Energy Efficient Design for Body Sensor Nodes
Abstract
:1. Overview of BSNs
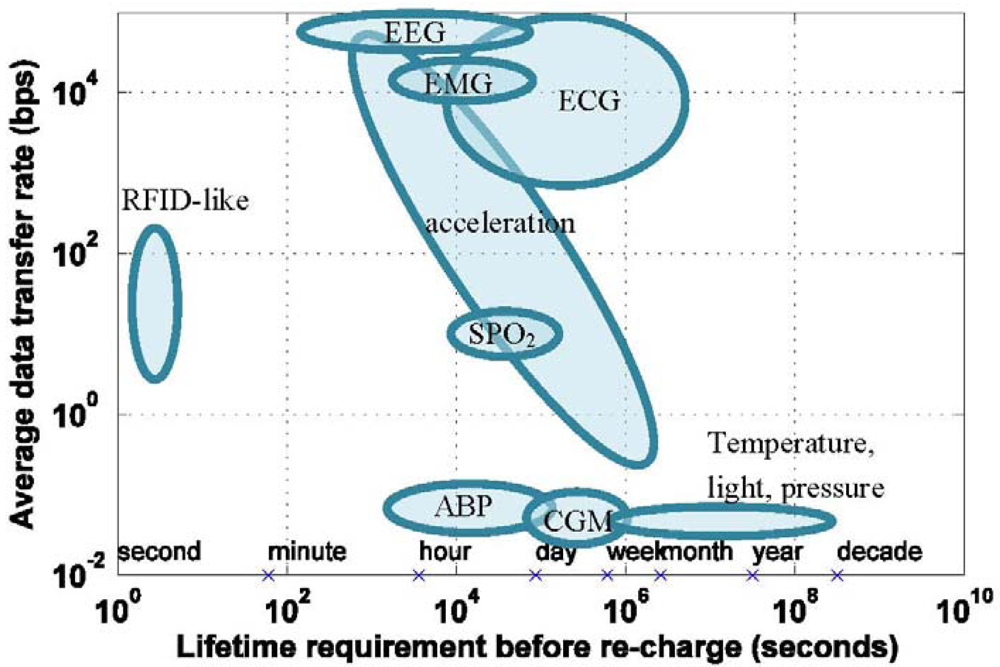
BSN Requirements
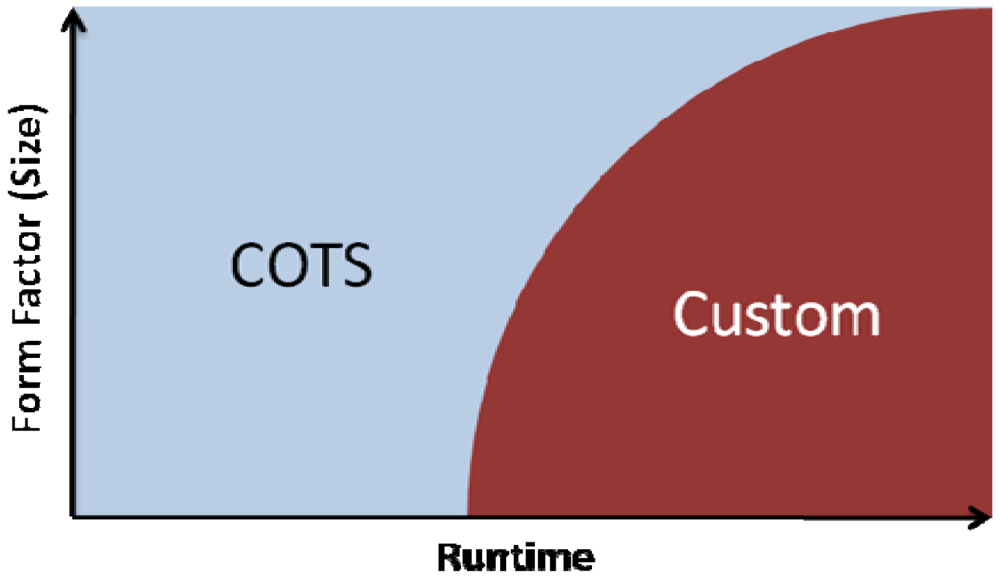
2. Hardware Selection—Commercial off the Shelf or Custom?
3. General Strategies for Energy Efficient BSN Hardware
