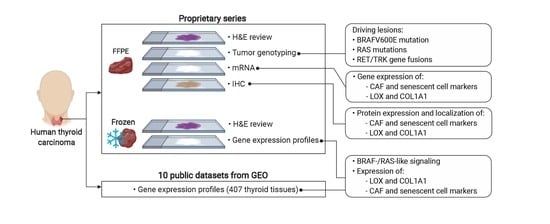
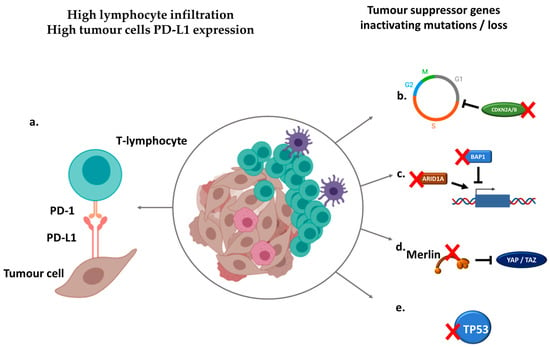
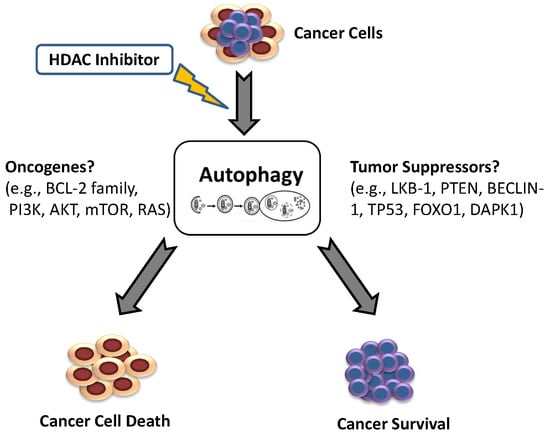
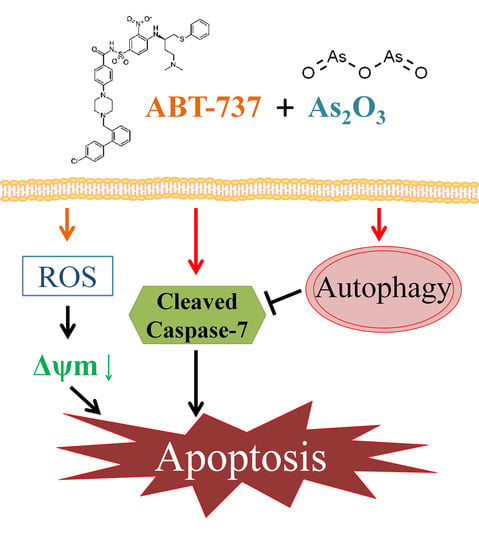
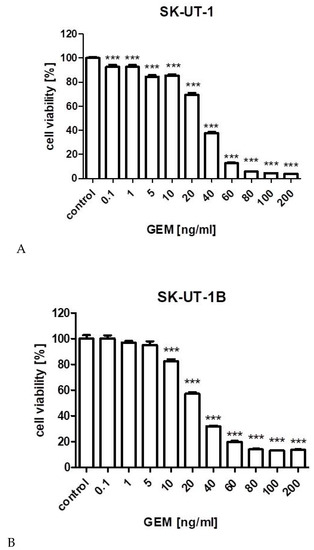
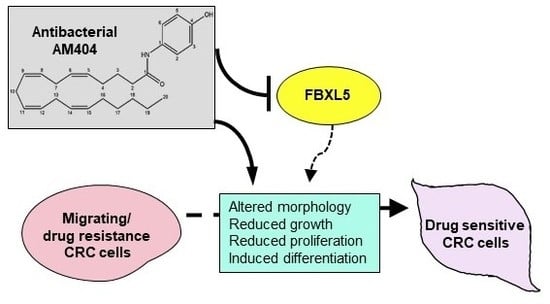
Cancers 2020, 12(1), 119; https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010119 - 2 Jan 2020
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 3626
Abstract
►
Show Figures
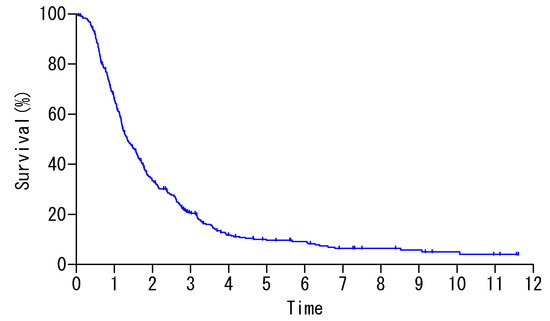
Melanoma patients carrying an oncogenic NRAS mutation represent 20% of all cases and present worse survival, relapse rate and therapy response than patients with wild type NRAS or with BRAF mutations. Nevertheless, no efficient targeted therapy has emerged so far for this group
[...] Read more.
Melanoma patients carrying an oncogenic NRAS mutation represent 20% of all cases and present worse survival, relapse rate and therapy response than patients with wild type NRAS or with BRAF mutations. Nevertheless, no efficient targeted therapy has emerged so far for this group of patients in comparison with the classical combination of BRAF and MEK inhibitors for the patient group carrying a BRAF mutation. NRAS key downstream actors should therefore be identified for drug targeting, possibly in combination with MEK inhibitors. Here, we investigated the influence of different melanoma-associated NRAS mutations (codon 12, 13 or 61) on several parameters such as oncogene-induced senescence, cell proliferation, migration or colony formation in immortalized melanocytes and in melanoma cell lines. We identified AXL/STAT3 axis as a main regulator of NRASQ61–induced oncogene-induced senescence (OIS) and observed that NRASQ61 mutations are not only more tumorigenic than NRASG12/13 mutations but also associated to STAT3 activation. In conclusion, these data bring new evidence of the potential tumorigenic role of STAT3 in NRAS-mutant melanomas and will help improving current therapy strategies for this particular patient group.
Full article