Targets for the Induction of Protective Immunity Against Influenza A Viruses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
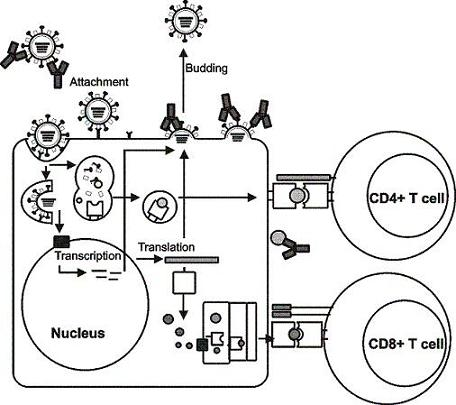
2. Influenza viruses and their proteins
3. Immunity to influenza viruses
4. Influenza A virus vaccines
5. Viral targets for the induction of humoral immunity
5.1. Hemagglutinin
5.2. Neuraminidase
5.3. M2 protein
5.4. Nucleoprotein
6. Viral targets for the induction of cellular immunity
6.1. Hemagglutinin and neuraminidase
6.2. Structural proteins, polymerases and NS proteins
| Protein | Number of> MHC Class I epitopes | Number of MHC Class II epitopes |
|---|---|---|
| HA | 6 | 46 |
| NA | 5 | 13 |
| M1 | 15 | 31 |
| M2 | 2 | 0 |
| NP | 25 | 32 |
| PA | 8 | 2 |
| PB1 | 21 | 5 |
| PB2 | 1 | 1 |
| NS1 | 2 | 1 |
| NS2 | 2 | 0 |
7. Concluding remarks
| Viral antigen | Mode of action | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| HA | Prevents virus attachment to host cells | - Antibodies must have proper specificity |
| - strain specific | ||
| NA | Inhibits enzymatic activity of NA and spread of virus | - Antibodies must have proper specificity |
| M2 | Induction of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and elimination of infected cells | - M2 is highly conserved |
| - Hyperimmunization induces cross | ||
| - protective immunity | ||
| NP | Largely unknown, complex formation? | - Non-neutralizing |
| - Mode of action and effectiveness unknown |

| Viral antigens | Type of response | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| All viral proteins | CD4+ T helper cell response | - Polarization (Th1/Th2) dependent on antigen delivery |
| - Essential for B-cell and CD8+ CTL responses | ||
| - Direct action against infected cells | ||
| - HLA restricted | ||
| PB1/PB2/PA/NP/M1/M2/NS1 | CD8+ CTL response | - Key role in elimination of infected cells |
| - Cytokine production | ||
| - HLA restriction dictates magnitude of response | ||
| - Only marginal response to HA |
Acknowledgments
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Influenza (Seasonal) Fact sheet No 211. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs211/en/index.html (Accessed 25 August 2009).
- Bush, R.M.; Bender, C.A.; Subbarao, K.; Cox, N.J.; Fitch, W.M. Predicting the evolution of human influenza A. Science 1999, 286, 1921–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.J.; Lapedes, A.S.; de Jong, J.C.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Fouchier, R.A. Mapping the antigenic and genetic evolution of influenza virus. Science 2004, 305, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, R.G.; Bean, W.J.; Gorman, O.T.; Chambers, T.M.; Kawaoka, Y. Evolution and ecology of influenza A viruses. Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 56, 152–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Update: infections with a swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus--United States and other countries, April 28, 2009. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2009, 58, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garten, R.J.; Davis, C.T.; Russell, C.A.; Shu, B.; Lindstrom, S.; Balish, A.; Sessions, W.M.; Xu, X.; Skepner, E.; Deyde, V.; Okomo-Adhiambo, M.; Gubareva, L.; Barnes, J.; Smith, C.B.; Emery, S.L.; Hillman, M.J.; Rivailler, P.; Smagala, J.; de Graaf, M.; Burke, D.F.; Fouchier, R.A.; Pappas, C.; Alpuche-Aranda, C.M.; Lopez-Gatell, H.; Olivera, H.; Lopez, I.; Myers, C.A.; Faix, D.; Blair, P.J.; Yu, C.; Keene, K.M.; Dotson, P.D.; Boxrud, D.; Sambol, A.R.; Abid, S.H.; St George, K.; Bannerman, T.; Moore, A.L.; Stringer, D.J.; Blevins, P.; Demmler-Harrison, G.J.; Ginsberg, M.; Kriner, P.; Waterman, S.; Smole, S.; Guevara, H.F.; Belongia, E.A.; Clark, P.A.; Beatrice, S.T.; Donis, R.; Katz, J.; Finelli, L.; Bridges, C.B.; Shaw, M.; Jernigan, D.B.; Uyeki, T.M.; Smith, D.J.; Klimov, A.I.; Cox, N.J. Antigenic and genetic characteristics of swine-origin 2009 A(H1N1) influenza viruses circulating in humans. Science 2009, 325, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, L. Possible origin of current influenza A H1N1 viruses. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 456–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 - update 81. Available online: http://www.who.int/csr/don/2009_12_30/en/index.html (Accessed 30 December 2009). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, J.C.; Claas, E.C.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Webster, R.G.; Lim, W.L. A pandemic warning? Nature 1997, 389, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbarao, K.; Klimov, A.; Katz, J.; Regnery, H.; Lim, W.; Hall, H.; Perdue, M.; Swayne, D.; Bender, C.; Huang, J.; Hemphill, M.; Rowe, T.; Shaw, M.; Xu, X.; Fukuda, K.; Cox, N. Characterization of an avian influenza A (H5N1) virus isolated from a child with a fatal respiratory illness. Science 1998, 279, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Halloran, M.E.; Sugimoto, J.D.; Longini Jr., I.M. Detecting human-to-human transmission of avian influenza A (H5N1). Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1348–1353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ungchusak, K.; Auewarakul, P.; Dowell, S.F.; Kitphati, R.; Auwanit, W.; Puthavathana, P.; Uiprasertkul, M.; Boonnak, K.; Pittayawonganon, C.; Cox, N.J.; Zaki, S.R.; Thawatsupha, P.; Chittaganpitch, M.; Khontong, R.; Simmerman, J.M.; Chunsutthiwat, S. Probable person-to-person transmission of avian influenza A (H5N1). N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Confirmed human cases of avian influenza A H5N1. Available online: http://www.who.int/csr/disease/avian_influenza/country/cases_table_2009_12_30/en/index.html (Accessed 30 December 2009). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Ito, T.; Suzuki, T.; Holland, R.E.; Chambers, T.M.; Kiso, M.; Ishida, H.; Kawaoka, Y. Sialic acid species as a determinant of the host range of influenza A viruses. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 11825–11831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.P.; Shaw, M.; Gregory, V.; Cameron, K.; Lim, W.; Klimov, A.; Subbarao, K.; Guan, Y.; Krauss, S.; Shortridge, K.; Webster, R.; Cox, N.; Hay, A. Avian-to-human transmission of H9N2 subtype influenza A viruses: relationship between H9N2 and H5N1 human isolates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 9654–9658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouchier, R.A.; Schneeberger, P.M.; Rozendaal, F.W.; Broekman, J.M.; Kemink, S.A.; Munster, V.; Kuiken, T.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Schutten, M.; Van Doornum, G.J.; Koch, G.; Bosman, A.; Koopmans, M.; Osterhaus, A.D. Avian influenza A virus (H7N7) associated with human conjunctivitis and a fatal case of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, T.; Sagara, H.; Yen, A.; Takada, A.; Kida, H.; Cheng, R.H.; Kawaoka, Y. Architecture of ribonucleoprotein complexes in influenza A virus particles. Nature 2006, 439, 490–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knipe, D.M.; Howley, P.M.; Griffin, D.E.; Lamb, R.A.; Martin, M.A.; Roizman, B.; Strauss, S.E. Field's Virology. 2007; 5th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA; p. 3177. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Calvo, P.A.; Malide, D.; Gibbs, J.; Schubert, U.; Bacik, I.; Basta, S.; O'Neill, R.; Schickli, J.; Palese, P.; Henklein, P.; Bennink, J.R.; Yewdell, J.W. A novel influenza A virus mitochondrial protein that induces cell death. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 1306–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Tsibane, T.; McGraw, P.A.; House, F.S.; Keefer, C.J.; Hicar, M.D.; Tumpey, T.M.; Pappas, C.; Perrone, L.A.; Martinez, O.; Stevens, J.; Wilson, I.A.; Aguilar, P.V.; Altschuler, E.L.; Basler, C.F.; Crowe Jr., J.E. Neutralizing antibodies derived from the B cells of 1918 influenza pandemic survivors. Nature 2008, 455, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, K.; Veguilla, V.; Lu, X.; Zhong, W.; Butler, E.N.; Sun, H.; Liu, F.; Dong, L.; DeVos, J.R.; Gargiullo, P.M.; Brammer, T.L.; Cox, N.J.; Tumpey, T.M.; Katz, J.M. Cross-reactive antibody responses to the 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza virus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1945–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memorandum, W. A revision of the system of nomenclature for influenza viruses: a WHO memorandum. Bull World Health Organ. 1980, 58, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grebe, K.M.; Yewdell, J.W.; Bennink, J.R. Heterosubtypic immunity to influenza A virus: where do we stand? Microbes Infect. 2008, 10, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulman, J.L.; Kilbourne, E.D. Induction of Partial Specific Heterotypic Immunity in Mice by a Single Infection with Influenza a Virus. J. Bacteriol. 1965, 89, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kreijtz, J.H.; Bodewes, R.; van den Brand, J.M.; de Mutsert, G.; Baas, C.; van Amerongen, G.; Fouchier, R.A.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. Infection of mice with a human influenza A/H3N2 virus induces protective immunity against lethal infection with influenza A/H5N1 virus. Vaccine 2009, 27, 4983–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Neill, E.; Krauss, S.L.; Riberdy, J.M.; Webster, R.G.; Woodland, D.L. Heterologous protection against lethal A/HongKong/156/97 (H5N1) influenza virus infection in C57BL/6 mice. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 2689–2696. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yetter, R.A.; Barber, W.H.; Small Jr., P.A. Heterotypic immunity to influenza in ferrets. Infect. Immun. 1980, 29, 650–653. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.H.; van Ginkel, F.W.; Vu, H.L.; McGhee, J.R.; Mestecky, J. Heterosubtypic immunity to influenza A virus infection requires B cells but not CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, S.L.; Lo, C.Y.; Misplon, J.A.; Lawson, C.M.; Hendrickson, B.A.; Max, E.E.; Subbarao, K. Mechanisms of heterosubtypic immunity to lethal influenza A virus infection in fully immunocompetent, T cell-depleted, beta2-microglobulin-deficient, and J chain-deficient mice. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carragher, D.M.; Kaminski, D.A.; Moquin, A.; Hartson, L.; Randall, T.D. A novel role for non-neutralizing antibodies against nucleoprotein in facilitating resistance to influenza virus. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 4168–4176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flynn, K.J.; Belz, G.T.; Altman, J.D.; Ahmed, R.; Woodland, D.L.; Doherty, P.C. Virus-specific CD8+ T cells in primary and secondary influenza pneumonia. Immunity 1998, 8, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegerlehner, A.; Schmitz, N.; Storni, T.; Bachmann, M.F. Influenza A vaccine based on the extracellular domain of M2: weak protection mediated via antibody-dependent NK cell activity. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 5598–5605. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benton, K.A.; Misplon, J.A.; Lo, C.Y.; Brutkiewicz, R.R.; Prasad, S.A.; Epstein, S.L. Heterosubtypic immunity to influenza A virus in mice lacking IgA, all Ig, NKT cells, or gamma delta T cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 7437–7445. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McMichael, A.J.; Gotch, F.M.; Noble, G.R.; Beare, P.A. Cytotoxic T-cell immunity to influenza. N. Engl. J. Med. 1983, 309, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Epstein, S.L. Prior H1N1 influenza infection and susceptibility of Cleveland Family Study participants during the H2N2 pandemic of 1957: an experiment of nature. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 193, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonoguchi, T.; Naito, H.; Hara, M.; Takeuchi, Y.; Fukumi, H. Cross-subtype protection in humans during sequential, overlapping, and/or concurrent epidemics caused by H3N2 and H1N1 influenza viruses. J. Infect. Dis. 1985, 151, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cox, M.M. Progress on baculovirus-derived influenza vaccines. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2008, 10, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kreijtz, J.H.; Suezer, Y.; de Mutsert, G.; van den Brand, J.M.; van Amerongen, G.; Schnierle, B.S.; Kuiken, T.; Fouchier, R.A.; Lower, J.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Sutter, G.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. Recombinant modified vaccinia virus Ankara expressing the hemagglutinin gene confers protection against homologous and heterologous H5N1 influenza virus infections in macaques. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govorkova, E.A.; Webby, R.J.; Humberd, J.; Seiler, J.P.; Webster, R.G. Immunization with reverse-genetics-produced H5N1 influenza vaccine protects ferrets against homologous and heterologous challenge. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 194, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, J.D.; Edwards, D.C.; Brand, C.M.; Heath, T.D. Formation of virosomes from influenza subunits and liposomes. Lancet 1975, 2, 899–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, F.S.; Huang, C.; Compans, R.W.; Kang, S.M. Virus-like particle vaccine induces protective immunity against homologous and heterologous strains of influenza virus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 3514–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, J.C.; Palache, A.M.; Beyer, W.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Boon, A.C.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E. Haemagglutination-inhibiting antibody to influenza virus. Dev. Biol. (Basel) 2003, 115, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fouchier, R.A.; Munster, V.; Wallensten, A.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Herfst, S.; Smith, D.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Olsen, B.; Osterhaus, A.D. Characterization of a novel influenza A virus hemagglutinin subtype (H16) obtained from black-headed gulls. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 2814–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaverin, N.V.; Rudneva, I.A.; Ilyushina, N.A.; Varich, N.L.; Lipatov, A.S.; Smirnov, Y.A.; Govorkova, E.A.; Gitelman, A.K.; Lvov, D.K.; Webster, R.G. Structure of antigenic sites on the haemagglutinin molecule of H5 avian influenza virus and phenotypic variation of escape mutants. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 2497–2505. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaverin, N.V.; Rudneva, I.A.; Govorkova, E.A.; Timofeeva, T.A.; Shilov, A.A.; Kochergin-Nikitsky, K.S.; Krylov, P.S.; Webster, R.G. Epitope mapping of the hemagglutinin molecule of a highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza virus by using monoclonal antibodies. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12911–12917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaverin, N.V.; Rudneva, I.A.; Ilyushina, N.A.; Lipatov, A.S.; Krauss, S.; Webster, R.G. Structural differences among hemagglutinins of influenza A virus subtypes are reflected in their antigenic architecture: analysis of H9 escape mutants. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, D.C.; Wilson, I.A.; Skehel, J.J. Structural identification of the antibody-binding sites of Hong Kong influenza haemagglutinin and their involvement in antigenic variation. Nature 1981, 289, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, I.A.; Skehel, J.J.; Wiley, D.C. Structure of the haemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus at 3 A resolution. Nature 1981, 289, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, P.S.; Jeffries, S.; Yates, P.; Schild, G.C.; Rogers, G.N.; Paulson, J.C.; Wharton, S.A.; Douglas, A.R.; Skehel, J.J.; Wiley, D.C. The receptor-binding and membrane-fusion properties of influenza virus variants selected using anti-haemagglutinin monoclonal antibodies. Embo J. 1987, 6, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Knossow, M.; Skehel, J.J. Variation and infectivity neutralization in influenza. Immunology 2006, 119, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caton, A.J.; Robertson, J.S. Structure of the host-derived sequences present at the 5' ends of influenza virus mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980, 8, 2591–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, E.; Sugawara, K.; Hongo, S.