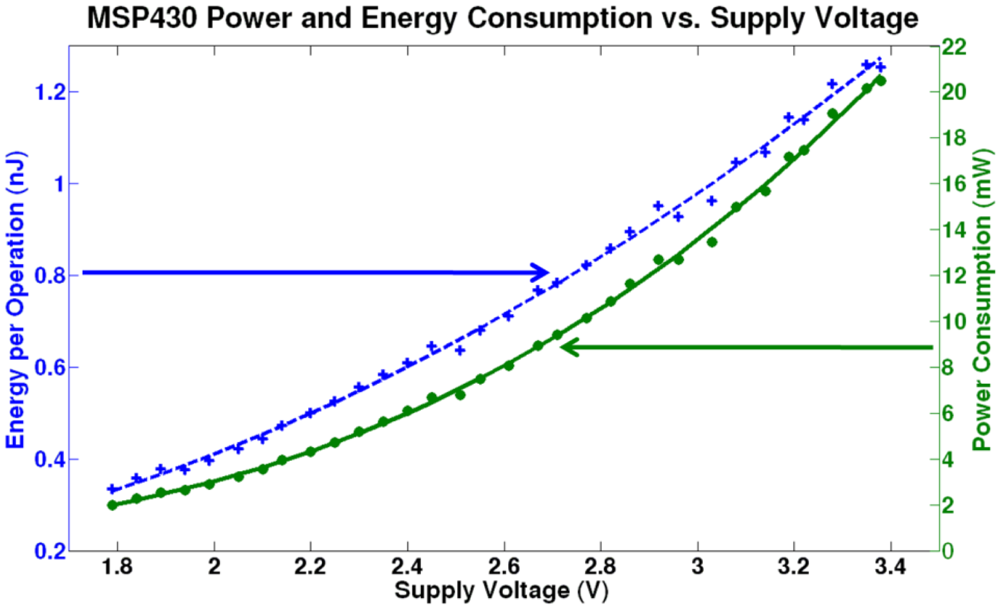
3.1. Supply Voltage Management
3.2. Communication versus Computation
3.3. Flexibility versus Efficiency
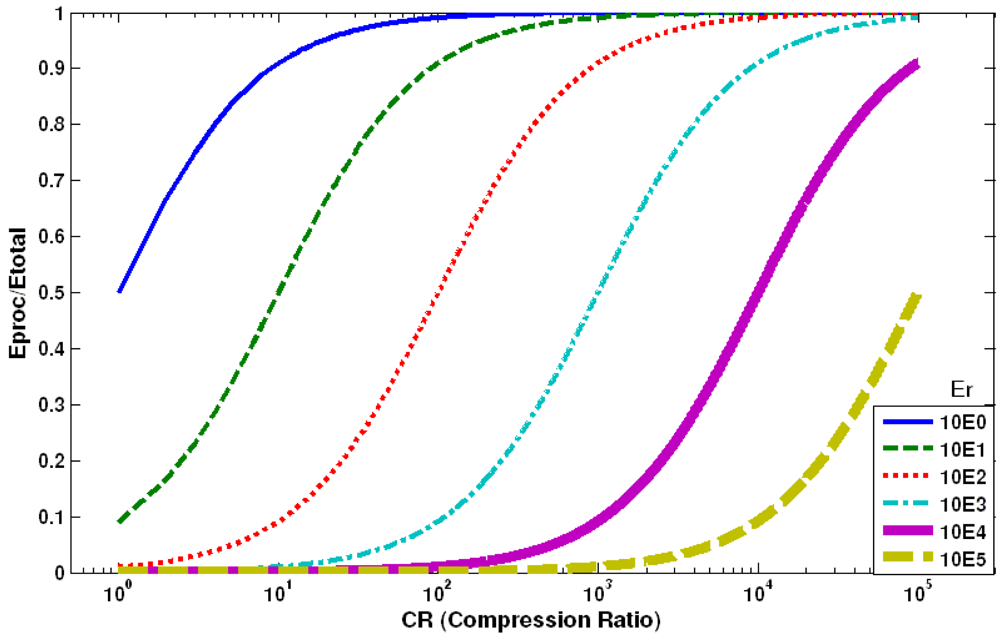
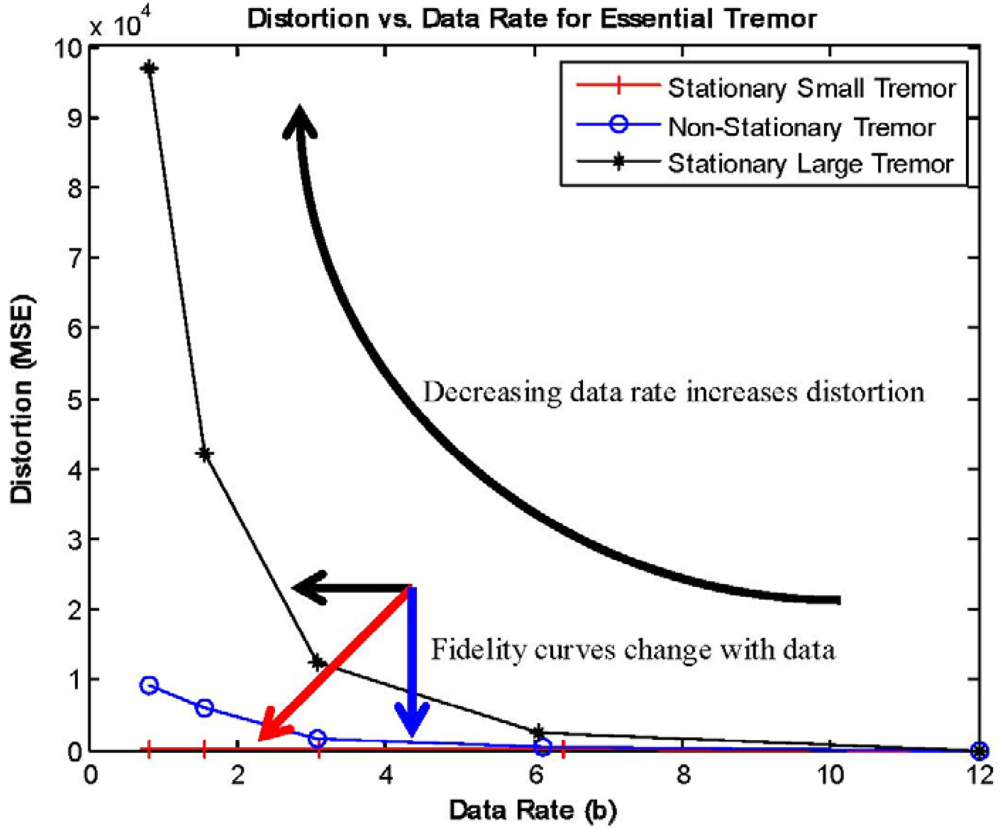
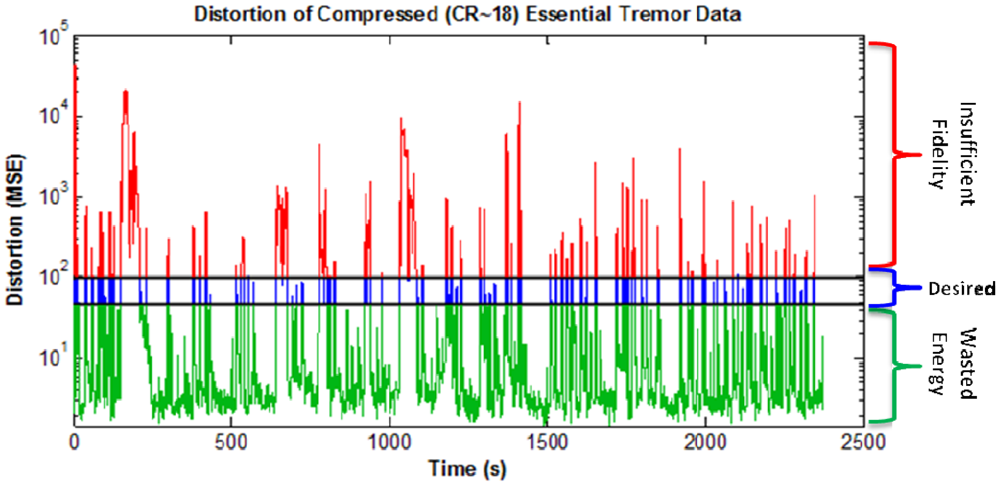
3.4. Data Fidelity versus Energy
- capable of being implemented on resource-constrained BSN embedded processors;
- capable of executing in low-latency and soft real-time applications;
- adjustable by key knobs to alter expected data reduction rates.
