Journal Description
Viruses
Viruses
is a peer-reviewed, open access journal of virology, published monthly online by MDPI. The Spanish Society for Virology (SEV), Canadian Society for Virology (CSV), Italian Society for Virology (SIV-ISV), Australasian Virology Society (AVS), Brazilian Society for Virology (BSV) and others are affiliated with Viruses and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, Embase, PubAg, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Virology) / CiteScore - Q1 (Virology/Infectious Diseases)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 18.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journal: Zoonotic Diseases.
Impact Factor:
3.5 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.7 (2024)
Latest Articles
Dissecting the Unique Self-Assembly Landscape of the HIV-2 Capsid Protein
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1384; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101384 (registering DOI) - 17 Oct 2025
Abstract
Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2) is a lentivirus closely related to HIV-1 but exhibits distinct molecular and clinical features that influence viral infectivity and efficacy of antiretroviral therapy. The HIV capsid is a critical structural component with multifaceted roles during infection and
[...] Read more.
Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2) is a lentivirus closely related to HIV-1 but exhibits distinct molecular and clinical features that influence viral infectivity and efficacy of antiretroviral therapy. The HIV capsid is a critical structural component with multifaceted roles during infection and mediates some of the observed divergence between HIV-1 and HIV-2. Unlike HIV-1, study of the HIV-2 capsid is limited and standard protocols for the in vitro assembly of HIV-1 capsid protein (CA) lattice structures have not been successfully translated to the HIV-2 context. This work identifies effective approaches for the assembly of the HIV-2 CA lattice and leverages this to biochemically characterize HIV-2 CA assemblies and mutant phenotypes. Our findings elaborate on the sensitivity of HIV-2 CA to chemical conditions and reveal that it assembles into a more varied spectrum of particle morphologies compared to HIV-1. Utilizing these assemblies, we tested the hypothesis that HIV-1 and HIV-2 employ divergent mechanisms to stabilize CA oligomer forms and investigate the effects of non-conserved substitutions at the CA inter-protomer interfaces. This work advances our understanding of the key biochemical determinants of HIV-2 CA assembly that are distinct from HIV-1 and may contribute to their divergent virological properties.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Structural and Mechanistic Advances in Retroviral Biology)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Predicting the Landscape Epidemiology of Foot-and-Mouth Disease in Endemic Regions: An Interpretable Machine Learning Approach
by
Moh A. Alkhamis, Hamad Abouelhassan, Abdulaziz Alateeqi, Abrar Husain, John M. Humphreys, Jonathan Arzt and Andres M. Perez
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1383; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101383 (registering DOI) - 17 Oct 2025
Abstract
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) remains a devastating threat to livestock health and food security in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA), where complex interactions among host, environmental, and anthropogenic factors constitute an optimal endemic landscape for virus circulation. Here, we applied an interpretable
[...] Read more.
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) remains a devastating threat to livestock health and food security in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA), where complex interactions among host, environmental, and anthropogenic factors constitute an optimal endemic landscape for virus circulation. Here, we applied an interpretable machine learning (ML) statistical framework to model the epidemiological landscape of FMD between 2005 and 2025. Furthermore, we compared the ecological niche of serotypes O and A in the MENA region. Our ML algorithms demonstrated high predictive performance (accuracies > 85%) in identifying the geographical extent of high-risk areas, including under-reported regions such as the Southern and Northeastern Arabian Peninsula. Sheep density emerged as the dominant predictor for all FMD outbreaks and serotype O, with significant non-linear relationships with wind, temperature, and human population density. In contrast, serotype A risk was primarily influenced by buffalo density and proximity to roads and cropland. Our in-depth interaction and Shapley value analyses provided fine-scale interpretability by interrogating the threshold effects of each feature in shaping the spatial risk of FMD. Further implementation of our analytical pipeline to guide risk-based surveillance programs and intervention efforts will help reduce the economic and public health impacts of this devastating animal pathogen.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Endemic and Emerging Viral Diseases in Livestock: 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Oropouche Virus: An Overview of the Current Status of Diagnostics
by
Daniele Lapa, Maria Anele Romeo, Alessandra Spina, Eliana Specchiarello and Fabrizio Maggi
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1382; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101382 (registering DOI) - 17 Oct 2025
Abstract
The Orthobunyavirus Oropouche (OROV) has become an urgent public health threat in Central and South America, as well as in other countries worldwide. Since its initial identification, there have been over 30 outbreaks, with the largest reported in late 2024 in Brazil. This
[...] Read more.
The Orthobunyavirus Oropouche (OROV) has become an urgent public health threat in Central and South America, as well as in other countries worldwide. Since its initial identification, there have been over 30 outbreaks, with the largest reported in late 2024 in Brazil. This outbreak prompted an epidemiological alert due to a significant increase in OF cases in non-Amazonian states in the Americas region, as well as in European countries, where 44 imported cases were identified. Humans become infected predominantly through the bite of the Culicoides paraensis midge, and the symptoms could be misinterpreted due to their similarity to those of other arboviral infections. Due to the lack of a point-of-care test, RT-qPCR is currently the key diagnostic test during the acute phase of the disease. This review focuses primarily on the available molecular and serological diagnostic methods. The latter could indeed be used as a confirmation test to monitor the patient’s immunological status and better distinguish between cross-reacting arboviruses. In addition, this review explains also the existing sequencing methods required to enforce the surveillance system for OROV reassortant species that could cause a new worldwide outbreak. The information gathered could provide a valuable basis for implementing additional surveillance systems in those countries lacking up-to-date data.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Oropouche Virus (OROV): An Emerging Peribunyavirus (Bunyavirus))
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Acute HIV Infection and ART Response: Insights into T Cell Subsets, Activation, Exhaustion, and Blood and GALT HIV Reservoir
by
Soraia Santana de Moura, Diogo Gama Caetano, Monick Lindenmeyer Guimarães, Rayana Katylin Mendes da Silva, Natasha Cabral, Simone da Costa Cruz Silva, Marcelo Ribeiro-Alves, Sylvia L. M. Teixeira, Ingebourg Georg, Desirée Vieira Gomes dos Santos, Sandro Nazer, Rafael Teixeira Fraga, Brenda Hoagland, Larissa Villela, Beatriz Gilda Jegerhorn Grinsztejn, Valdiléa Gonçalves Veloso, Fernanda Heloise Côrtes and Sandra W. Cardoso
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1381; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101381 - 16 Oct 2025
Abstract
Investigating immunological and viral reservoir dynamics in blood and GALT during acute HIV phase advances understanding of HIV persistence. Dynamics of T cells and HIV reservoirs immediately after early ART require further investigation. We evaluated the ART impact at 12 (M12) and 24
[...] Read more.