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Muraki, Y.; Li, Z.N.; Nakamura, K. Antigenic structure of the haemagglutinin of human influenza A/H2N2 virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 2475–2484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sui, J.; Hwang, W.C.; Perez, S.; Wei, G.; Aird, D.; Chen, L.M.; Santelli, E.; Stec, B.; Cadwell, G.; Ali, M.; Wan, H.; Murakami, A.; Yammanuru, A.; Han, T.; Cox, N.J.; Bankston, L.A.; Donis, R.O.; Liddington, R.C.; Marasco, W.A. Structural and functional bases for broad-spectrum neutralization of avian and human influenza A viruses. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.T.; Palese, P. Universal epitopes of influenza virus hemagglutinins? Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 233–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Fauquier, A.; Villanueva, N.; Melero, J.A. Isolation of cross-reactive, subtype-specific monoclonal antibodies against influenza virus HA1 and HA2 hemagglutinin subunits. Arch. Virol. 1987, 97, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkacova, M.; Vareckova, E.; Baker, I.C.; Love, J.M.; Ziegler, T. Evaluation of monoclonal antibodies for subtyping of currently circulating human type A influenza viruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 1196–1198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okuno, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Isegawa, Y.; Ueda, S. Protection against the mouse-adapted A/FM/1/47 strain of influenza A virus in mice by a monoclonal antibody with cross-neutralizing activity among H1 and H2 strains. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okuno, Y.; Isegawa, Y.; Sasao, F.; Ueda, S. A common neutralizing epitope conserved between the hemagglutinins of influenza A virus H1 and H2 strains. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 2552–2558. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smirnov, Y.A.; Lipatov, A.S.; Gitelman, A.K.; Claas, E.C.; Osterhaus, A.D. Prevention and treatment of bronchopneumonia in mice caused by mouse-adapted variant of avian H5N2 influenza A virus using monoclonal antibody against conserved epitope in the HA stem region. Arch. Virol. 2000, 145, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnov, Y.A.; Lipatov, A.S.; Gitelman, A.K.; Okuno, Y.; Van Beek, R.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Claas, E.C. An epitope shared by the hemagglutinins of H1, H2, H5, and H6 subtypes of influenza A virus. Acta Virol. 1999, 43, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hanson, B.J.; Boon, A.C.; Lim, A.P.; Webb, A.; Ooi, E.E.; Webby, R.J. Passive immunoprophylaxis and therapy with humanized monoclonal antibody specific for influenza A H5 hemagglutinin in mice. Respir. Res. 2006, 7, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gocnik, M.; Fislova, T.; Sladkova, T.; Mucha, V.; Kostolansky, F.; Vareckova, E. Antibodies specific to the HA2 glycopolypeptide of influenza A virus haemagglutinin with fusion-inhibition activity contribute to the protection of mice against lethal infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 951–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, R.; Igarashi, M.; Ozaki, H.; Kishida, N.; Tomabechi, D.; Kida, H.; Ito, K.; Takada, A. Cross-protective potential of a novel monoclonal antibody directed against antigenic site B of the hemagglutinin of influenza A viruses. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Throsby, M.; van den Brink, E.; Jongeneelen, M.; Poon, L.L.; Alard, P.; Cornelissen, L.; Bakker, A.; Cox, F.; van Deventer, E.; Guan, Y.; Cinatl, J.; ter Meulen, J.; Lasters, I.; Carsetti, R.; Peiris, M.; de Kruif, J.; Goudsmit, J. Heterosubtypic neutralizing monoclonal antibodies cross-protective against H5N1 and H1N1 recovered from human IgM+ memory B cells. PLoS One 2008, 3, e3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tumpey, T.M.; Renshaw, M.; Clements, J.D.; Katz, J.M. Mucosal delivery of inactivated influenza vaccine induces B-cell-dependent heterosubtypic cross-protection against lethal influenza A H5N1 virus infection. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 5141–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, D.C.; Kilbourne, E.D.; Johansson, B.E. Neuraminidase-specific antibody responses to inactivated influenza virus vaccine in young and elderly adults. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1996, 3, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johansson, B.E.; Bucher, D.J.; Kilbourne, E.D. Purified influenza virus hemagglutinin and neuraminidase are equivalent in stimulation of antibody response but induce contrasting types of immunity to infection. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qiu, M.; Fang, F.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, Q.; Chang, H.; Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Z. Protection against avian influenza H9N2 virus challenge by immunization with hemagglutinin- or neuraminidase-expressing DNA in BALB/c mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 343, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, B.E.; Grajower, B.; Kilbourne, E.D. Infection-permissive immunization with influenza virus neuraminidase prevents weight loss in infected mice. Vaccine 1993, 11, 1037–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulman, J.L.; Khakpour, M.; Kilbourne, E.D. Protective effects of specific immunity to viral neuraminidase on influenza virus infection of mice. J. Virol. 