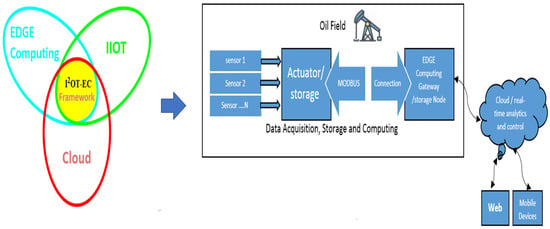
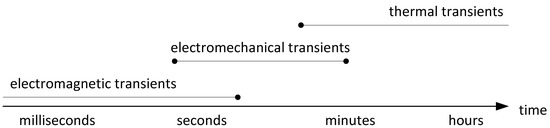
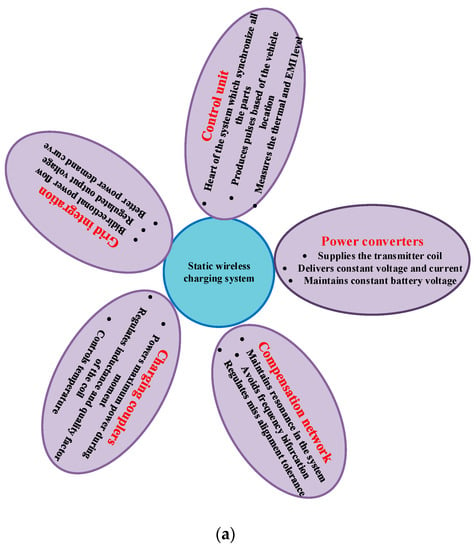
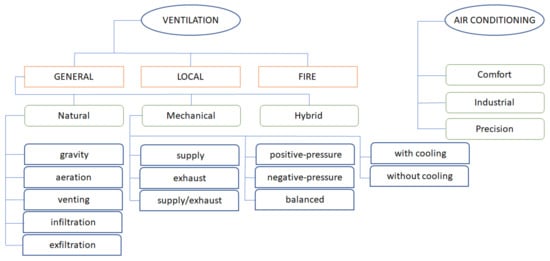
Energies 2023, 16(4), 1809; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041809 - 11 Feb 2023
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 6333
Abstract
The article aims to systematize the state of knowledge of and research on the inclusion of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) risk in companies’ business models, with a special stress on energy sector companies. Many publications address incorporating ESG, but only some deal
[...] Read more.
The article aims to systematize the state of knowledge of and research on the inclusion of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) risk in companies’ business models, with a special stress on energy sector companies. Many publications address incorporating ESG, but only some deal with it from the perspective of business models. This paper fills that gap. The methods of incorporating ESG risk into a sustainable business model, identified on the basis of the literature review, were verified based on the examples of three companies from the energy industry. A two-stage review of publications from the WoS and Scopus databases was carried out, considering a more comprehensive (sustainability) and a narrower (ESG risk) range of keywords, and the period from 2000 to 2022. The result showed that SMEs and large enterprises consider ESG risk in their risk management systems (ERMs), while small enterprises and start-ups do not. In Europe, Asia, and Australia, it is common to include ESG risk in an ERM, while it is rare in Latin America. In developing countries, companies in the service sector are more likely to include ESG risk in ERMs than those in the manufacturing sector. These findings may be useful for policymakers who wish to provide support and financial incentives for companies transforming their business models toward sustainability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section C: Energy Economics and Policy)
►
Show Figures