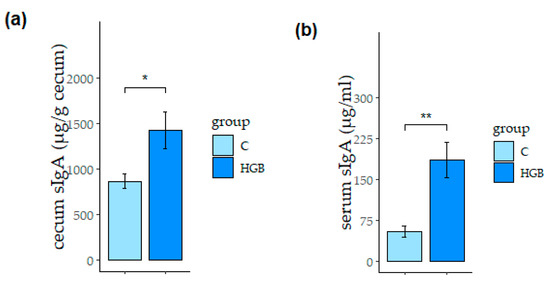
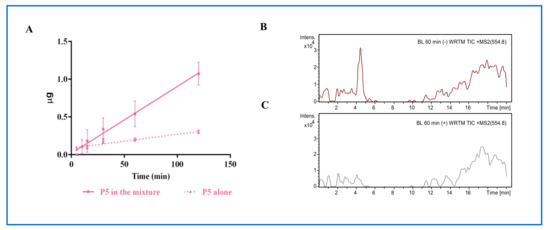
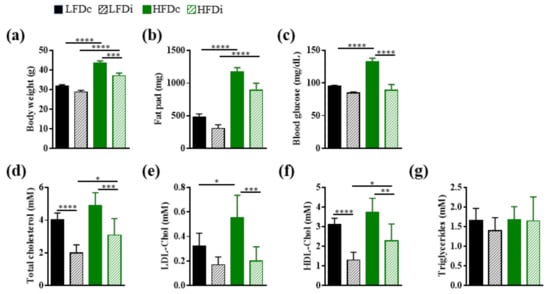
Nutrients 2021, 13(3), 764; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13030764 - 26 Feb 2021
Cited by 27 | Viewed by 10306
Abstract
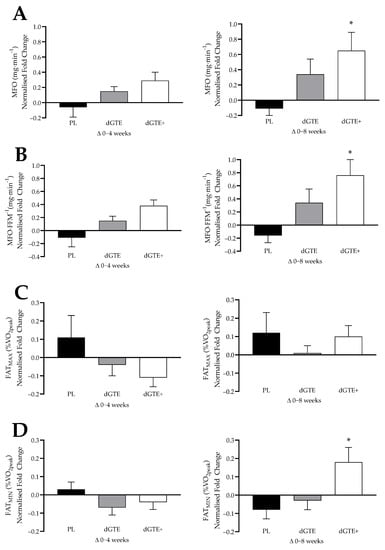
This study investigated the effect of decaffeinated green tea extract (dGTE), with or without antioxidant nutrients, on fat oxidation, body composition and cardio-metabolic health measures in overweight individuals engaged in regular exercise. Twenty-seven participants (20 females, 7 males; body mass: 77.5 ± 10.5
[...] Read more.
This study investigated the effect of decaffeinated green tea extract (dGTE), with or without antioxidant nutrients, on fat oxidation, body composition and cardio-metabolic health measures in overweight individuals engaged in regular exercise. Twenty-seven participants (20 females, 7 males; body mass: 77.5 ± 10.5 kg; body mass index: 27.4 ± 3.0 kg·m2; peak oxygen uptake (
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Effect of Phytochemicals on Fat Oxidation during Exercise)
►
Show Figures