Investigating immunological and viral reservoir dynamics in blood and GALT during acute HIV phase advances understanding of HIV persistence. Dynamics of T cells and HIV reservoirs immediately after early ART require further investigation. We evaluated the ART impact at 12 (M12) and 24 months (M24) on immunological, virological and reservoir markers of 24 participants starting ART at Fiebig ≤ V (Baseline = D0) in a Brazilian cohort. We measured the frequency of T cell activation, exhaustion, memory subsets, Th17 and pTfh cells by flow cytometry and quantified total HIV DNA by qPCR in PBMC and GALT. Most participants were cisgender MSM (95.9%), with a median age of 27 years (IQR 25–36). At enrollment (D0), four participants used triple ART as PEP, and two were under oral PrEP and they exhibited higher CD4/CD8 ratios. Higher CD4/CD8 ratios were also observed in participants classified as Fiebig I to III. A total of 92% achieved viral suppression at M12 and 96% at M24. CD4 counts rose from 646 to 861 cells/mm3, and the CD4/CD8 ratio improved from 0.76 to 1.24 (p < 0.01). HIV DNA in PBMCs decreased 4-fold by M12 and 61-fold by M24, with 50% of participants reaching undetectable levels by M24 (p < 0.01). In GALT, undetectable HIV DNA increased from 27% at D0 to 75% at M12. HIV DNA in PBMCs and GALT correlated with plasma VL, while the CD4/CD8 ratio was inversely linked to PBMC reservoirs (rho = −0.66; p < 0.05). Early ART reduced activated CD8+ T cells (p < 0.05) but had minimal effects on CD4+ T cells or exhaustion markers. By M24, CD8+ TCM increased, and CD8+ TEF decreased (p < 0.01), while Th17 and pTfh levels remained stable. Early ART led to viral suppression and immune restoration, and influenced reservoir dynamics. The CD4/CD8 ratio was shown to be a key marker of early treatment success. Since a quarter of the participants were identified while initiating PrEP/PEP, it is important to consider the acute phase window according to vulnerability. Recent PEP/PrEP use often excludes participants from clinical trials on bNAbs and therapeutic vaccines targeting viral reservoirs during the acute phase of HIV. Since these are the populations that may benefit from these strategies, larger studies including those people are needed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue HIV Reservoirs, Latency, and the Factors Responsible)
Open AccessArticle
Different Susceptibility of Mammalian Cell Lines to Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection
by
Marla Anggita, Samuel Nyampong, Weiyin Hu, Hiroshi Shimoda and Daisuke Hayasaka
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1380; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101380 - 16 Oct 2025
Abstract
Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (SFTS) is an emerging tick-borne infectious disease that poses a significant public health threat. SFTS virus (SFTSV) has a broad host range, including humans, cats, and natural reservoir species. Therefore, cultured cell lines derived from different mammalian species
[...] Read more.
Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (SFTS) is an emerging tick-borne infectious disease that poses a significant public health threat. SFTS virus (SFTSV) has a broad host range, including humans, cats, and natural reservoir species. Therefore, cultured cell lines derived from different mammalian species are useful for understanding the susceptibility of SFTSV in hosts. In this study, we evaluated pathogenicity and infectivity, focusing on cytopathic effect (CPE) induction and growth kinetics of SFTSV in several mammalian cell lines, including our original tiger-derived TLT, wild deer–derived DFKT and DFLT, and hedgehog-derived HHoVT. Following SFTSV infection, TLT, CRFK (cat), FCWF-4 (cat), and CPK (porcine) cells exhibited CPE, whereas Vero E6 (monkey), A549 (human), BHK-21 (hamster), DFKT, DFLT, and HHoVT cells did not. Infectious viral yields in the supernatants of TLT, CRFK, FCWF-4, Vero E6, and BHK-21 were higher than those of CPK, A549, DFLT, and DFKT. SFTSV infection in hedgehog-derived HHoVT cells was very limited. These observations suggest that features such as viral CPE and virus yield following SFTSV infection depend on cell type. It is noteworthy that TLT formed clear plaques that were easy to count, indicating that TLT cells are useful for the titration of infectious SFTSV by plaque-forming assay. Our results provide useful information and tools for further elucidating the mechanisms of SFTSV infectivity, proliferation, and pathogenicity using in vitro models.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Viruses)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Refractory CMV Enteritis in Small Bowel Transplantation: A Case Highlighting the Challenges of Balancing Immunosuppression and Novel Antiviral Therapies
by
Abdulrahman A. Al-Saud, Ehab H. Abufarhaneh, Madain S. Alsanea, Reem M. Alameer, Amani H. Yamani, Fatimah S. Alhamlan and Reem S. Almaghrabi
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1379; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101379 - 15 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Cytomegalovirus (CMV) remains a formidable complication in small bowel transplantation (SBT) due to the graft’s high immunogenicity and profound immunosuppression required, with refractory disease representing a particularly devastating challenge. Case: We report an 18-year-old male who underwent SBT, complicated by recurrent acute
[...] Read more.
