Explore, Synthesize, and Repeat: Unraveling Complex Water Management Issues through the Stakeholder Engagement Wheel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
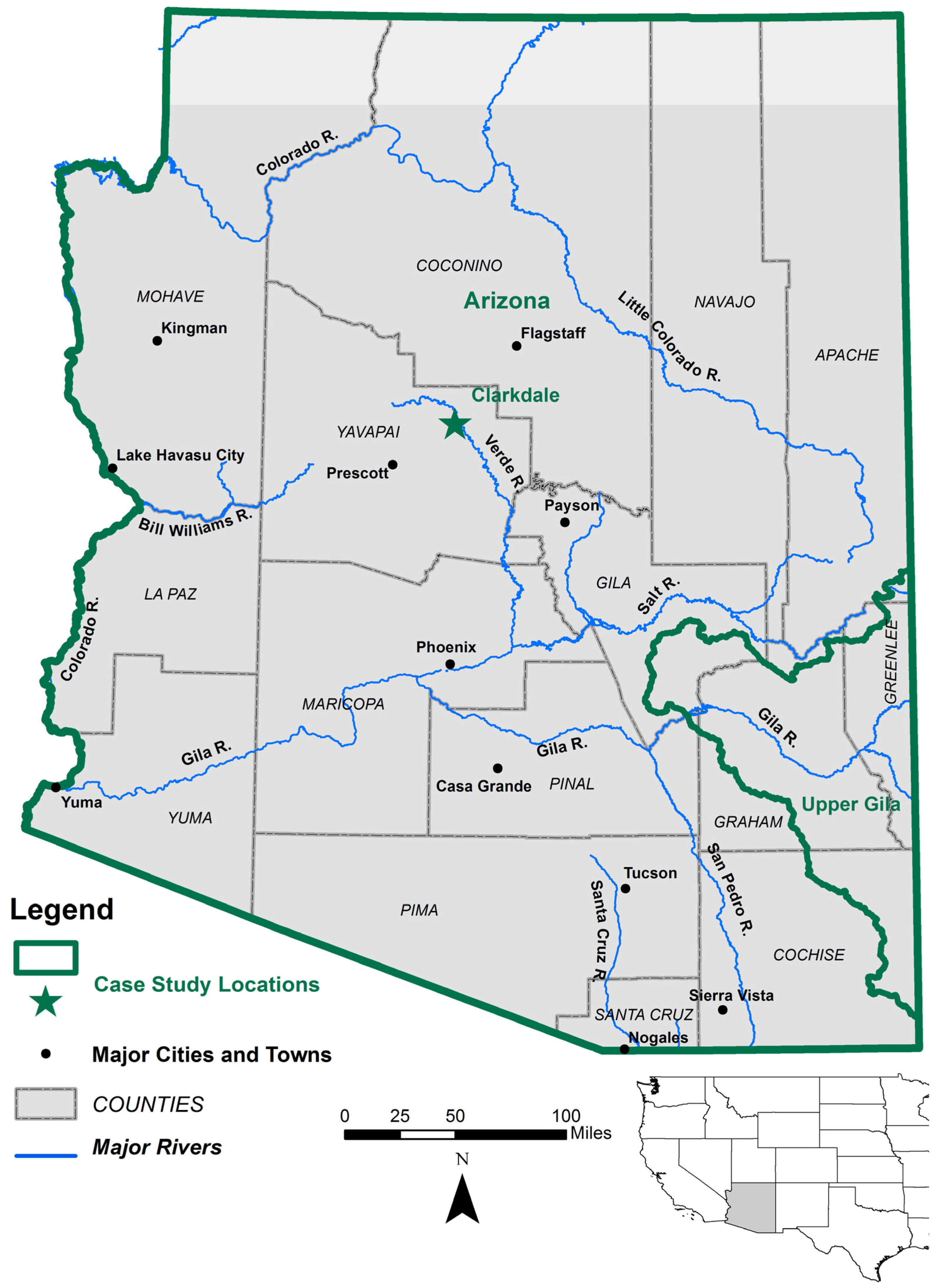
2. Study Areas and Key Project Aspects
2.1. Statewide Geographic Scale: Arizona
2.2. Watershed Scale: Upper Gila River Watershed
2.3. Town Scale: Town of Clarkdale
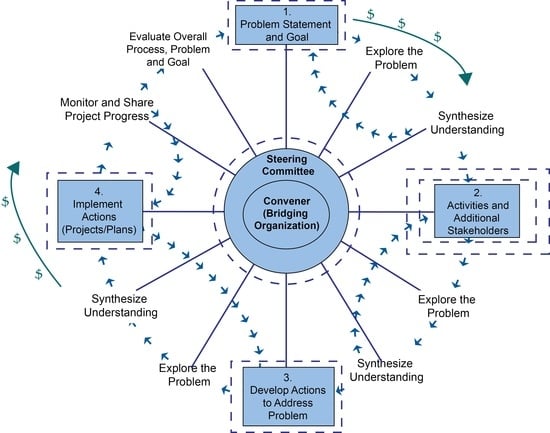
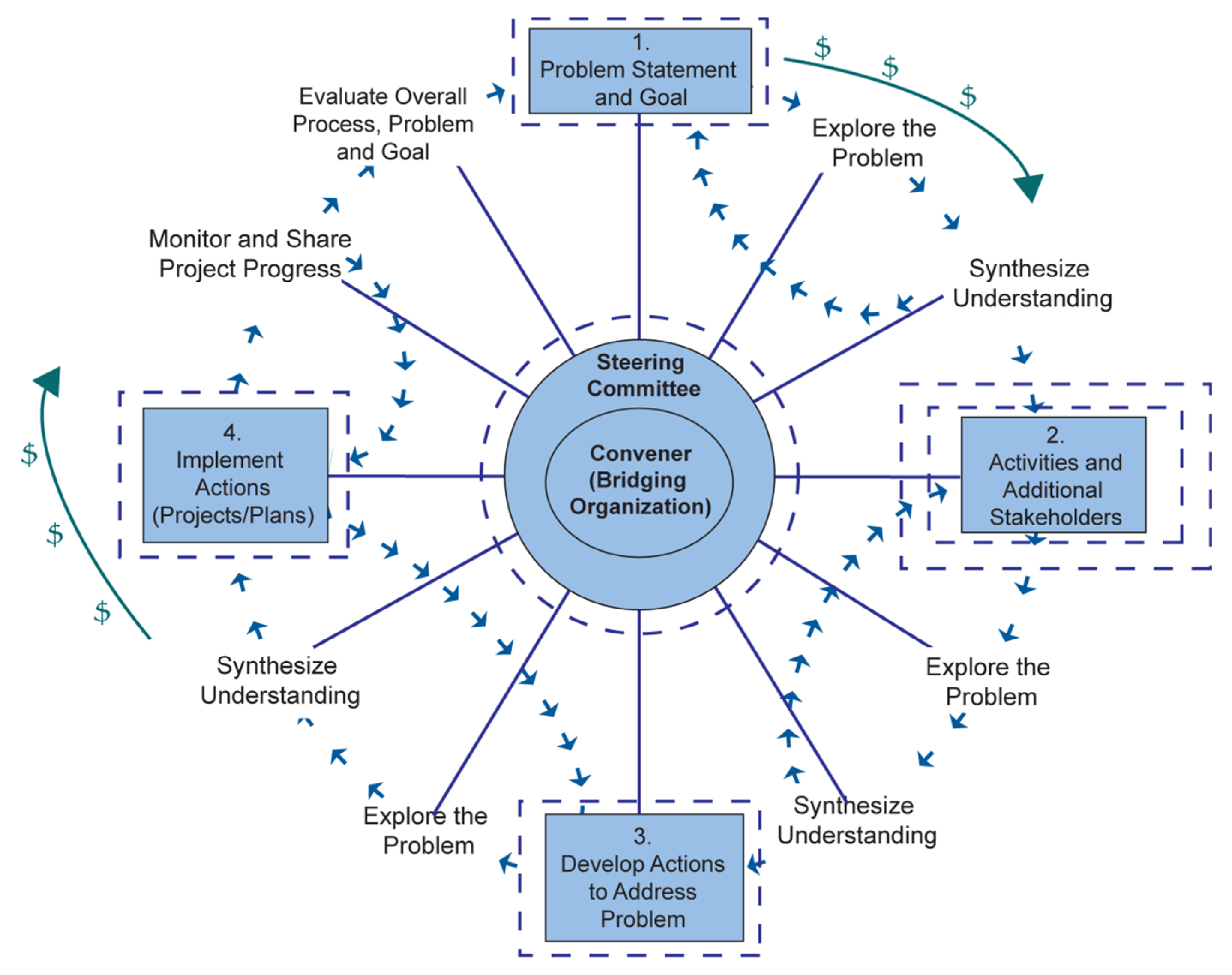
3. The Stakeholder Engagement Wheel
3.1. Getting Started—The Importance of the Convener and the Steering Committee
3.2. Setting the Wheel in Motion—Creating a Problem Statement and Goal (Step 1)
3.3. Maintaining the Momentum—Engagement Activities (Step 2)
3.4. Getting Traction—Developing and Implementing Action Items (Steps 3 and 4)
3.5. Coming Full Circle—Evaluation of Effectiveness
4. Discussion and Final Remarks
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lennox, J.; Proctor, W.; Russell, S. Structuring Stakeholder Participation in New Zealand’s Water Resource Governance. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, P.; Kallis, G.; Videira, N.; Santos, R. Participation and Evaluation for Sustainable River Basin Governance. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.R.; Wentholt, M.T.; Rowe, G.; Frewer, L.J. Expert Involvement in Policy Development: A Systematic Review of Current Practice. Sci. Public Policy 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahl-Wostl, C. A Conceptual Framework for Analysing Adaptive Capacity and Multi-Level Learning Processes in Resource Governance Regimes. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2009, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turton, A.R.; Hattingh, J.; Claassen, M.; Roux, D.J.; Ashton, P.J. Towards a Model for Ecosystem Governance: An Integrated Water Resource Management Example. In Governance as a Trialogue: Government-Society-Science in Transition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Mathur, V.N.; Price, A.D.; Austin, S. Conceptualizing Stakeholder Engagement in the Context of Sustainability and Its Assessment. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2008, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, J.J.; Brown, R.R.; Farrelly, M.A. A Design Framework for Creating Social Learning Situations. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumler, L.M.; Lemos, M.C. Managing Waters of the Paraíba Do Sul River Basin, Brazil: A Case Study in Institutional Change and Social Learning. Ecol. Soc. 2008, 13, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, M.; Evely, A.C.; Cundill, G.; Fazey, I.R.A.; Glass, J.; Laing, A.; Newig, J.; Parrish, B.; Prell, C.; Raymond, C.; et al. What Is Social Learning? Ecol. Soc. 2010, 15, r1. [Google Scholar]
- Berkes, F. Evolution of Co-Management: Role of Knowledge Generation, Bridging Organizations and Social Learning. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternlieb, F.; Bixler, R.P.; Huber-Stearns, H. A Question of Fit: Reflections on Boundaries, Organizations and Social–Ecological Systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, K.; Lebel, L.; Buizer, J.; Addams, L.; Matson, P.; McCullough, E.; Garden, P.; Saliba, G.; Finan, T. Linking Knowledge with Action in the Pursuit of Sustainable Water-Resources Management. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C. Hybrid Management: Boundary Organizations, Science Policy, and Environmental Governance in the Climate Regime. Sci. Technol. Hum. Values 2001, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.; Wilkinson, R. Beyond Participation: Boundary Organizations as a New Space for Farmers and Scientists to Interact. Soc. Nat. Resour. 2005, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, K.E.M.; Xiu, B.C.; Megdal, S.B. Building Common Ground for Environmental Flows using Traditional Techniques and Novel Engagement Approaches. Environ. Manag. 2016, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, C.; York, A.M.; White, D.; Schoon, M.L.; Bodner, G.S. Navigating a Murky Adaptive Comanagement Governance Network: Agua Fria Watershed, Arizona, USA. Ecol. Soc. 2013, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.S. Stakeholder Participation for Environmental Management: A Literature Review. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areizaga, J.; Sano, M.; Medina, R.; Juanes, J. Improving Public Engagement in ICZM: A Practical Approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolibert, C.; Wesselink, A. Research Impacts and Impact on Research in Biodiversity Conservation: The Influence of Stakeholder Engagement. Environ. Sci. Policy 2012, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thought Stream. Five Criteria for Effective Stakeholder Engagement in Education. 2013. Available online: http://www.thoughtstream.ca/downloads/5-criteria-for-effective-se-may2013.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2014).
