Sustainability 2020, 12(5), 1893; https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051893 - 2 Mar 2020
Cited by 68 | Viewed by 13716
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Faced with a number of socio-economic challenges and a continuously rising risk of more frequent and higher-impact disasters, the Japanese government, in cooperation with the private sector, has formulated a new comprehensive strategy, under the name of “Society 5.0”, which is to utilize
[...] Read more.
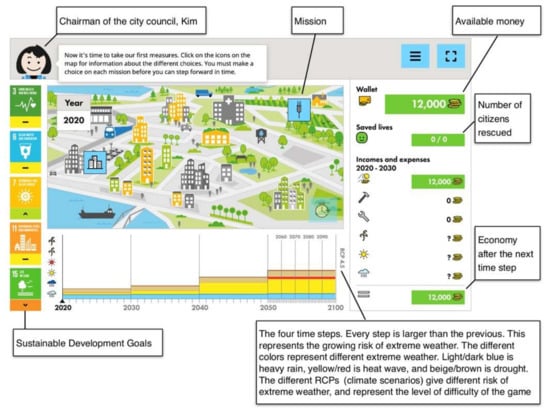
Faced with a number of socio-economic challenges and a continuously rising risk of more frequent and higher-impact disasters, the Japanese government, in cooperation with the private sector, has formulated a new comprehensive strategy, under the name of “Society 5.0”, which is to utilize a number of various technological innovative solutions in an attempt to provide a secure future for its citizens, centering around several important sectors. The current paper aims to discuss disaster risk and climate change policies in Society 5.0 in particular, with some special focus on adaptation and inclusiveness. We start with giving details on the Society 5.0 concept and its goals, after which we focus more specifically on how disaster and climate change policies are integrated into the new strategy and proceed to discuss several contentious issues which represent both opportunities and risks or challenges for implementing the concept in a truly sustainable way. The paper tries to present various points of view and hopes to provide some food for future thought and research, rather than solutions or specific suggestions.
Full article