Background: Cytomegalovirus (CMV) remains a formidable complication in small bowel transplantation (SBT) due to the graft’s high immunogenicity and profound immunosuppression required, with refractory disease representing a particularly devastating challenge. Case: We report an 18-year-old male who underwent SBT, complicated by recurrent acute rejection episodes requiring intensive immunosuppression. He developed refractory CMV disease, marked by non-response to first line therapy with ganciclovir—despite the absence of genotypic resistance—necessitating sequential use of foscarnet, dual antivirals, CMV immunoglobulin, and novel agents (maribavir and letermovir). Discussion: This case illustrates the multifactorial drivers of refractory CMV disease in SBT recipients, including donor–recipient serostatus mismatch, profound immunosuppression through T-cell-depleting induction, corticosteroid exposure, and biologic therapy. It highlights the distinction between refractory and resistant CMV, and the role of combination antiviral strategies including novel agents to achieve disease control. Outcomes remain dismal despite aggressive and innovative therapies, underscoring the limited efficacy of interventions in the context of severe immunologic compromise. Conclusions: Refractory CMV enteritis in SBT exemplifies the extreme difficulty of balancing viral control with rejection management. Despite exhausting antiviral strategies, survival remains poor. Highlights: Refractory CMV enteritis is a significant challenge in small bowel transplant recipients due to intense immunosuppression. Persistent CMV disease may occur despite antiviral prophylaxis and the absence of resistant gene mutations. Combination antiviral strategies, including maribavir, demonstrated significant clinical improvement. Profound immunosuppression required to manage acute graft rejection episodes complicates antiviral management and disease clearance. Despite best efforts in CMV management in this population, outcomes may still be compromised by unrelated or compounding factors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Human Cytomegalovirus Therapeutic Strategies and Clinical Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
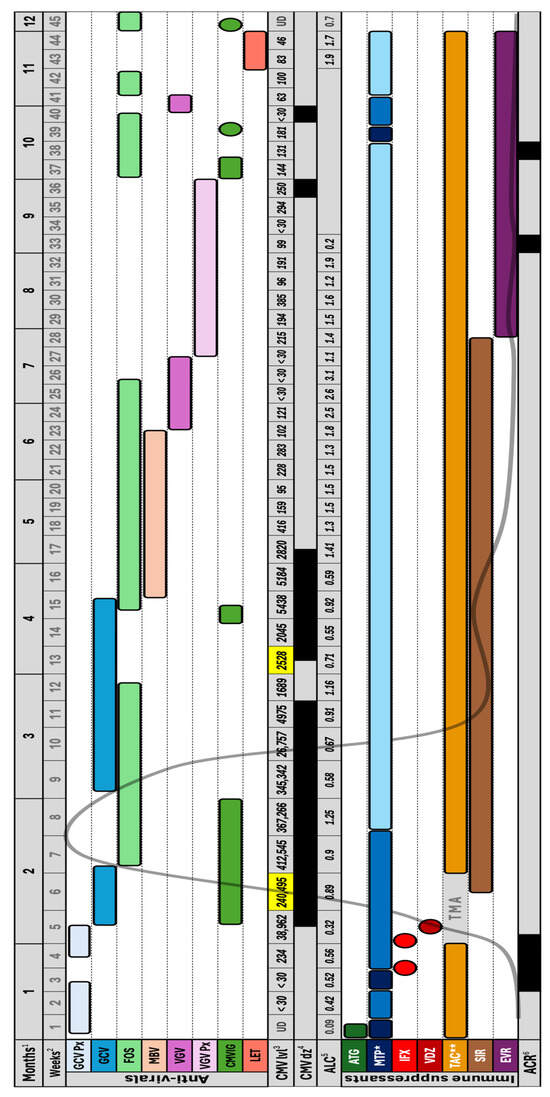
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Quantifying the Inhibitory Efficacy of HIV-1 Therapeutic Interfering Particles at a Single CD4 T-Cell Resolution
by
Igor Sazonov, Dmitry Grebennikov, Rostislav Savinkov, Andreas Meyerhans and Gennady Bocharov
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1378; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101378 - 15 Oct 2025
Abstract
Efficient control of HIV-1 infection relies on highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). However, this therapy is not curative and requires continuous drug administration. Application of HIV-1 defective interfering particles (DIPs), engineered with ablations in key viral protein expressions (e.g., Tat, Rev, Vpu, and
[...] Read more.
Efficient control of HIV-1 infection relies on highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). However, this therapy is not curative and requires continuous drug administration. Application of HIV-1 defective interfering particles (DIPs), engineered with ablations in key viral protein expressions (e.g., Tat, Rev, Vpu, and Env), suggests a therapeutic potential transforming them into Therapeutic Interfering Particles (TIPs). A recent animal HIV model study in non-human primates reports a substantial reduction in viral load after a single intravenous injection of TIPs. In contrast, human clinical trials demonstrate no beneficial effect of defective interfering particles (DIPs) in people living with HIV-1. This discrepancy highlights the importance of further investigation of HIV-TIP interactions. A quantitative view of intracellular replication for HIV-1 in the presence of TIPs is still missing. Here, we develop a high-resolution mathematical model to study various aspects of the interference of a specific engineered TIP-2 particle characterized by a 2.5-kb deletion in the HIV pol-vpr region with HIV-1 replication within infected CD4+ T cells. We define the conditions in terms of the number of homozygous HIV-1 virions and TIP-2 particles that enable the reduction of the wild-type virus replication rate to the value of about one. The deterministic model predicts that at a ratio of 1 HIV-1 to 10 TIP-2 particles, the infected cell still produces some viruses, although in a minor quantity, i.e., about two virions per cycle. Pre-activation of the interferon type I (IFN-I) system results in a complete block of HIV-1 production by TIP-2 co-infected cells. Overall, the modelling results suggest that to improve the effectiveness of TIPs in reducing HIV infection, their combination with other types of antiviral protection should be considered. Our results can be used in the development of combination therapy aimed at treating HIV-1 infection.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Viral Immunology, Vaccines, and Antivirals)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Impact of Vaccinating Adult Women Who Are HPV-Positive or with Confirmed Cervical SIL with the 9-Valent Vaccine—A Systematic Review
by
Dominik Pruski, Sonja Millert-Kalińska, Robert Jach, Jakub Żurawski and Marcin Przybylski
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1377; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101377 - 15 Oct 2025
Abstract
Infection with oncogenic human papillomavirus (HPV) remains a leading cause of cervical cancer and other HPV-related diseases. This situation persists despite the availability of effective prophylactic vaccines. While global vaccination programs have significantly reduced the incidence of HPV in adolescents and young adults,
[...] Read more.