- Jeffery, N. Stakeholder Engagement: A Road Map to Meaningful Engagement. Doughty Centre, Cranfield University School of Management, 2009. Available online: http://www.som.cranfield.ac.uk/som/dinamic-content/research/doughty/stakeholder/Guide.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2016).
- Muro, M.; Jeffrey, P. Time to Talk? How the Structure of Dialog Processes Shapes Stakeholder Learning in Participatory Water Resources Management. Ecol. Soc. 2012, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, A. Varieties of Participation in Complex Governance. Public Admin. Rev. 2006, 66, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, E.; Baker, H.; Smith, M.; Moore, E.; Morgan, V. BiodivERsA Stakeholder Engagement Handbook; BiddivERsA: Paris, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Stakeholder Research Associates Canada Inc. From Words to Action: The Stakeholder Engagement Manual Volume 1; Stakeholder Research Associates Canada Inc.: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, M.; Arizona Department of Water Resources, Phoenix, AZ, USA. Personal communication, 2015.
- Megdal, S.B.; Gerlak, A.K.; Varady, R.G.; Huang, L.Y. Groundwater Governance in the United States: Common Priorities and Challenges. Groundwater 2015, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, K.L. Balancing Competing Interests: The History of State and Federal Water Laws. In Arizona Water Policy: Management Innovations in an Urbanizing, Arid Region, 1st ed.; Jacobs, K., Colby, B.G., Eds.; Resources for the Future: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; pp. 26–44. [Google Scholar]
- Glennon, R. The Disconnect between Water Law and Hydrology. In Arizona Water Policy: Management Innovations in an Urbanizing, Arid Region, 1st ed.; Resources for the Future: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; pp. 106–120. [Google Scholar]
- Mott Lacroix, K.E.; Xiu, B.C.; Nadeau, J.B.; Megdal, S.B. Synthesizing environmental flow needs data for water management in a water-scarce state: The Arizona Environmental Water Demands Database. River Res. Appl. 2016, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colby, B.G.; Thorson, J.E.; Britton, S. Negotiating Tribal Water Rights: Fulfilling Promises in the Arid West; University of Arizona Press: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Arizona Department of Water Resources. Arizona Water Atlas Volume 3: Southeastern Arizona Planning Area; Arizona Department of Water Resources: Phoenix, AZ, USA, 2009; p. 619.
- Bannister, K.; Chan, D.; Driscoll, J.M.; Fullerton, C.; Lien, A.; Lacroix, K.M. Atlas of the Upper Gila River Watershed; University of Arizona Water Resources Research Center: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix, K.M.; Hullinger, A.; Fullerton, C. Scenarios for Upper Gila River Watershed; University of Arizona Water Resources Research Center: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Von Gausig, D.; O’Banion, B.; Rooney, C. Verde River Economic Development Final Report. 2011. Available online: http://clarkdalesustainabilitypark.org/Verde%20River%20Reports%202011/VREDS%20Final%20Report-public-8-12-2011.pdf (accessed on 7 December 2015).
