Energies 2022, 15(24), 9656; https://doi.org/10.3390/en15249656 - 19 Dec 2022
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 4185
Abstract
Battery degradation is a main concern for electric vehicle (EV) users, and a reliable capacity estimation is of major importance. Every EV battery management system (BMS) provides a variety of information, including measured current and voltage, and estimated capacity of the battery. However,
[...] Read more.
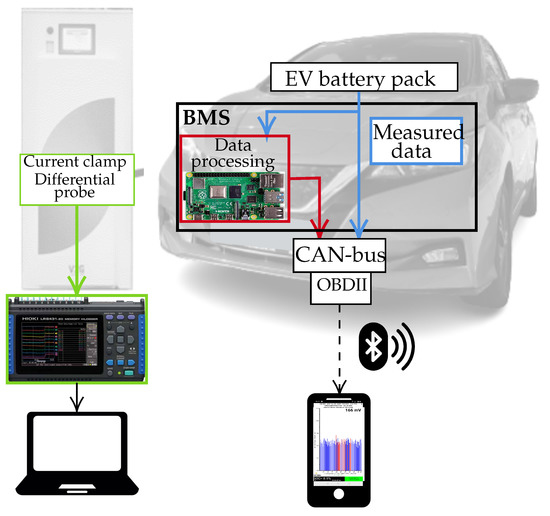
Battery degradation is a main concern for electric vehicle (EV) users, and a reliable capacity estimation is of major importance. Every EV battery management system (BMS) provides a variety of information, including measured current and voltage, and estimated capacity of the battery. However, these estimations are not transparent and are manufacturer-specific, although measurement accuracy is unknown. This article uses extensive measurements from six diverse EVs to compare and assess capacity estimation with three different methods: (1) reading capacity estimation from the BMS through the central area network (CAN)-bus, (2) using an empirical capacity estimation (ECE) method with external current measurements, and (3) using the same method with measurements coming from the BMS. We show that the use of BMS current measurements provides consistent capacity estimation (a difference of approximately 1%) and can circumvent the need for costly experimental equipment and DC chargers. This data can simplify the ECE method only by using an on-board diagnostics port (OBDII) reader and an AC charger, as the car measures the current directly at the battery terminals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Smart Electric Vehicle Charging Approaches for Demand Response)
►
Show Figures