Infection with oncogenic human papillomavirus (HPV) remains a leading cause of cervical cancer and other HPV-related diseases. This situation persists despite the availability of effective prophylactic vaccines. While global vaccination programs have significantly reduced the incidence of HPV in adolescents and young adults, many women presenting with HPV infection or squamous intraepithelial lesions (SIL) were not covered by primary prevention. This review was performed with the aim of evaluating the impact of administering the 9-valent HPV vaccine in adult women who are HPV-positive or have histologically confirmed cervical precancerous lesions. Following the PRISMA 2020 guidelines, a search was performed in the MEDLINE, Scopus, and Cochrane Library databases. A total of 653 studies were retrieved, of which 7 studies, including 19,414 women, met the inclusion criteria. According to the literature, vaccination was linked to significant reductions in persistent HPV infection, progression of SIL, and recurrence of high-grade lesions after surgical removal. Complete HPV remission was achieved in up to 72.4% of vaccinated women, compared to 45.7% among unvaccinated controls. Vaccination after conization lowered the recurrence risk of CIN2+ lesions by 87%, with benefits seen regardless of timing. The most significant effect was observed when vaccine administration was performed before the surgical procedure. Furthermore, HPV vaccination notably enhanced viral clearance and decreased the likelihood of repeated surgical interventions. Despite differences in study design and follow-up definitions, the overall evidence supports additional vaccination in HPV-positive adult women as an effective measure to reduce recurrence and promote viral remission. These findings emphasize the need for clear guidelines and wider access to HPV vaccination for adult populations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Viral Infections in Gynecological Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Genetic and Serological Analysis of H7N3 Avian Influenza Viruses in Mexico for Pandemic Risk Assessment
by
Guadalupe Ayora-Talavera, Irma López-Martínez, Gisela Barrera-Badillo, Rodrigo Aparicio-Antonio, Nidia Aréchiga-Ceballos, Anita Aguirre-Barbosa, Rosa Maria Wong-Chew, Daniel Canul-Canul and Mario Solís-Hernández
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1376; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101376 - 15 Oct 2025
Abstract
Avian influenza A viruses pose ongoing threats to human and animal health, with H7 subtypes causing outbreaks globally. In Mexico, highly pathogenic H7N3 viruses have circulated in poultry since 2012, causing sporadic human infections. Here we analyzed genetic markers in hemagglutinin sequences from
[...] Read more.
Avian influenza A viruses pose ongoing threats to human and animal health, with H7 subtypes causing outbreaks globally. In Mexico, highly pathogenic H7N3 viruses have circulated in poultry since 2012, causing sporadic human infections. Here we analyzed genetic markers in hemagglutinin sequences from Mexican H7N3 isolates and conducted serological assays on human populations with poultry exposure. Our results show conserved avian-like receptor binding sites, thus limiting human adaptation, alongside antigenic drift and acquisition of glycosylation sites likely driven by vaccination. Serological testing of 1103 individuals revealed no detectable antibodies against H7N3, indicating a naïve population. Phylogenetic analyses revealed multiple virus clades circulating regionally. These findings suggest that while current H7N3 viruses have limited capacity for sustained human transmission, the lack of population immunity underscores the importance of continued surveillance and risk assessment to mitigate potential pandemic threats.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular Epidemiology, Evolution, and Transmission of Avian Influenza Viruses)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Behavioral Predictors of Intentional and Unintentional Nonadherence to Antiretroviral Therapy and Their Implications for Virological Failure Among People with HIV in Taiwan
by
Su-Han Hsu, Chien-Chun Wang, Yung-Feng Yen, Tsen-Fang Yen, Po-Tsen Yeh and Hsin-Hao Lai
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1375; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101375 - 14 Oct 2025
Abstract
Adherence to antiretroviral therapy (ART) is critical for HIV management and sustained virological suppression. Differentiating intentional from unintentional nonadherence is essential for developing tailored interventions, yet evidence from Asian populations remains limited. A cross-sectional study of 846 people with HIV (PWH) in northern
[...] Read more.
Adherence to antiretroviral therapy (ART) is critical for HIV management and sustained virological suppression. Differentiating intentional from unintentional nonadherence is essential for developing tailored interventions, yet evidence from Asian populations remains limited. A cross-sectional study of 846 people with HIV (PWH) in northern Taiwan assessed ART adherence using the MARS-5 scale. Participants were categorized into good, unintentional, or intentional non-adherence groups. Logistic regression identified associated behavioral and psychosocial factors. Recreational drug use and younger age were independently linked to both unintentional and intentional poor adherence. Higher income and the use of single-tablet regimens were protective against intentional nonadherence, whereas disclosure of HIV status to a partner and an unsuppressed viral load were significantly associated with intentional nonadherence. Reported reasons included being too busy, emotional distress, and running out of medication. These findings suggest that intentional and unintentional nonadherence represent distinct behavioral patterns, with intentional lapses more strongly linked to virological failure. Addressing substance use, simplifying regimens, and providing psychosocial support after disclosure are essential to optimize adherence and achieve UNAIDS 2030 targets.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Research on HIV Drug Resistance and Other Determinants of Treatment Success: 3rd Edition)
Open AccessArticle
Epidemiology and Evolution of Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus (BVDV) in Uruguay: A 10-Year Study
by
Leticia Maya, Matias Castells, Caroline Silveira, Federico Giannitti, Ingryd Merchioratto, Maria Barrandeguy, Alejo Menchaca and Rodney Colina
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1374; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101374 - 14 Oct 2025
Abstract
Bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) is a pathogen of worldwide economic importance. In Uruguay, BVDV is endemic, with seroprevalence >80% at the farm level. This study analyzed 912 samples collected from January 2018 to October 2024 by reverse transcription PCR and sequencing, from
[...] Read more.
Bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) is a pathogen of worldwide economic importance. In Uruguay, BVDV is endemic, with seroprevalence >80% at the farm level. This study analyzed 912 samples collected from January 2018 to October 2024 by reverse transcription PCR and sequencing, from calves with diarrhea, aborted fetuses, heifers with a history of abortions, and animals exhibiting symptoms of Mucosal Disease. This work summarizes ten years (2014–2024) of molecular epidemiology and evolution of BVDV. Analysis of the BVDV 5′UTR/Npro genomic region revealed that the BVDV-1a, 1e, 1i, and 2b subtypes circulate in Uruguay. BVDV-1a remains the most prevalent subtype, followed by BVDV-2b, whose prevalence has been increasing. Our previous studies revealed that BVDV-1a showed geographical diversification in Uruguay. In this work, evolutionary studies conducted with Npro genomic region showed that BVDV-2b is evolving at a substitution rate of 6.09 × 10−4 substitutions/site/year and has been introduced from Brazil in six separate events between 1870 and 1928, showing no geographical diversification. This work demonstrates that BVDV-1a and BVDV-2b are evolving differently in Uruguay. This evolutionary divergence is notable when comparing patterns observed in other countries where these subtypes circulate. Our findings provide crucial knowledge that should be considered for developing effective BVDV control measures in Uruguay.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Bovine Viral Diarrhea Viruses and Other Pestiviruses)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Intranasal Challenge Model in African Green Monkeys (Chlorocebus aethiops) for Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19 Disease Caused by Subvariant XBB.1.5
by
Nadia Storm, Ming Lo, Nicholas Crossland, Margaux Seyler-Schmidt, Hilary Staples, Daniela Silva-Ayala, Ambre M. Laprise, Lauren St. Denis, Kyle Grosz, Aoife O’Connell, Hans Gertje, Tillie Ripin, Claire Decker, M. Mazur, Colleen Thurman, Marlene Espinoza, Gavin Morrow, Christopher L. Parks, Christopher L. Cooper and Anthony Griffiths
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1373; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101373 - 14 Oct 2025
Abstract
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) primarily causes mild to moderate respiratory illness in humans, but infection can also lead to long-term complications, including chronic fatigue, respiratory and cardiac issues, or even death. In November 2021, the emergence of the highly transmissible
[...] Read more.
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) primarily causes mild to moderate respiratory illness in humans, but infection can also lead to long-term complications, including chronic fatigue, respiratory and cardiac issues, or even death. In November 2021, the emergence of the highly transmissible Omicron variant marked a significant shift in the pandemic, with its subvariants rapidly spreading and continuing to evolve worldwide. The continuing introduction of Omicron subvariants underscores the need for the development of up-to-date vaccines, as well as for appropriate animal models in which they can be evaluated. Among these subvariants, XBB.1.5 stands out for its ability to evade the immune response from previous infection or vaccination. The objective of this study was to determine the disease course in African green monkeys (AGMs) following intranasal exposure to the XBB.1.5 subvariant. In four intranasally exposed AGMs, histopathological findings in the lungs consistent with SARS-CoV-2 infection included lymphohistiocytic and neutrophilic bronchiolitis with variable numbers of syncytial cells, to terminal bronchiole-centric, bronchointerstitial pneumonia with alveolar type II (AT2) pneumocyte hyperplasia, with evidence of acute alveolar injury, including alveolar septal necrosis and hyaline membrane formation. The two males showed more severe pneumonia compared to the two females. SARS-CoV-2 RNA was detected in the lungs or tracheobronchial lymph nodes in the males but not in the females, which correlated with higher cumulative lung pathology scores in the males. In the females, SARS-CoV-2 RNA was limited to the colon and nasal turbinates. Our results indicate that AGMs exhibit a disease course similar to most humans when exposed intranasally, making them a suitable model for studying mild to moderate SARS-CoV-2 infection. Therefore, further work is warranted to determine if this model could have utility for the evaluation of vaccine and therapeutic candidates against contemporary SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Coronaviruses)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Toward Effective Vaccines Against Piscine Orthoreovirus: Challenges and Current Strategies
by
Daniela Espinoza and Andrea Rivas-Aravena
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1372; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101372 - 14 Oct 2025
Abstract
Piscine orthoreovirus (PRV) is a globally distributed viral pathogen that causes heart and skeletal muscle inflammation (HSMI) in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and affects other salmonids, yet no commercial vaccines are currently available. Major barriers to vaccine development include the inability
[...] Read more.
Piscine orthoreovirus (PRV) is a globally distributed viral pathogen that causes heart and skeletal muscle inflammation (HSMI) in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and affects other salmonids, yet no commercial vaccines are currently available. Major barriers to vaccine development include the inability to propagate PRV in cell lines and the low, variable immunogenicity of its proteins, particularly the outer capsid protein σ1, which mediates viral attachment. This protein is hypothesized to be immunologically relevant due to its homology with Mammalian orthoreoviruses. Recombinant σ1 expressed in conventional systems exhibits poor antibody recognition, whereas structural modifications such as lipidation or fusion with molecular chaperones improve epitope exposure. Formalin-inactivated vaccines have shown inconsistent protection, often failing to elicit robust innate or adaptive responses, especially under cohabitation challenge. In contrast, DNA vaccines encoding σ1 and the non-structural protein μNS have demonstrated partial efficacy, likely due to enhanced intracellular expression and antigen presentation. Nonetheless, the considerable variability observed in immune responses among individual fish and viral genotypes, together with suggestions that PRV may interfere with antiviral pathways, represent additional barriers to achieving consistent vaccine efficacy. This review summarizes the current status of PRV vaccine development and discusses future directions for rational design based on optimized antigens and intracellular delivery platforms.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Viral Pathogenesis and Novel Vaccines for Fish Viruses)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Semen Quality in Rams Is Severely but Temporarily Affected by Bluetongue Virus Serotype 3 Infection
by
Ludovic Martinelle, Sophie Egyptien, Lola Dechene, Marielle Somville, Frédéric Derkenne and Stéfan Deleuze
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1371; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101371 - 13 Oct 2025
Abstract
Bluetongue virus serotype 3 (BTV-3) emerged in northwestern Europe in 2023–2024, raising concerns about its potential reproductive impact on rams, similar to previous outbreaks with BTV-8. This study assessed the effect of natural BTV-3 infection on the semen quality of 49 rams in
[...] Read more.
