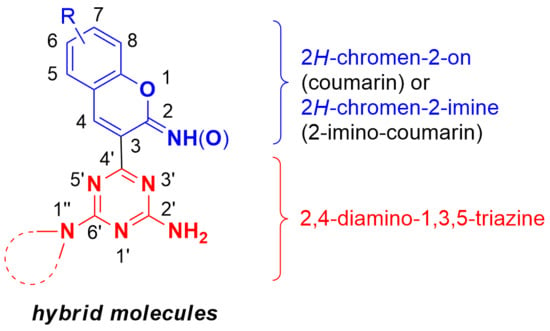
A series of 2-imino-2
H-chromen-3-yl-1,3,5-triazine compounds
5–
12, which are namely hybrids of 2,4-diamino-1,3,5-triazines and 2-imino-coumarins, was synthesized by reacting 2-(4,6-diamine-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)acetonitriles
1–
4 with 2-hydroxybenzaldehydes. After this, upon heating in aqueous DMF, 2-imino-2
H-chromen-3-yl-1,3,5-triazines
10 and
12 were
[...] Read more.
A series of 2-imino-2
H-chromen-3-yl-1,3,5-triazine compounds
5–
12, which are namely hybrids of 2,4-diamino-1,3,5-triazines and 2-imino-coumarins, was synthesized by reacting 2-(4,6-diamine-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)acetonitriles
1–
4 with 2-hydroxybenzaldehydes. After this, upon heating in aqueous DMF, 2-imino-2
H-chromen-3-yl-1,3,5-triazines
10 and
12 were converted into the corresponding 2
H-chromen-3-yl-1,3,5-triazines
13 and
14, which are essentially hybrids of 2,4-diamino-1,3,5-triazines and coumarins. The in vitro anticancer activity of the newly prepared compounds was evaluated against five human cancer cell lines: DAN-G, A-427, LCLC-103H, SISO and RT-4. The greatest cytotoxic activity displayed 4-[7-(diethylamino)-2-imino-2
H-chromen-3-yl]-6-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-amine (11, IC
50 in the range of 1.51–2.60 μM).
Full article