1968, 2, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Couch, R.B.; Kasel, J.A.; Gerin, J.L.; Schulman, J.L.; Kilbourne, E.D. Induction of partial immunity to influenza by a neuraminidase-specific vaccine. J. Infect. Dis. 1974, 129, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johansson, B.E.; Matthews, J.T.; Kilbourne, E.D. Supplementation of conventional influenza A vaccine with purified viral neuraminidase results in a balanced and broadened immune response. Vaccine 1998, 16, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Kadowaki, S.; Hagiwara, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Matsuo, K.; Kurata, T.; Tamura, S. Cross-protection against a lethal influenza virus infection by DNA vaccine to neuraminidase. Vaccine 2000, 18, 3214–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilbourne, E.D.; Pokorny, B.A.; Johansson, B.; Brett, I.; Milev, Y.; Matthews, J.T. Protection of mice with recombinant influenza virus neuraminidase. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matrosovich, M.N.; Matrosovich, T.Y.; Gray, T.; Roberts, N.A.; Klenk, H.D. Neuraminidase is important for the initiation of influenza virus infection in human airway epithelium. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 12665–12667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beutner, K.R.; Chow, T.; Rubi, E.; Strussenberg, J.; Clement, J.; Ogra, P.L. Evaluation of a neuraminidase-specific influenza A virus vaccine in children: antibody responses and effects on two successive outbreaks of natural infection. J. Infect. Dis. 1979, 140, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johansson, B.E.; Moran, T.M.; Kilbourne, E.D. Antigen-presenting B cells and helper T cells cooperatively mediate intravirionic antigenic competition between influenza A virus surface glycoproteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 6869–6873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilbourne, E.D.; Laver, W.G.; Schulman, J.L.; Webster, R.G. Antiviral activity of antiserum specific for an influenza virus neuraminidase. J. Virol. 1968, 2, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murphy, B.R.; Kasel, J.A.; Chanock, R.M. Association of serum anti-neuraminidase antibody with resistance to influenza in man. N. Engl. J. Med. 1972, 286, 1329–1332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sandbulte, M.R.; Jimenez, G.S.; Boon, A.C.; Smith, L.R.; Treanor, J.J.; Webby, R.J. Cross-reactive neuraminidase antibodies afford partial protection against H5N1 in mice and are present in unexposed humans. PLoS Med 2007, 4, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, R.A.; Zebedee, S.L.; Richardson, C.D. Influenza virus M2 protein is an integral membrane protein expressed on the infected-cell surface. Cell 1985, 40, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, L.H.; Holsinger, L.J.; Lamb, R.A. Influenza virus M2 protein has ion channel activity. Cell 1992, 69, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holsinger, L.J.; Lamb, R.A. Influenza virus M2 integral membrane protein is a homotetramer stabilized by formation of disulfide bonds. Virology 1991, 183, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treanor, J.J.; Tierney, E.L.; Zebedee, S.L.; Lamb, R.A.; Murphy, B.R. Passively transferred monoclonal antibody to the M2 protein inhibits influenza A virus replication in mice. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 1375–1377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zebedee, S.L.; Lamb, R.A. Influenza A virus M2 protein: monoclonal antibody restriction of virus growth and detection of M2 in virions. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 2762–2772. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fiers, W.; De Filette, M.; Birkett, A.; Neirynck, S.; Min Jou, W. A "universal" human influenza A vaccine. Virus Res. 2004, 103, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neirynck, S.; Deroo, T.; Saelens, X.; Vanlandschoot, P.; Jou, W.M.; Fiers, W. A universal influenza A vaccine based on the extracellular domain of the M2 protein. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schotsaert, M.; De Filette, M.; Fiers, W.; Saelens, X. Universal M2 ectodomain-based influenza A vaccines: preclinical and clinical developments. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2009, 8, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filette, M.; Fiers, W.; Martens, W.; Birkett, A.; Ramne, A.; Lowenadler, B.; Lycke, N.; Jou, W.M.; Saelens, X. Improved design and intranasal delivery of an M2e-based human influenza A vaccine. Vaccine 2006, 24, 6597–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filette, M.; Min Jou, W.; Birkett, A.; Lyons, K.; Schultz, B.; Tonkyro, A.; Resch, S.; Fiers, W. Universal influenza A vaccine: optimization of M2-based constructs. Virology 2005, 337, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slepushkin, V.A.; Katz, J.M.; Black, R.A.; Gamble, W.C.; Rota, P.A.; Cox, N.J. Protection of mice against influenza A virus challenge by vaccination with baculovirus-expressed M2 protein. Vaccine 1995, 13, 1399–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zharikova, D.; Mozdzanowska, K.; Feng, J.; Zhang, M.; Gerhard, W. Influenza type A virus escape mutants emerge in vivo in the presence of antibodies to the ectodomain of matrix protein 2. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 6644–6654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.H. N-terminus of M2 protein could induce antibodies with inhibitory activity against influenza virus replication. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 35, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukeno, N.; Otsuki, Y.; Konno, J.; Yamane, N.; Odagiri, T.; Arikawa, J.; Ishida, N. Anti-nucleoprotein antibody response in influenza A infection. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 1979, 128, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhard, W.; Mozdzanowska, K.; Furchner, M.; Washko, G.; Maiese, K. Role of the B-cell response in recovery of mice from primary influenza virus infection. Immunol. Rev. 1997, 159, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel-Moreno, J.; Carragher, D.M.; Misra, R.S.; Kusser, K.; Hartson, L.; Moquin, A.; Lund, F.E.; Randall, T.D. B cells promote resistance to heterosubtypic strains of influenza via multiple mechanisms. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Zhang, Y.; He, H.; Marinova, E.; Switzer, K.; Wansley, D.; Mbawuike, I.; Han, S. Rectification of age-associated deficiency in cytotoxic T cell response to influenza A virus by immunization with immune complexes. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 6153–6159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Swain, S.L.; Agrewala, J.N.; Brown, D.M.; Jelley-Gibbs, D.M.; Golech, S.; Huston, G.; Jones, S.C.; Kamperschroer, C.; Lee, W.H.; McKinstry, K.K.; Roman, E.; Strutt, T.; Weng, N.P. CD4+ T-cell memory: generation and multi-faceted roles for CD4+ T cells in protective immunity to influenza. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 211, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.D.; Okada, T.; Cyster, J.G. Germinal-center organization and cellular dynamics. Immunity 2007, 27, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzavecchia, A. Antigen-specific interaction between T and B cells. Nature 1985, 314, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHeyzer-Williams, L.J.; McHeyzer-Williams, M.G. Antigen-specific memory B cell development. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 23, 487–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernasconi, N.L.; Traggiai, E.; Lanzavecchia, A. Maintenance of serological memory by polyclonal activation of human memory B cells. Science 2002, 298, 2199–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellino, F.; Germain, R.N. Cooperation between CD4+ and CD8+ T cells: when, where, and how. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 24, 519–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevan, M.J. Helping the CD8(+) T-cell response. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northrop, J.K.; Shen, H. CD8+ T-cell memory: only the good ones last. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2004, 16, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, E.M.; Lemmens, E.E.; Wolfe, T.; Christen, U.; von Herrath, M.G.; Schoenberger, S.P. CD4+ T cells are required for secondary expansion and memory in CD8+ T lymphocytes. Nature 2003, 421, 852–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.M.; Roman, E.; Swain, S.L. CD4 T cell responses to influenza infection. Semin. Immunol. 2004, 16, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkhoff, E.G.; Geelhoed-Mieras, M.M.; Jonges, M.; Smith, D.J.; Fouchier, R.A.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. An amino acid substitution in the influenza A virus hemagglutinin associated with escape from recognition by human virus-specific CD4+ T-cells. Virus Res. 2007, 126, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Boon, A.C.; Voeten, J.T.; Berkhoff, E.G.; Fouchier, R.A.; Osterhaus, A.D. Sequence variation in the influenza A virus nucleoprotein associated with escape from cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Virus Res. 2004, 103, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roti, M.; Yang, J.; Berger, D.; Huston, L.; James, E.A.; Kwok, W.W. Healthy human subjects have CD4+ T cells directed against H5N1 influenza virus. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 1758–1768. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.Y.; Ha, D.L.; Simmons, C.; de Jong, M.D.; Chau, N.V.; Schumacher, R.; Peng, Y.C.; McMichael, A.J.; Farrar, J.J.; Smith, G.L.; Townsend, A.R.; Askonas, B.A.; Rowland-Jones, S.; Dong, T. Memory T cells established by seasonal human influenza A infection cross-react with avian influenza A (H5N1) in healthy individuals. J. Clin. Invest. 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jameson, J.; Cruz, J.; Terajima, M.; Ennis, F.A. Human CD8+ and CD4+ T lymphocyte memory to influenza A viruses of swine and avian species. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 7578–7583. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jameson, J.; Cruz, J.; Ennis, F.A. Human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte repertoire to influenza A viruses. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 8682–8689. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sweetser, M.T.; Braciale, V.L.; Braciale, T.J. Class I major histocompatibility complex-restricted T lymphocyte recognition of the influenza hemagglutinin. Overlap between class I cytotoxic T lymphocytes and antibody sites. J. Exp. Med. 1989, 170, 1357–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braciale, T.J.; Sweetser, M.T.; Morrison, L.A.; Kittlesen, D.J.; Braciale, V.L. Class I major histocompatibility complex-restricted cytolytic T lymphocytes recognize a limited number of sites on the influenza hemagglutinin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosor Krnic, E.; Gagro, A.; Drazenovic, V.; Kuzman, I.; Jeren, T.; Cecuk-Jelicic, E.; Kerhin-Brkljacic, V.; Gjenero-Margan, I.; Kaic, B.; Rakusic, S.; Sabioncello, A.; Markotic, A.; Rabatic, S.; Mlinaric-Galinovic, G.; Dekaris, D. Enumeration of haemagglutinin-specific CD8+ T cells after influenza vaccination using MHC class I peptide tetramers. Scand J. Immunol. 2008, 67, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goy, K.; Von Bibra, S.; Lewis, J.; Laurie, K.; Barr, I.; Anderson, D.; Hellard, M.; Ffrench, R. Heterosubtypic T-cell responses against avian influenza H5 haemagglutinin are frequently detected in individuals vaccinated against or previously infected with human subtypes of influenza. Influenza Other Respi. Viruses 2008, 2, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, B.; Sidney, J.; Bourne, P.; Bui, H.H.; Buus, S.; Doh, G.; Fleri, W.; Kronenberg, M.; Kubo, R.; Lund, O.; Nemazee, D.; Ponomarenko, J.V.; Sathiamurthy, M.; Schoenberger, S.; Stewart, S.; Surko, P.; Way, S.; Wilson, S.; Sette, A. The immune epitope database and analysis resource: from vision to blueprint. PLoS Biol 2005, 3, e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Immune Epitope Database and Analysis Resource (IEDB). Available online: www.immuneepitope.org (Accessed 26 August 2009). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berkhoff, E.G.; Geelhoed-Mieras, M.M.; Fouchier, R.A.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. Assessment of the extent of variation in influenza A virus cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitopes by using virus-specific CD8+ T-cell clones. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voeten, J.T.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Nieuwkoop, N.J.; Fouchier, R.A.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. Antigenic drift in the influenza A virus (H3N2) nucleoprotein and escape from recognition by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 6800–6807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boon, A.C.; de Mutsert, G.; Graus, Y.M.; Fouchier, R.A.; Sintnicolaas, K.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. Sequence variation in a newly identified HLA-B35-restricted epitope in the influenza A virus nucleoprotein associated with escape from cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 2567–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkhoff, E.G.; Boon, A.C.; Nieuwkoop, N.J.; Fouchier, R.A.; Sintnicolaas, K.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. A mutation in the HLA-B*2705-restricted NP383-391 epitope affects the human influenza A virus-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response in vitro. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 5216–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkhoff, E.G.; Geelhoed-Mieras, M.M.; Verschuren, E.J.; van Baalen, C.A.; Gruters, R.A.; Fouchier, R.A.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. The loss of immunodominant epitopes affects interferon-gamma production and lytic activity of the human influenza virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte response in vitro. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007, 148, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkhoff, E.G.; de Wit, E.; Geelhoed-Mieras, M.M.; Boon, A.C.; Symons, J.; Fouchier, R.A.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. Functional constraints of influenza A virus epitopes limit escape from cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 11239–11246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkhoff, E.G.; de Wit, E.; Geelhoed-Mieras, M.M.; Boon, A.C.; Symons, J.; Fouchier, R.A.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. Fitness costs limit escape from cytotoxic T lymphocytes by influenza A viruses. Vaccine 2006, 24, 6594–6596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zweerink, H.J.; Courtneidge, S.A.; Skehel, J.J.; Crumpton, M.J.; Askonas, B.A. Cytotoxic T cells kill influenza virus infected cells but do not distinguish between serologically distinct type A viruses. Nature 1977, 267, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askonas, B.A.; Taylor, P.M.; Esquivel, F. Cytotoxic T cells in influenza infection. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 1988, 532, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kees, U.; Krammer, P.H. Most influenza A virus-specific memory cytotoxic T lymphocytes react with antigenic epitopes associated with internal virus determinants. J. Exp. Med. 1984, 159, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Lamberth, K.; Harndahl, M.; Roder, G.; Stryhn, A.; Larsen, M.V.; Nielsen, M.; Lundegaard, C.; Tang, S.T.; Dziegiel, M.H.; Rosenkvist, J.; Pedersen, A.E.; Buus, S.; Claesson, M.H.; Lund, O. CTL epitopes for influenza A including the H5N1 bird flu; genome-, pathogen-, and HLA-wide screening. Vaccine 2007, 25, 2823–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, K.L.; Ada, G.L.; McKenzie, I.F. Transfer of specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes protects mice inoculated with influenza virus. Nature 1978, 273, 238–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, K.L.; Ada, G.L. The recovery of mice from influenza virus infection: adoptive transfer of immunity with immune T lymphocytes. Scand J. Immunol. 