Bluetongue virus serotype 3 (BTV-3) emerged in northwestern Europe in 2023–2024, raising concerns about its potential reproductive impact on rams, similar to previous outbreaks with BTV-8. This study assessed the effect of natural BTV-3 infection on the semen quality of 49 rams in Belgium using two cross-sectional sampling sessions during the 2024 outbreak. Semen and blood were tested for BTV RNA via RT-qPCR, and a composite semen quality score (SQS) was established based on key sperm parameters. On the first sampling date, 75% of rams were viremic, and 19% presented azoospermia. Rams with BTV RNA detectable in both semen and blood had significantly lower SQS and sperm concentrations than those with viral RNA in blood only or none at all. By the second sampling, 53 days later, semen quality had improved markedly, indicating a transient effect of infection. These findings confirm that BTV-3 can severely but temporarily impair ram fertility, particularly when viral replication occurs in the reproductive tract. Given the seasonal overlap between vector activity and breeding programs, these results underscore the importance of integrating reproductive health monitoring into outbreak response strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Bluetongue, Epizootic Haemorrhagic Disease, and Other Emerging Orbiviruses, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
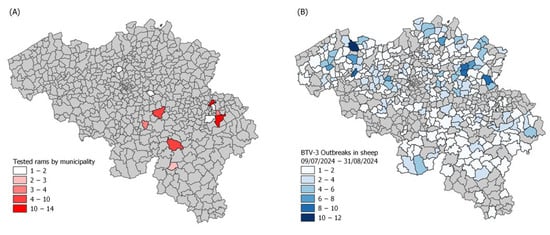
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Genetic Characterization and Pathogenesis of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus A (H5N1) Isolated in Egypt During 2021–2023
by
Mina Nabil Kamel, Yassmin Moatasim, Basma Emad Aboulhoda, Mokhtar Gomaa, Ahmed El Taweel, Omnia Kutkat, Mohamed El Sayes, Mohamed GabAllah, Hend AbdAllah, Refaat M. Gabre, Maha M. AlKhazindar, Ahmed Kandeil, Pamela P. McKenzie, Richard J. Webby, Mohamed Ahmed Ali, Ghazi Kayali and Rabeh El-Shesheny
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1370; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101370 - 13 Oct 2025
Abstract
Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) viruses have recently had a substantial impact on global poultry production and public health. In Egypt, clade 2.3.4.4b HPAI H5N1 viruses were first isolated from wild birds in 2021 and then became dominant in domestic poultry. In this
[...] Read more.
Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) viruses have recently had a substantial impact on global poultry production and public health. In Egypt, clade 2.3.4.4b HPAI H5N1 viruses were first isolated from wild birds in 2021 and then became dominant in domestic poultry. In this study, we aimed to genetically characterize the H5N1 viruses isolated in Egypt during 2021–2023 and examine the pathogenicity and transmissibility of two H5N1 strains isolated from wild and domestic poultry in chickens. We collected 7588 specimens from live bird markets including poultry, wild birds, and environmental samples. Influenza A viruses were detected in 20.94% (484/2311) of tested samples, and 17 isolates were identified as H5N1 through complete genome sequencing. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that all H5N1 viruses were closely related to Eurasian viruses and classified into three distinct genetic groups, suggesting multiple introductions likely linked to migratory birds. Experimental infections of chickens with two H5N1 isolates, A/Pintail/Egypt/RA19853OP/2021 and A/duck/Egypt/BA20361C/2022, showed efficient replication, systemic infection, and transmission by direct contact. These findings underscore the need for continued surveillance of H5N1 at the poultry-wild bird interface to identify circulating strains, evaluate their biological characteristics, and assess their zoonotic potential.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section General Virology)
►▼
Show Figures
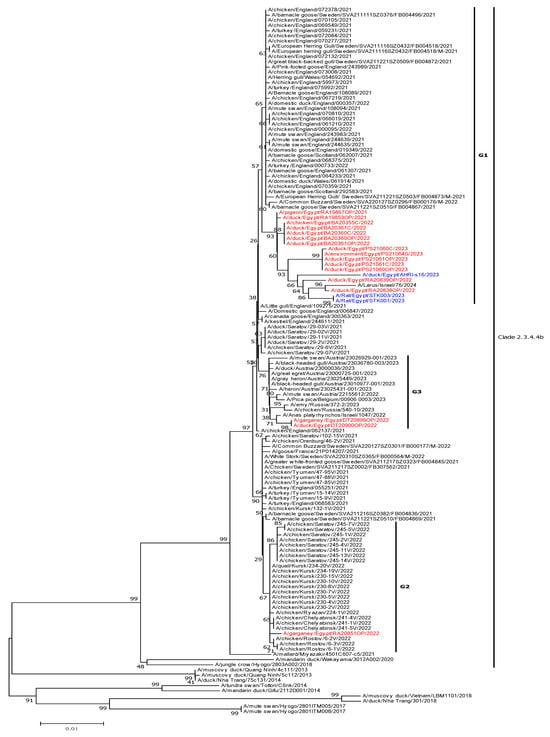
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cellular eEF1G Inhibits Porcine Deltacoronavirus Replication by Binding Nsp12 and Disrupting Its Interaction with Viral Genomic RNA
by
Weijia Yin, Xinna Ge, Lei Zhou, Xin Guo, Jun Han, Yongning Zhang and Hanchun Yang
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1369; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101369 - 13 Oct 2025
Abstract
Porcine deltacoronavirus (PDCoV) is an emerging pathogen that causes severe, often fatal, diarrhea in suckling piglets and has zoonotic potential. Its nonstructural protein 12 (Nsp12), functioning as the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), is a central component of the viral replication–transcription complex and a
[...] Read more.
