Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23(8), 4110; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084110 - 8 Apr 2022
Cited by 175 | Viewed by 21531
Abstract
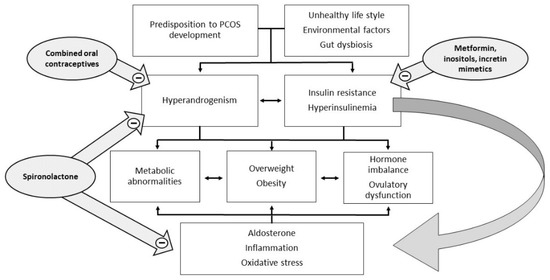
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a heterogeneous and extremely common disease with symptoms that vary with the age of the patient, typically characterized by hyperandrogenism, chronic oligo-anovulation, and/or several metabolic disorders. The syndrome includes various phenotypes, and the pathogenesis is multifactorial, often involving
[...] Read more.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a heterogeneous and extremely common disease with symptoms that vary with the age of the patient, typically characterized by hyperandrogenism, chronic oligo-anovulation, and/or several metabolic disorders. The syndrome includes various phenotypes, and the pathogenesis is multifactorial, often involving insulin resistance. This feature is closely related to ovarian dysfunction, inflammation, hyperandrogenism, and metabolic disorders, which characterize and complicate the syndrome. Therapy currently considers both lifestyle improvements and medications, and must be tailored on a case-by-case basis. To date, the published studies have not arrived at a definition of the most suitable therapy for each individual case and many of the drugs used are still off-label. In this review, we discuss some controversial diagnostic and therapeutic aspects of PCOS, such as the role of insulin resistance, inflammation, and hyperandrogenism. We also evaluated the advantages and disadvantages of contraceptive therapy and antiandrogens.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advance in Reproductive Biology and Related Diseases)
►
Show Figures