- Lacroix, K.M.; Fullerton, C.; Rupprecht, C. Town of Clarkdale Water Resources Management Program Recommendations Report; University of Arizona Water Resources Research Center: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Saarikoski, H.; Tikkanen, J.; Leskinen, L.A. Public Participation in Practice—Assessing Public Participation in the Preparation of Regional Forest Programs in Northern Finland. For. Policy Econ. 2010, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.A.; Varady, R.G.; Meza, F.; Montaña, E.; de Raga, G.B.; Luckman, B.; Martius, C. Science-Policy Dialogues for Water Security: Addressing Vulnerability and Adaptation to Global Change in the Arid Americas. Environ. Sci. Policy Sustain. Dev. 2012, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.B.; Senecah, S.L.; Daniels, S.E. From the Forest to the River: Citizens’ Views of Stakeholder Engagement. Hum. Ecol. Rev. 2006, 13, 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- De Stefano, L. Facing the Water Framework Directive Challenges: A Baseline of Stakeholder Participation in the European Union. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, A.I.; Helgenberger, S.; Wiek, A.; Scholz, R.W. Measuring Societal Effects of Transdisciplinary Research Projects: Design and Application of an Evaluation Method. Eval. Program Plan. 2007, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnstein, S.R. A Ladder of Citizen Participation. J. Am. Inst. Plan. 1969, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyet, V.; Schlaepfer, R.; Parlange, M.B.; Buttler, A. A framework to implement Stakeholder participation in environmental projects. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, S.; Williams, L.J. Monitoring the Success of Stakeholder Engagement: Literature Review. In People, Communities and Economies of the Lake Eyre Basin; DKCRC Research Report 45; Measham, T.G., Brake, L., Eds.; Desert Knowledge Cooperative Research Centre: Alice Springs, Australia, 2009; pp. 251–298. [Google Scholar]
- Slocum, N. Participatory Methods Toolkit: A Practitioner’s Manual. King Baudouin Foundation and the Flemish Institute for Science and Technology Assessment, 2003. Available online: http://archive.unu.edu/hq/library/Collection/PDF_files/CRIS/PMT.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2014).
- Burgin, S.; Webb, T.; Rae, D. Stakeholder Engagement in Water Policy: Lessons from Peri-Urban Irrigation. Land Use Policy 2013, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susskind, L.; Camacho, A.E.; Schenk, T. A Critical Assessment of Collaborative Adaptive Management in Practice: Collaborative Adaptive Management. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawole, J.N. Public Hearing or “Hearing Public”? An Evaluation of the Participation of Local Stakeholders in Environmental Impact Assessment of Ghana’s Jubilee Oil Fields. Environ. Manag. 2013, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innes, J.E.; Booher, D.E. Reframing Public Participation: Strategies for the 21st Century. Plan. Theory Pract. 2004, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cundill, G. Monitoring Social Learning Processes in Adaptive Comanagement: Three Case Studies from South Africa. Ecol. Soc. 2010, 15, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Gleason, M.; McCreary, S.; Miller-Henson, M.; Ugoretz, J.; Fox, E.; Merrifield, M.; McClintock, W.; Serpa, P.; Hoffman, K. Science-Based and Stakeholder-Driven Marine Protected Area Network Planning: A Successful Case Study from North Central California. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2010, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.; Tan, P.L.; Mooney, C.; Hoverman, S.; White, I. Principles and Guidelines for Good Practice in Indigenous Engagement in Water Planning. J. Hydrol. 2012, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, W.; Furman, C.A.; Royce, F.; Ortiz, B.; Zierden, D.; Fraisse, C. Developing a Learning Community: Lessons from a Climate Working Group for Agriculture in the Southeast USA. Available online: http://www.seclimate.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/2012-bartels-et-al-secc-technical-series-developing-a-learning-community.pdf (accessed on 22 march 2016).