1978, 7, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, M.A.; Ennis, F.A.; Albrecht, P. Recovery from a viral respiratory infection II. Passive transfer of immune spleen cells to mice with influenza pneumonia. J. Immunol. 1981, 126, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lukacher, A.E.; Braciale, V.L.; Braciale, T.J. In vivo effector function of influenza virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte clones is highly specific. J. Exp. Med. 1984, 160, 814–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, P.M.; Askonas, B.A. Influenza nucleoprotein-specific cytotoxic T-cell clones are protective in vivo. Immunology 1986, 58, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Mozdzanowska, K.; Palladino, G.; Gerhard, W. Heterosubtypic immunity to influenza type A virus in mice. Effector mechanisms and their longevity. J. Immunol. 1994, 152, 1653–1661. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.A.; Norbury, C.C.; Chen, W.; Bennink, J.R.; Yewdell, J.W. Cutting edge: recombinant adenoviruses induce CD8 T cell responses to an inserted protein whose expression is limited to nonimmune cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 4809–4812. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ulmer, J.B.; Donnelly, J.J.; Parker, S.E.; Rhodes, G.H.; Felgner, P.L.; Dwarki, V.J.; Gromkowski, S.H.; Deck, R.R.; DeWitt, C.M.; Friedman, A.; et al. Heterologous protection against influenza by injection of DNA encoding a viral protein. Science 1993, 259, 1745–1749. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; McElhaney, J.E. Correlates of protection: novel generations of influenza vaccines. Vaccine 2008, 26, D41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laddy, D.J.; Yan, J.; Kutzler, M.; Kobasa, D.; Kobinger, G.P.; Khan, A.S.; Greenhouse, J.; Sardesai, N.Y.; Draghia-Akli, R.; Weiner, D.B. Heterosubtypic protection against pathogenic human and avian influenza viruses via in vivo electroporation of synthetic consensus DNA antigens. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liniger, M.; Zuniga, A.; Naim, H.Y. Use of viral vectors for the development of vaccines. Expert Rev Vaccines 2007, 6, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiNapoli, J.M.; Yang, L.; Suguitan, A.; Elankumaran, S.; Dorward, D.W.; Murphy, B.R.; Samal, S.K.; Collins, P.L.; Bukreyev, A. Immunization of primates with a Newcastle disease virus-vectored vaccine via the respiratory tract induces a high titer of serum neutralizing antibodies against highly pathogenic avian influenza virus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 11560–11568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoelscher, M.A.; Singh, N.; Garg, S.; Jayashankar, L.; Veguilla, V.; Pandey, A.; Matsuoka, Y.; Katz, J.M.; Donis, R.; Mittal, S.K.; Sambhara, S. A broadly protective vaccine against globally dispersed clade 1 and clade 2 H5N1 influenza viruses. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 1185–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Soloff, A.C.; Lu, X.; Montecalvo, A.; Nguyen, D.C.; Matsuoka, Y.; Robbins, P.D.; Swayne, D.E.; Donis, R.O.; Katz, J.M.; Barratt-Boyes, S.M.; Gambotto, A. Protection of mice and poultry from lethal H5N1 avian influenza virus through adenovirus-based immunization. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Sutter, G. Candidate influenza vaccines based on recombinant modified vaccinia virus Ankara. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2009, 8, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutter, G.; Wyatt, L.S.; Foley, P.L.; Bennink, J.R.; Moss, B. A recombinant vector derived from the host range-restricted and highly attenuated MVA strain of vaccinia virus stimulates protective immunity in mice to influenza virus. Vaccine 1994, 12, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, A.; Bodmer, H. Antigen recognition by class I-restricted T lymphocytes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1989, 7, 601–624. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Novel H1N1 Flu: Facts and Figures. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/H1N1FLU/surveillanceqa.html ( Accessed 25 August 2009). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smallman-Raynor, M.; Cliff, A.D. Avian influenza A (H5N1) age distribution in humans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 510–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Share and Cite
Bodewes, R.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. Targets for the Induction of Protective Immunity Against Influenza A Viruses. Viruses 2010, 2, 166-188. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2010166
Bodewes R, Osterhaus ADME, Rimmelzwaan GF. Targets for the Induction of Protective Immunity Against Influenza A Viruses. Viruses. 2010; 2(1):166-188. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2010166
Chicago/Turabian StyleBodewes, Rogier, Albert D.M.E. Osterhaus, and Guus F. Rimmelzwaan. 2010. "Targets for the Induction of Protective Immunity Against Influenza A Viruses" Viruses 2, no. 1: 166-188. https://doi.org/10.3390/v2010166