4. Case Studies
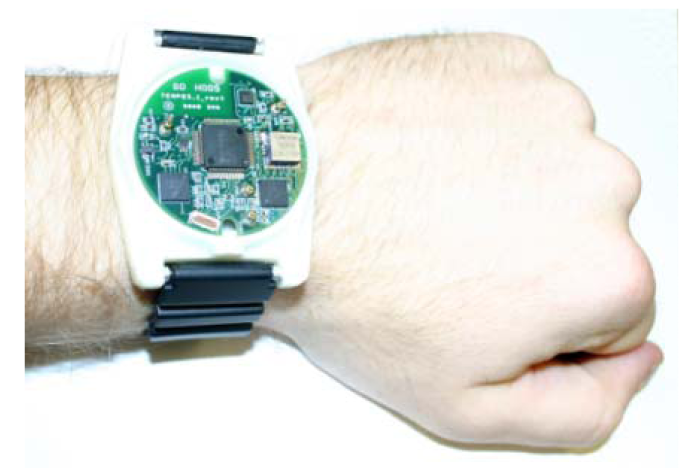
4.1. Case Study of COTS System: TEMPO
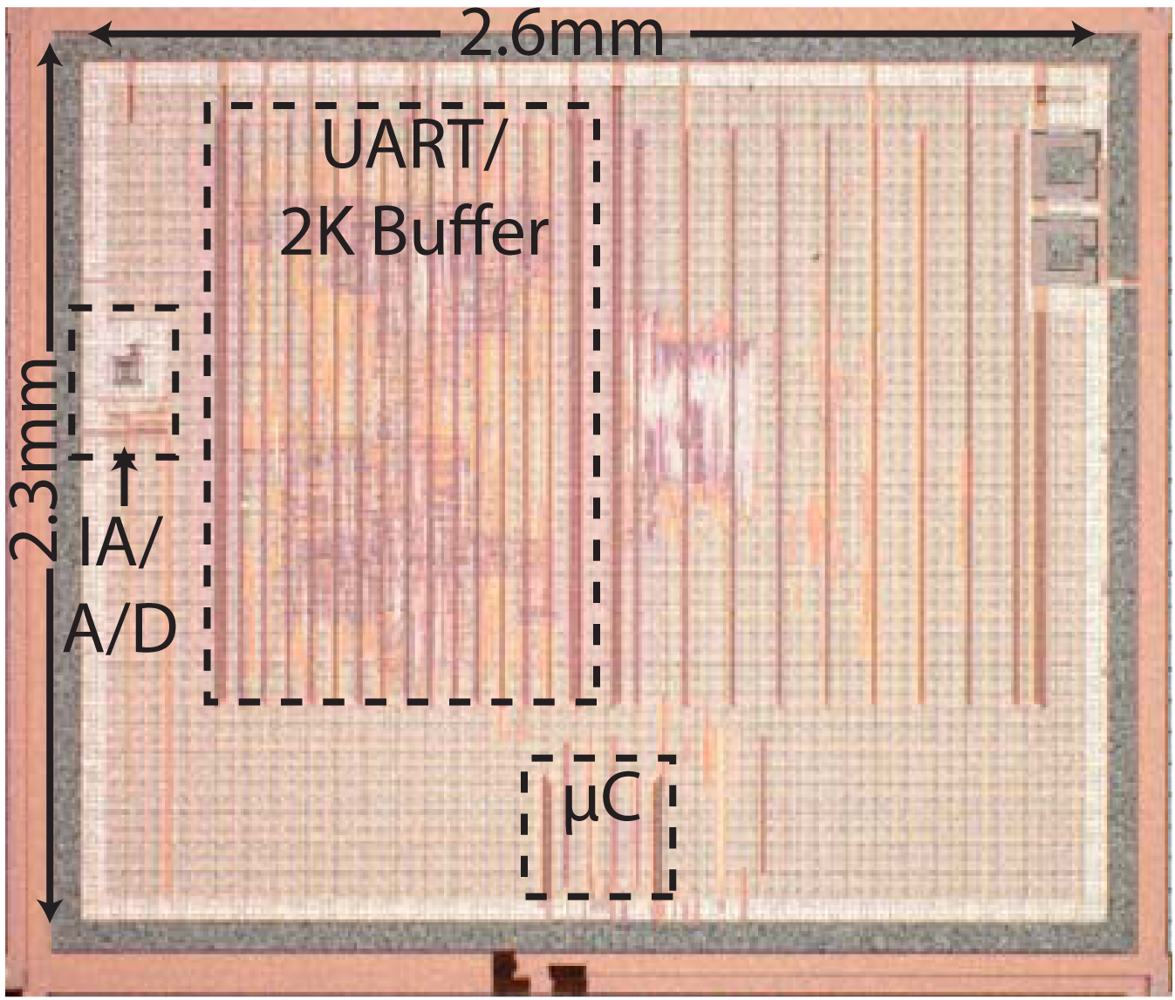
4.2. Case Study of Custom IC System
5. Conclusions




| Energy per Instruction | Energy per Processed Sample | Delay per Sample | Estimate Max Achievable Data Rate | GOPS/W | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPP (from [7]) | 2.62 pJ | 210 pJ | 8 μs (80 clock cycles) | 125 kHz | 4.76 |
| FPGA (from [26]) | N/A | 2.22 pJ | 94.5 ns (1 clock cycle) | 10 MHz | 450 |
| ASIC | N/A | 0.23pJ | 6.18 ns (1 clock cycle) | 150 MHz | 4348 |
References
- Yang, G.Z. (Ed.) Body Sensor Networks; Springer-Verlag: London, UK, 2006.
- Barth, A.T.; Hanson, M.A.; Powell, H.C., Jr.; Lach, J. TEMPO 3.1: A Body Area Sensor Network Platform for Continuous Movement Assessment. Proceedings of the 2009 Sixth International Workshop on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks, Berkeley, CA, USA, 3–5 June 2009; pp. 71–76.
- Bequette, B.W. A critical assessment of algorithms and challenges in the development of a closed-loop artificial pancreas. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2005, 7, 28–47. [Google Scholar]
- Jurik, A.; Weaver, A. Remote medical monitoring. IEEE Comput. 2008, 41, 96–99. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, M.A.; Powell, H.C., Jr.; Barth, A.T.; Ringgenberg, K.; Calhoun, B.H.; Aylor, J.H.; Lach, J. Body area sensor networks: Challenges and opportunities. IEEE Comput. 2009, 42, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chandrakasan, A.; Kosonocky, S. Optimal Supply and Threshold Scaling for Sub-threshold CMOS Circuits. Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI 2002, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 25–26 April 2002; pp. 7–11.
- Jocke, S.; Bolus, J.; Wooters, S.N.; Jurik, A.D.; Weaver, A.C.; Blalock, T.N.; Calhoun, B.H. A 2.6-μW Sub-threshold Mixed-signal ECG SoC. Proceedings of the Symposium on VLSI Circuits 2009, Kyoto, Japan, 16–18 June 2009; pp. 60–61.