- Jacobs, M.H.; Buijs, A.E. Understanding Stakeholders’ Attitudes toward Water Management Interventions: Role of Place Meanings: Stakeholders’ attitudes toward water management. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
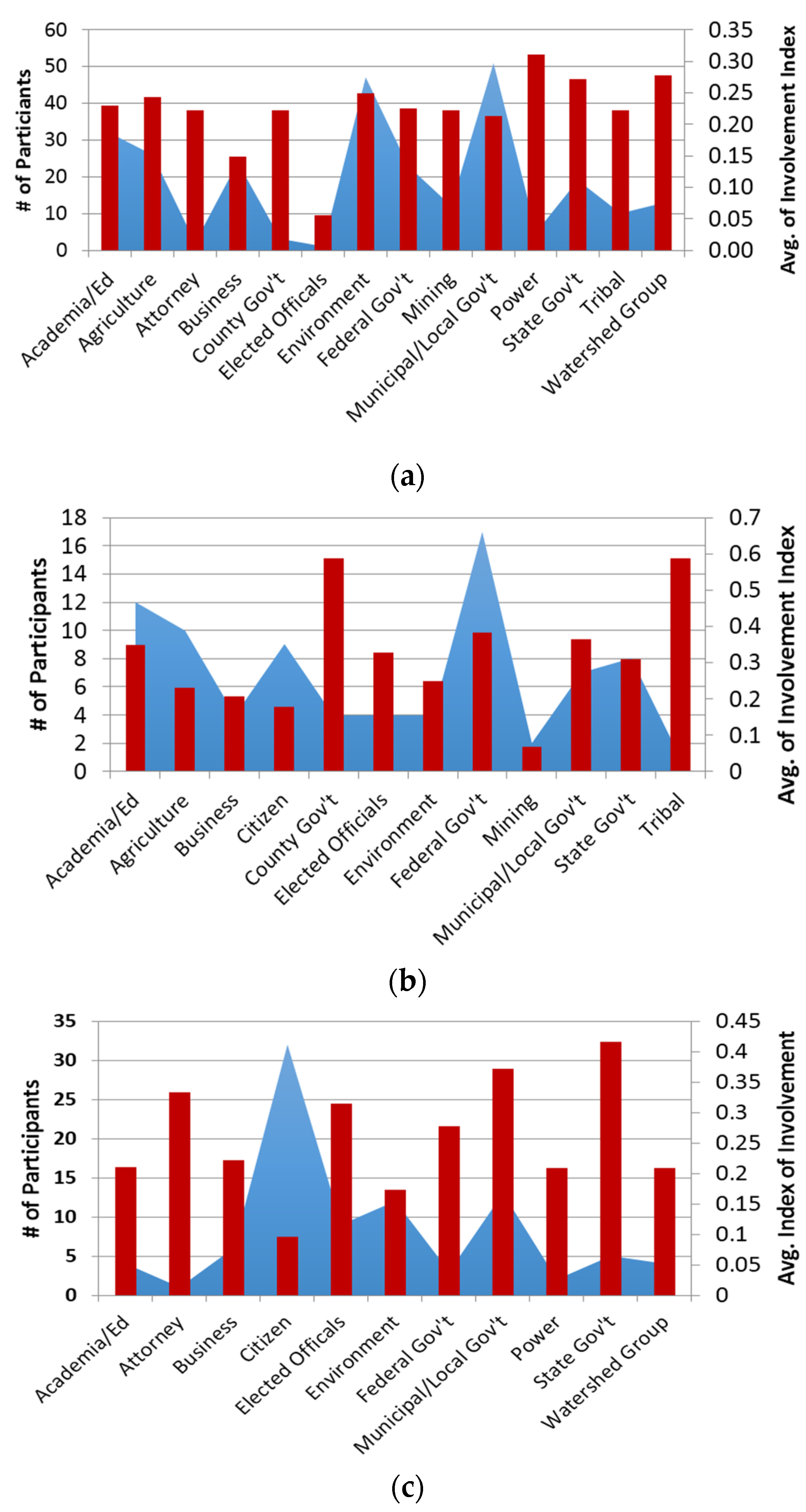

| Project | Activity Name | Number | No. of People | Key Issues Addressed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | ||||
| Duration | ||||
| Roadmap | Presentations on Water for Natural Areas | 38 | 800+ | What do we know about water for natural areas? How can the WRRC database on water needs of riparian and aquatic ecosystems be used for management and planning? |
| 11 counties | ||||
| 1 hour | ||||
| Phase II Kick-off Meeting | 2 | 52 | What are the goals of this project? What do we hope to accomplish? | |
| Regional | ||||
| 3 hours | ||||
| Survey | 1 | 171 | What makes a community decide to consider water natural areas? And What makes water for natural areas vulnerable? | |
| Statewide | ||||
| NA | ||||
| Benefits and Challenges Workshop | 1 | 39 | What are the benefits, challenges, and reasons for including natural areas in water management and planning? | |
| Statewide | ||||
| ½ day | ||||
| Focus Groups | 43 | 247 | How should we consider water for natural areas in water management and planning and what incentives would make it more attractive to do so? | |
| 10 Counties | ||||
| 1 hour | ||||
| Action Items Workshop | 4 | 79 | What strategies and actions should be taken to improve education, facilitate collaboration, set priorities, create incentives and encourage water conservation to include natural areas in water management and planning? | |
| Regional | ||||
| ½ day | ||||
| Gila | Science Coordination Workshop | 1 | 40 | What data do you have and what data do you need? How can we better coordinate data collection and use in the watershed? |
| Watershed | ||||
| 1.5 day | ||||
| Shared History Timeline | 1 | 43 | What is the history of the watershed? How can we learn from that history as we move forward? | |
| Watershed | ||||
| 3 hours | ||||
| Key Informant Interviews | 8 | 10 | What do you think the watershed will look like in the future? What were the biggest surprises from the past? | |
| Watershed | ||||
| 1 hour | ||||
| Scenario Drivers Workshop | 1 | 16 | What are the key drivers of change in the watershed? What drivers of change are most uncertain? | |
| Watershed | ||||
| 1 day | ||||
