental growth factor were significantly associated with poor OS in univariate Cox regression analyses. When adjusting for performance status, location, and stage, the association was significant only for IL-6 (hazard ratio (HR) = 1.25, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.08–1.46) and IL-15 (HR = 2.23, 95% CI 1.48–3.35). Receiver operating characteristic analyses confirmed IL-6 and IL-15 as the strongest predictors of survival. Combining several proteins into signatures further improved the ability to distinguish between patients with short (<6 months) and long survival (>18 months). The study identified several circulating proteins as prognostic biomarkers in patients, with BTC, IL-6, and IL-15 being the most promising markers. Combining proteins in a prognostic signature improved prognostic performance, but future studies are needed to determine the optimal combination and thresholds.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Cancer Biomarkers in Body Fluids)
►
Show Figures