- Calhoun, B.H.; Chandrakasan, A.P. Ultra-dynamic voltage scaling (UDVS) using sub-threshold operation and local voltage dithering. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2006, 41, 238–245. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, H.C., Jr.; Barth, A.T.; Lach, J. Dynamic Voltage-frequency Scaling in Body Area Sensor Networks Using COTS Components. Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Body Area Networks, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1–3 April 2009.
- Si, W.W.; Husted, P.; Weber, D.; Abdollahi-Alibeik, S.; Lee, M.; Chang, R.; Dogan, H.; Gan, H.; Rajavi, Y.; Luschas, S.; Ozgur, S.; Zargari, M. A single-chip CMOS Bluetooth v2.1 radio SoC. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2008, 43, 2896–2904. [Google Scholar]
- van Zeijl, P.; Eikenbroek, J.W.; Vervoort, P.P.; Setty, S.; Tangenberg, J.; Shipton, G.; Kooistra, E.; Keekstra, I.; Belot, D. A Bluetooth radio in 0.18-μm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2002, 37, 1679–1687. [Google Scholar]
- Kohno, R.; Hamaguchi, K.; Li, H.; Takizawa, K. R&D and Standardization of Body Area Network (BAN) for Medical Healthcare. Proceedings of the International Conference on Ultra-Wideband, Hannover, Germany, 10–12 September 2008; pp. 5–8.
- Drago, S.; Leenaerts, D.; Sebastiano, F.; Breems, L.; Makinwa, K.A.A.; Nauta, B. A 2.4 GHz 830 pJ/bit Duty-cycled Wake-up Receiver with -82 dBm Sensitivity for Crystal-less Wireless Sensor Nodes. Proceedings of the International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 7–11 February 2010; pp. 224–225.
- Ayers, J.; Mayaram, K.; Fiez, T.S. An ultralow-power receiver for wireless sensor networks. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2010, 45, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar]
- Pletcher, N.; Gambini, S.; Rabaey, J. A 65 μW, 1.9 GHz RF to Digital Baseband Wakeup Receiver for Wireless Sensor Nodes. Proceedings of the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 16–19 September 2007; pp. 539–542.
- Daly, D.C.; Chandrakasan, A.P. An energy-efficient OOK transceiver for wireless sensor networks. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2007, 42, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Rabaey, J.M.; Abnous, A.; Ichikawa, Y.; Seno, K.; Wan, M. Heterogeneous Reconfigurable Systems. Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Signal Processing Systems, SiPS 97 Design and Implementation formerly VLSI Signal Processing, Leicester, UK, 3–5 November 1997; pp. 24–34.
- Zhang, H.; Prabhu, V.; George, V.; Wan, M.; Benes, M.; Abnous, A.; Rabaey, J.M. A 1-V heterogeneous reconfigurable DSP IC for wireless baseband digital signal processing. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2000, 35, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, B.; Nazhandali, L.; Olson, J.; Reeves, A.; Minuth, M.; Helfand, R.; Pant, S.; Blaauw, D.; Austin, T. A 2.60 pJ/inst Subthreshold Sensor Processor for Optimal Energy Efficiency. Proceedings of the Symposium on VLSI Technology and Circuits, Hawaii, HI, USA, 13–17 June 2006; pp. 154–155.
- Seok, M.; Hanson, S.; Lin, Y.S.; Foo, Z.; Kim, D.; Lee, Y.; Liu, N.; Sylvester, D.; Blaauw, D. The Phoenix Processor: A 30pW Platform for Sensor Applications. Proceedings of the Symposium on VLSI Technology and Circuits, Hawaii, HI, USA, 14–16 June 2008; pp. 188–189.
- Kwong, J.; Ramadass, Y.; Verma, N.; Chandrakasan, A. A 65 nm sub-Vt microcontroller with integrated SRAM and switched capacitor DC-DC converter. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2009, 44, 115–126. [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun, B.H.; Wang, A.; Chandrakasan, A. Modeling and sizing for minimum energy operation in sub-threshold circuits. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2005, 40, 1778–1786. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chandrakasan, A. A 180 mV FFT Processor Using Subthreshold Circuit Techniques. Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–10 February 2005; pp. 292–293.