Porcine deltacoronavirus (PDCoV) is an emerging pathogen that causes severe, often fatal, diarrhea in suckling piglets and has zoonotic potential. Its nonstructural protein 12 (Nsp12), functioning as the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), is a central component of the viral replication–transcription complex and a critical target for host antiviral mechanisms. Here, we identified eukaryotic elongation factor 1 gamma (eEF1G) as a host interactor of PDCoV Nsp12 by immunoprecipitation-coupled mass spectrometry in IPEC-J2 cells. This interaction was confirmed by co-immunoprecipitation, pull-down assays, and confocal microscopy. Functional analyses involving siRNA knockdown and overexpression of eEF1G, combined with viral titration, strand-specific real-time quantitative PCR, and RNA immunoprecipitation assays, demonstrated that eEF1G directly binds to Nsp12. Knockdown of eEF1G significantly enhanced viral replication and increased negative-stranded RNA synthesis, whereas overexpression did not affect viral proliferation. Furthermore, eEF1G was found to bind PDCoV genomic RNA and competitively disrupt the interaction between Nsp12 and viral RNA, thereby impairing RdRp activity. Our results indicate that eEF1G acts as a novel host restriction factor that inhibits PDCoV replication by competing with Nsp12 for genomic RNA binding, ultimately blocking negative-stranded RNA synthesis. This study unveils a new antiviral mechanism and highlights a potential target for developing interventions against PDCoV.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Porcine Viruses 2025)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Serological Evidence of Lassa Virus Exposure in Non-Mastomys Small Mammals Within a Hyperendemic Region of North-Central Nigeria: A Pilot Study
by
Augustine Ovie Edegbene, Temidayo Oluwatosin Omotehinwa, Joseph Anejo-Okopi, Sara El Yaagoubi, Oladapo Sunday Shittu, Onyemocho Audu, Evangeline Olohi Abah, Samuel Ijoganu, Genesis Kwaghgande, Celina Aju-Ameh, Adesanya Abimbola, Emmanuel Otache, Emmanuel Ameh, Joyce Danyi, Owoicho Ikwu, Esther Agmdalo Malachi Cegbeyi, Oludare Oladipo Agboola, Joseph Okoeguale, Reuben Agbons Eifediyi, Ediga Bede Agbo, John Alechenu Idoko, Innocent Otoboh Achanya Ujah and Stephen Obekpa Abahadd
Show full author list
remove
Hide full author list
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1368; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101368 - 13 Oct 2025
Abstract
Lassa fever (LF), a severe hemorrhagic disease endemic to West Africa, is primarily transmitted by rodents of the genus Mastomys, particularly Mastomys natalensis, which serve as the main reservoirs of Lassa virus (LASV). There have been reports of high prevalence of
[...] Read more.
Lassa fever (LF), a severe hemorrhagic disease endemic to West Africa, is primarily transmitted by rodents of the genus Mastomys, particularly Mastomys natalensis, which serve as the main reservoirs of Lassa virus (LASV). There have been reports of high prevalence of LF in Nigeria, and outbreaks tend to be recurrent yet geographically restricted, implying that additional ecological or epidemiological factors influence the distribution of the disease beyond the mere presence of M. natalensis. However, national-scale data on LASV prevalence in rodent populations remain scarce. To address this gap, a targeted small mammal survey was conducted over a four-month period (May to August 2024) in Otukpo Local Government Area (LGA) of Benue State, north-central Nigeria. Rodents and other small mammals were trapped across three purposively selected wards identified as high-risk areas based on prior reports of occurrence of such small mammals in the areas and the informal settlements in which the selected wards were located in in Otukpo LGA. Analysis of the samples revealed no statistically significant variation in LASV prevalence among the study sites, indicating a relatively uniform, low-level exposure risk across the LGA and region. However, a marginally significant difference in LASV detection between plasma and serum samples suggests that sample type and storage conditions may influence serological sensitivity. These findings highlight the importance of refining diagnostic protocols, broadening surveillance to include additional rodent hosts, and integrating ecological data with public health strategies to improve early warning systems and strengthen Lassa fever control efforts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section General Virology)
►▼
Show Figures
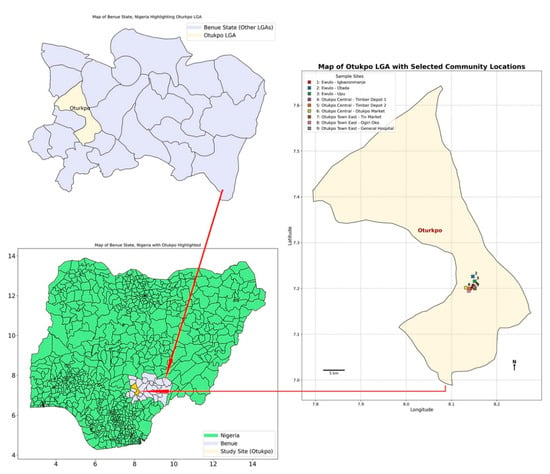
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
First Investigation of Grass Carp Reovirus (GCRV) Infection in Amphioxus: Insights into Pathological Effects, Transmission, and Transcriptomic Responses
by
Jingyuan Lin, Meng Yang, Huijuan Yang, Guangdong Ji and Zhenhui Liu
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1367; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101367 - 13 Oct 2025
Abstract
Amphioxus belongs to the subphylum Cephalochordata and occupies a transitional position in evolution between invertebrates and vertebrates. Due to the lack of viruses suitable for immunostimulation in amphioxus, this study for the first time explored the pathogenicity and waterborne transmission of Grass Carp
[...] Read more.
