Cancers 2021, 13(18), 4583; https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184583 - 12 Sep 2021
Cited by 45 | Viewed by 6633
Abstract
Hyperthermia has emerged as a promising alternative to conventional cancer therapies and in fact, traditional hyperthermia is now commonly used in combination with chemotherapy or surgery during cancer treatment. Nevertheless, non-specific application of hyperthermia generates various undesirable side-effects, such that nano-magnetic hyperthermia has
[...] Read more.
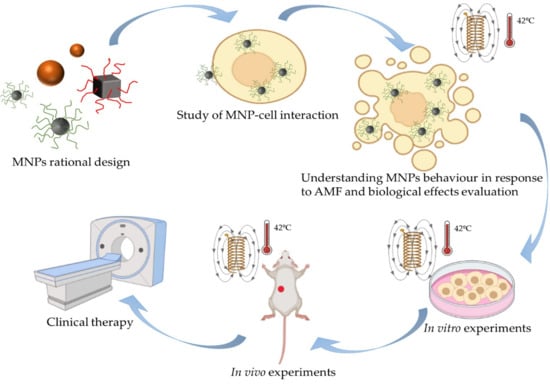
Hyperthermia has emerged as a promising alternative to conventional cancer therapies and in fact, traditional hyperthermia is now commonly used in combination with chemotherapy or surgery during cancer treatment. Nevertheless, non-specific application of hyperthermia generates various undesirable side-effects, such that nano-magnetic hyperthermia has arisen a possible solution to this problem. This technique to induce hyperthermia is based on the intrinsic capacity of magnetic nanoparticles to accumulate in a given target area and to respond to alternating magnetic fields (AMFs) by releasing heat, based on different principles of physics. Unfortunately, the clinical implementation of nano-magnetic hyperthermia has not been fluid and few clinical trials have been carried out. In this review, we want to demonstrate the need for more systematic and basic research in this area, as many of the sub-cellular and molecular mechanisms associated with this approach remain unclear. As such, we shall consider here the biological effects that occur and why this theoretically well-designed nano-system fails in physiological conditions. Moreover, we will offer some guidelines that may help establish successful strategies through the rational design of magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Prospects from Diagnosis to Treatment in Cancer Using Magnetic Methods)
►
Show Figures