- Pu, Y.; de Gyvez, J.P.; Corporaal, H.; Ha, Y. An Ultra-low-energy/frame Multi-standard JPEG co-processor in 65nm CMOS with Sub/near-threshold Power Supply. Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–12 February 2009; pp. 146–147.
- Kim, C.; Soeleman, H.; Roy, K. Ultra-low-power DLMS adaptive filter for hearing aid applications. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2003, 11, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, J.F.; Calhoun, B.H. A Sub-threshold FPGA with Low-swing Dual-VDD Interconnect in 90nm CMOS. Proceedings of the Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 18–21 September 2010.
- Texas Instruments MSP430F5172 Datasheet. Available online: http://www.ti.com (accessed on 24 January 2011).
- Hanson, M.A.; Powell, H.C., Jr.; Barth, A.T.; Lach, J. Enabling Data-centric Energy-fidelity Scalability in Wireless Body Area Sensor Networks. Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Body Area Networks, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1–3 April 2009.
- Barth, A.T.; Hanson, M.A.; Powell, H.C., Jr.; Lach, J. Online Data and Execution Profiling for Dynamic Energy-fidelity Optimization in Body Sensor Networks. Proceedings of the International Conference on Body Sensor Networks, Biopolis, Singapore, 7–9 June 2010; pp. 213–218.
- Hill, J.L.; Culler, D.E. Mica: A wireless platform for deeply embedded networks. IEEE Micro 2002, 22, 12–24. [Google Scholar]
- Polastre, J.; Szewczyk, R.; Culler, D. Telos: Enabling Ultra-low Power Wireless Research. Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 25–27 April 2005; pp. 364–369.
- Lo, B.; Thiemjarus, S.; King, R.; Yang, G.Z. Body Sensor Network—a Wireless Sensor Platform for Pervasive Healthcare Monitoring. Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference, PERVASIVE 2005, Munich, Germany, 8–13 May 2005.
- Microchip PIC16C5X Datasheet. Available online: http://www.microchip.com (accessed on 24 January 2011).
- Chen, G.; Ghaed, H.; Haque, R.; Wieckowski, M.; Kim, Y.; Kim, G.; Fick, D.; Kim, D.; Seok, M.; Wise, K.; Blaauw, D.; Sylvester, D. A 1 Cubic Millimeter Energy-autonomous Wireless Intraocular Pressure Monitor. Proceedings of the International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–24 February 2011; pp. 310–311.
- Liao, Y.; Yao, H.; Parviz, B.; Otis, B. 3 μW Wirelessly Powered CMOS Glucose Sensor for an Active Contact Lens. Proceedings of the International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–24 February 2011; pp. 38–39.
- Zou, X.; Xu, X.; Yao, L.; Lian, Y. A 1-V 450-nW fully integrated programmable biomedical sensor interface chip. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2009, 44, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Yoo, J.; Kim, B.; Yoo, H. A 0.5-μVrms 12-μW wirelessly powered patch-type healthcare sensor for wearable body sensor network. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2010, 45, 2356–2365. [Google Scholar]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Shakhsheer, Y.; Barth, A.T.; Powell Jr., H.C.; Ridenour, S.A.; Hanson, M.A.; Lach, J.; Calhoun, B.H. Energy Efficient Design for Body Sensor Nodes. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2011, 1, 109-130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea1010109
Zhang Y, Shakhsheer Y, Barth AT, Powell Jr. HC, Ridenour SA, Hanson MA, Lach J, Calhoun BH. Energy Efficient Design for Body Sensor Nodes. Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications. 2011; 1(1):109-130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea1010109
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yanqing, Yousef Shakhsheer, Adam T. Barth, Harry C. Powell Jr., Samuel A. Ridenour, Mark A. Hanson, John Lach, and Benton H. Calhoun. 2011. "Energy Efficient Design for Body Sensor Nodes" Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications 1, no. 1: 109-130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea1010109