Amphioxus belongs to the subphylum Cephalochordata and occupies a transitional position in evolution between invertebrates and vertebrates. Due to the lack of viruses suitable for immunostimulation in amphioxus, this study for the first time explored the pathogenicity and waterborne transmission of Grass Carp Reovirus (GCRV), a double-stranded RNA virus, during its infection of amphioxus. Soaking amphioxus in GCRV suspension can cause obvious damage to gill tissues and severely disrupt the structure of gill filaments. The virus survived in seawater for no more than 48 h. Infection kinetics studies showed that the expression of VP5 (a viral capsid protein) mRNA in gill tissues peaked at 14 h. After co-culturing GCRV-infected amphioxus with healthy amphioxus for 72 h, the gills of healthy amphioxus showed obvious pathological damage. Additionally, the presence of the virus was verified by RT-PCR amplification of VP5 expression, indicating that GCRV can be transmitted via water. Transcriptome sequencing analysis showed that the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK), calcium signaling pathway, and chitin metabolic pathway were significantly activated in amphioxus after GCRV stimulation. This study confirmed that GCRV can infect cephalochordates, revealing its gill-tropism and water-borne transmission ability, providing a new perspective for studying the cross-species infection mechanism of aquatic viruses and the prevention and control of aquatic diseases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Viruses)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Transcriptomics Analyses Identify DDX43 as a Cellular Regulator Involved in Suppressing HSV-2 Replication
by
Ranqing Cheng, Yuncheng Li, Yuhao Chen, Mudan Zhang, Qinxue Hu and Yalan Liu
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1366; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101366 - 13 Oct 2025
Abstract
HSV-2 is the main pathogen causing genital herpes, and its infection increases the infection and transmission of HIV-1. Currently, there are no vaccines to prevent HSV-2 infection or treatment that can fully cure it. Mining key host factors that regulate HSV-2 replication and
[...] Read more.
HSV-2 is the main pathogen causing genital herpes, and its infection increases the infection and transmission of HIV-1. Currently, there are no vaccines to prevent HSV-2 infection or treatment that can fully cure it. Mining key host factors that regulate HSV-2 replication and elucidating their specific regulatory mechanisms are crucial for understanding virus–host interactions and discovering new antiviral targets. In the current study, we identified DDX43 as a cellular factor involved in the suppression of HSV-2 replication through comparative transcriptomic analyses of HSV-2-infected epithelial cells, followed by experimental validation. Comprehensive transcriptomic profiling revealed distinct host cellular gene expression patterns in HeLa and ARPE-19 cell lines post HSV-2 infection. Subsequent orthogonal partial least-squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) pinpointed DDX43 as one of the principal mediators distinguishing the host response between HSV-2-infected HeLa and ARPE-19 cells. Furthermore, overexpression of DDX43 inhibited HSV-2 replication, whereas knockdown of endogenous DDX43 enhanced HSV-2 replication. Additional experiments revealed that human DDX43 inhibits HSV-2 replication in an interferon-independent manner. This study demonstrates that DDX43 serves as a host regulator against HSV-2 infection, underscoring the power of comparative transcriptomics in identifying novel host proteins that modulate viral replications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Cellular Restriction Factors against Viral Infection)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Transcontinental Spread of HPAI H5N1 from South America to Antarctica via Avian Vectors
by
Ruifeng Xu, Minhao Gao, Nailou Zhang, Zhenhua Wei, Zheng Wang, Lei Zhang, Yang Liu, Zhenhua Zheng, Liulin Chen, Haitao Ding and Wei Wang
Viruses 2025, 17(10), 1365; https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101365 - 13 Oct 2025
Abstract
During China’s 41st Antarctic research expedition, samples were collected from wildlife on the Fildes Peninsula, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Real-time RT-PCR screening confirmed H5N1 positivity, representing the first identification of the virus in brown skuas on the Fildes Peninsula. Whole-genome sequences obtained from
[...] Read more.
During China’s 41st Antarctic research expedition, samples were collected from wildlife on the Fildes Peninsula, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. Real-time RT-PCR screening confirmed H5N1 positivity, representing the first identification of the virus in brown skuas on the Fildes Peninsula. Whole-genome sequences obtained from positive samples via next-generation sequencing were subjected to phylogenetic and phylogeographic analyses. The results revealed that these Antarctic strains are most closely related to H5N1 viruses circulating in South America, particularly from Peru and Chile, suggesting a likely introduction via avian migration routes. Furthermore, a unique 17-amino-acid deletion was identified in the stalk region of the neuraminidase (NA) gene, which is uncommon among globally sampled clade 2.3.4.4b variants. This study confirms the arrival of HPAI H5N1 in the Antarctic continent and underscores the necessity for enhanced surveillance to understand the viral ecology and potential risks within this unique ecosystem.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Viruses)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Viruses Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
30 October–2 November 2025
The 11th Wuhan International Symposium on Modern Virology & Viruses 2025 Conference

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Viruses
Viral RNA and Its Interaction with the Host
Guest Editors: Redmond Smyth, Neva CaliskanDeadline: 24 October 2025
Special Issue in
Viruses
Pestivirus 2025
Guest Editors: Benjamin J. Lamp, Christiane M. RiedelDeadline: 30 October 2025
Special Issue in
Viruses
Viral Hemorrhagic Disease
Guest Editors: Joseph Golden, Aura GarrisonDeadline: 31 October 2025
Special Issue in
Viruses
HIV-1 Infection and Immunometabolism: Relevance to HIV Pathogenesis and Persistence 3.0
Guest Editor: Sonia MorettiDeadline: 31 October 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Viruses
Mathematical Modeling of Viral Infection
Collection Editors: Amber M. Smith, Ruian Ke
Topical Collection in
Viruses
Phage Therapy
Collection Editors: Nina Chanishvili, Jean-Paul Pirnay, Mikael Skurnik










