Molecules 2021, 26(7), 1864; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071864 - 25 Mar 2021
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 2917
Abstract
Abelmoschus manihot (L.) Medic (AM), called Huangshukui in Chinese, is a widely used medicinal plant. Each part of AM has medicinal value, including Abelmoschi Radix (AR), Abelmoschi Herba (AH), Abelmoschi Folium (AF), Abelmoschi Corolla (AC), and Abelmoschi Semen (AS). However, only AC is
[...] Read more.
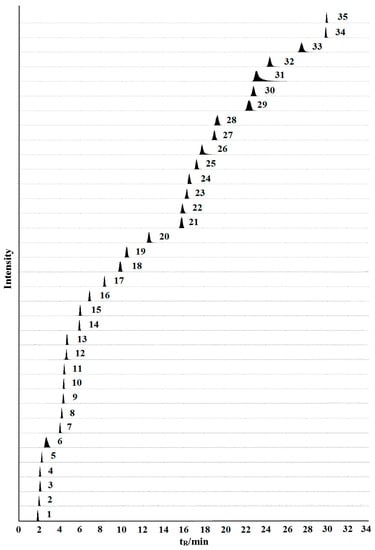
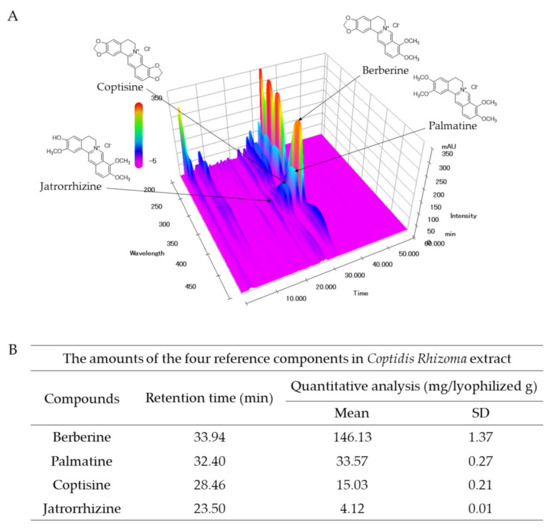
Abelmoschus manihot (L.) Medic (AM), called Huangshukui in Chinese, is a widely used medicinal plant. Each part of AM has medicinal value, including Abelmoschi Radix (AR), Abelmoschi Herba (AH), Abelmoschi Folium (AF), Abelmoschi Corolla (AC), and Abelmoschi Semen (AS). However, only AC is documented in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. In order to investigate whether there is any difference between AC and the other parts of AM, an analytical method based on ultra-fast performance liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole-linear ion trap mass spectrometry (UFLC-QTRAP-MS/MS) was established for the simultaneous determination of 35 constituents in different parts of AM. Moreover, principal components analysis (PCA) and partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) were applied to classify and evaluate the different parts of AM based on the content of the 35 constituents. The total contents of the 35 constituents in AC were significantly higher than in the other parts of AM and the results revealed significant differences between AC and the other parts of AM. Eight constituents were remarkably related to the sample classifications. This research does not just provide the basic information for revealing the distribution patterns in different parts of AM from the same origin, but also complements some of the scientific data for the comprehensive quality evaluation of AC.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Phytochemical and Pharmacological Evaluation of Natural Products)
►
Show Figures