| Survey | 1 | 27 | What scenarios would be most useful for your management concerns? What questions do you have about the scenarios? | |
| Watershed | ||||
| NA | ||||
| Scenario Narrative Interviews | 8 | 8 | Questions about the future of the Gila Watershed based on scenario frameworks determined through the survey. | |
| Watershed | ||||
| 1 hour | ||||
| Clarkdale | Water 101 & 102 Public Meetings | 2 | 52 | Information sessions on current water use and management in Clarkdale and regional groundwater modeling results. Attendees were “lay stakeholders”. |
| Regional | ||||
| 2 hour | ||||
| Open House | 1 | 25 | What concerns do you have about water in Clarkdale? What do you think about different management options that the Town is considering? | |
| Town | ||||
| 2 hour | ||||
| Water Experts Workshop | 1 | 27 | What should Clarkdale include or not include in its Water Resources Management Program (WRMP) and why? What management strategies will have the greatest impact? | |
| Statewide | ||||
| 1 day | ||||
| Water Expert Interviews | 8 | 8 | What should Clarkdale include or not include in its Water Resources Management Program (WRMP) and why? What management strategies will have the greatest impact? | |
| Multi-State | ||||
| 1 hour | ||||
| Small Town Water Forum | 1 | 29 | What should Clarkdale include in its WRMP? What challenges do small towns face in managing their water? How can towns in Arizona work together to improve water management? | |
| Statewide | ||||
| 1.5 day |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mott Lacroix, K.E.; Megdal, S.B. Explore, Synthesize, and Repeat: Unraveling Complex Water Management Issues through the Stakeholder Engagement Wheel. Water 2016, 8, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040118
Mott Lacroix KE, Megdal SB. Explore, Synthesize, and Repeat: Unraveling Complex Water Management Issues through the Stakeholder Engagement Wheel. Water. 2016; 8(4):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040118
Chicago/Turabian StyleMott Lacroix, Kelly E., and Sharon B. Megdal. 2016. "Explore, Synthesize, and Repeat: Unraveling Complex Water Management Issues through the Stakeholder Engagement Wheel" Water 8, no. 4: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040118
APA StyleMott Lacroix, K. E., & Megdal, S. B. (2016). Explore, Synthesize, and Repeat: Unraveling Complex Water Management Issues through the Stakeholder Engagement Wheel. Water, 8(4), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040118