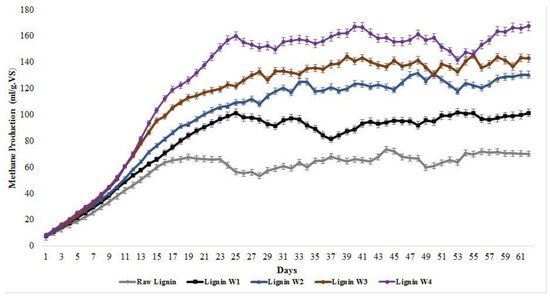
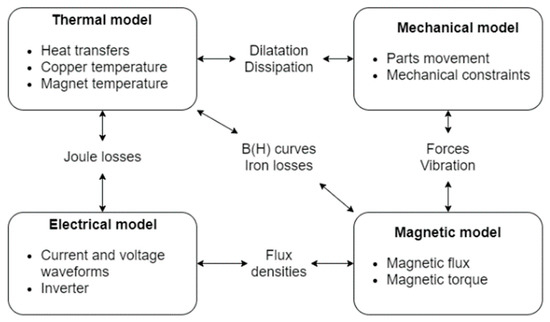
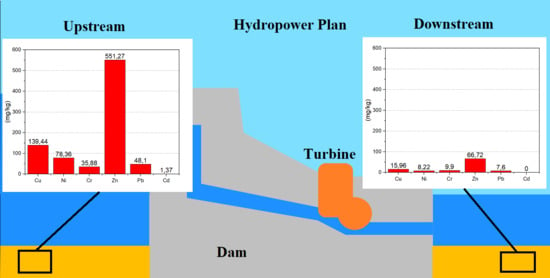
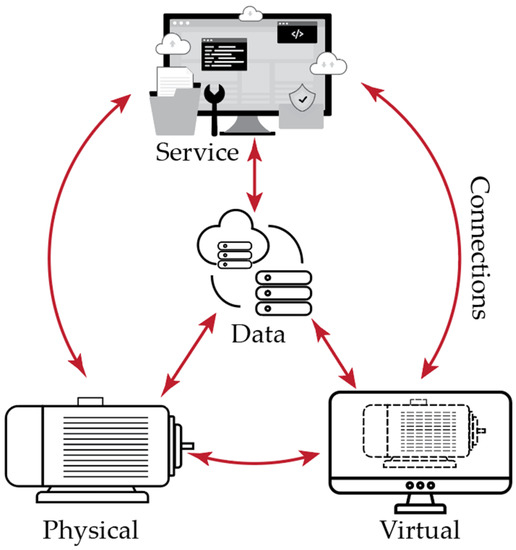
Energies 2021, 14(18), 5944; https://doi.org/10.3390/en14185944 - 18 Sep 2021
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 5094
Abstract
►
Show Figures
In recent years, perovskite solar cells (PSCs), often referred to as the third generation, have rapidly proliferated. Their most prominent deficiencies are their low efficiency and poor stability. To enhance their productivity, a combination of silicon and perovskite is employed. Here, we present
[...] Read more.
In recent years, perovskite solar cells (PSCs), often referred to as the third generation, have rapidly proliferated. Their most prominent deficiencies are their low efficiency and poor stability. To enhance their productivity, a combination of silicon and perovskite is employed. Here, we present a 3D simulation analysis of various electrical and optical properties of PSCs using the SILVACO simulation software. Using the inverted planar method with inorganic transport materials and the proper selection of anti-reflective coatings with a back contact layer increases the efficiency of PSCs to 28.064%, and enhances their stability without using silicone composites. Several materials, including CaF2, SiO2, and Al2O3, with various thicknesses have been employed to investigate the effect of anti-reflective coatings, and to improve the efficiency of the simulated PSC. The best thickness of the absorbent layer is 500 nm, using a CaF2 anti-reflective coating with an optimal thickness of 110 nm. A polymer composition of Spiro-OMeTAD and inorganic materials Cu2O and NiOx was used as the hole transport material (HTM) and inorganic ZnO was employed as the electron transport material (ETM) to optimize the solar cell efficiency, and an optimized thickness was considered for these materials. Yields of 29.261, 28.064 and 27.325% were obtained for Spiro-OMeTAD/ZnO, Cu2O/ZnO and NiOx/ZnO, respectively. Thus, Spiro-OMeTAD yields the highest efficiency. This material is highly expensive with a complex synthesis and high degradability. We proposed to employ Cu2O to alleviate these problems; however, this reduces the efficiency by 1.197%. As a graphene connector has high flexibility, reduces cell weight, and is cheaper and more accessible compared to other metals, it was regarded as an optimal alternative. The simulation results indicate that using the inverted planar method with inorganic transport materials for graphene-based PSCs is highly promising.
Full article