Mitochondria Targeting with Luminescent Rhenium(I) Complexes
Abstract
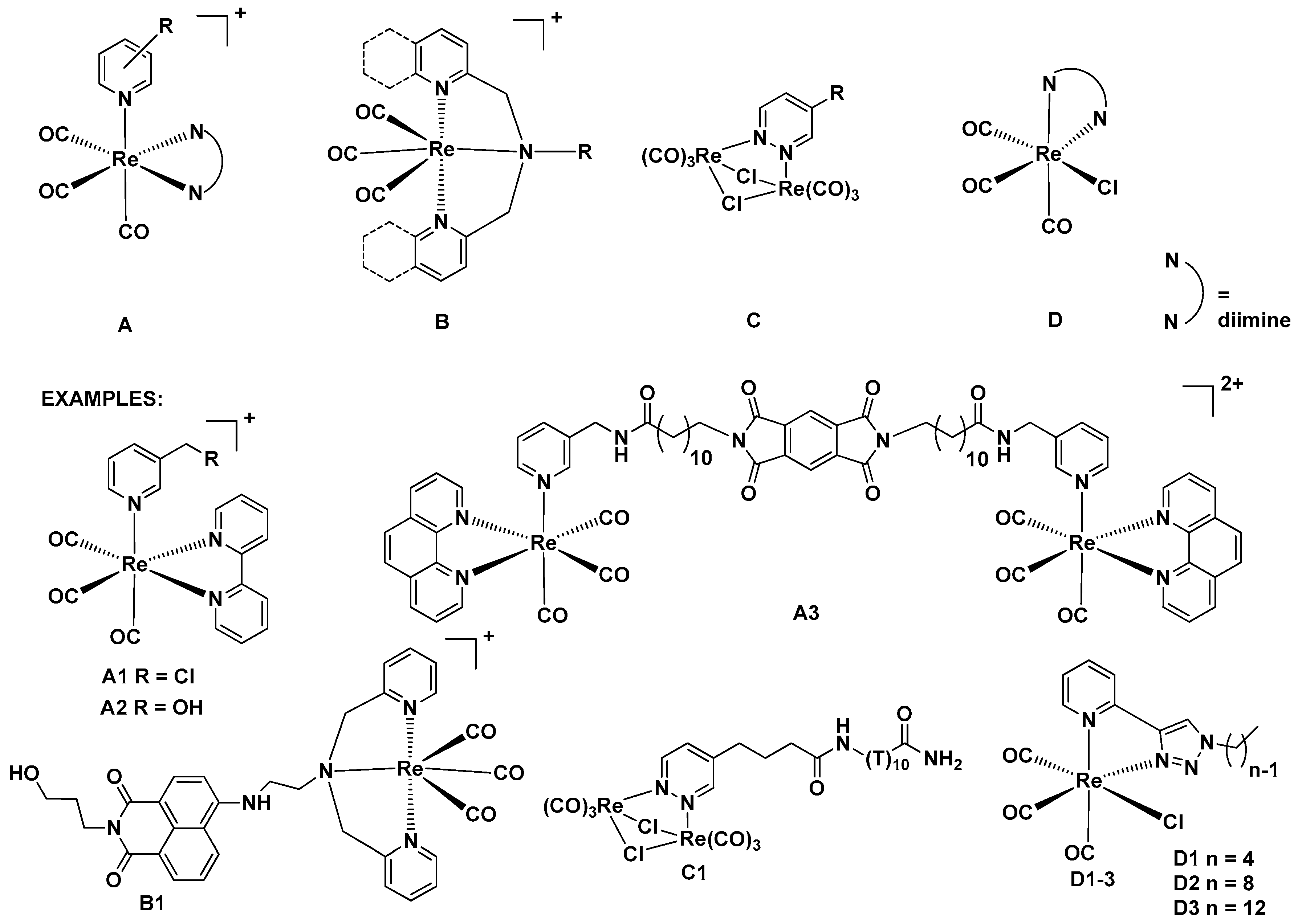
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
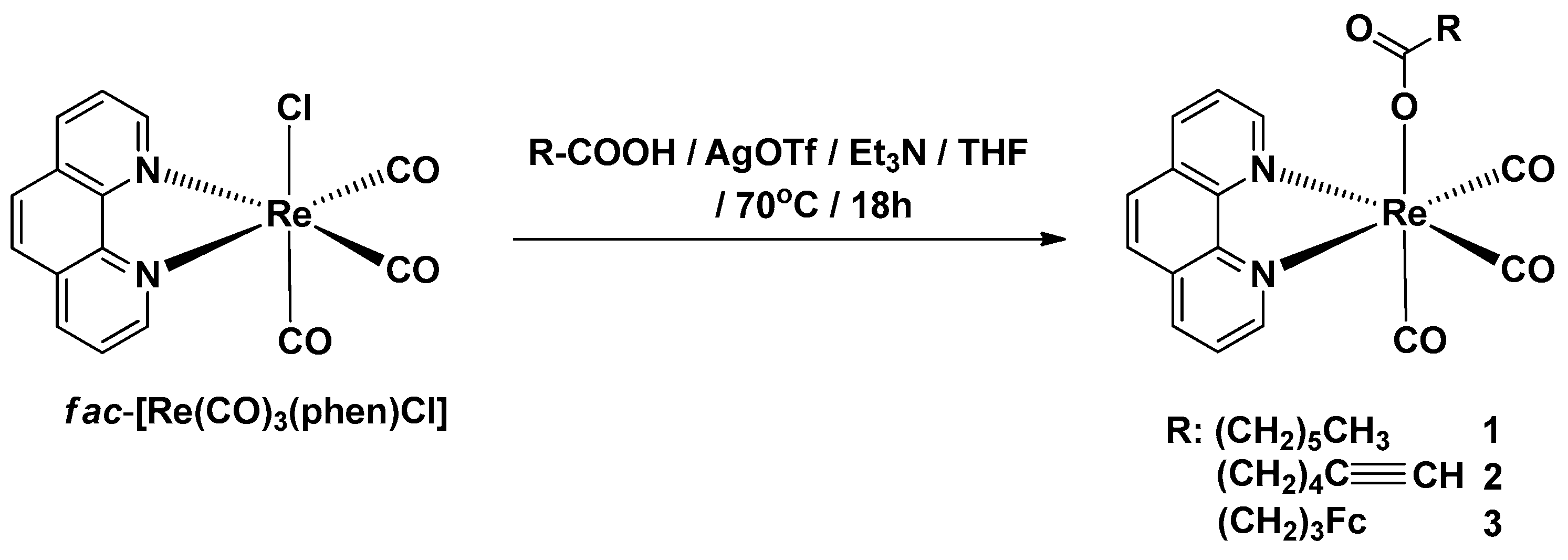
2.1. Synthesis of Complexes 1–3
2.2. Single-Crystal X-ray Structural Analysis of Complexes 1–3
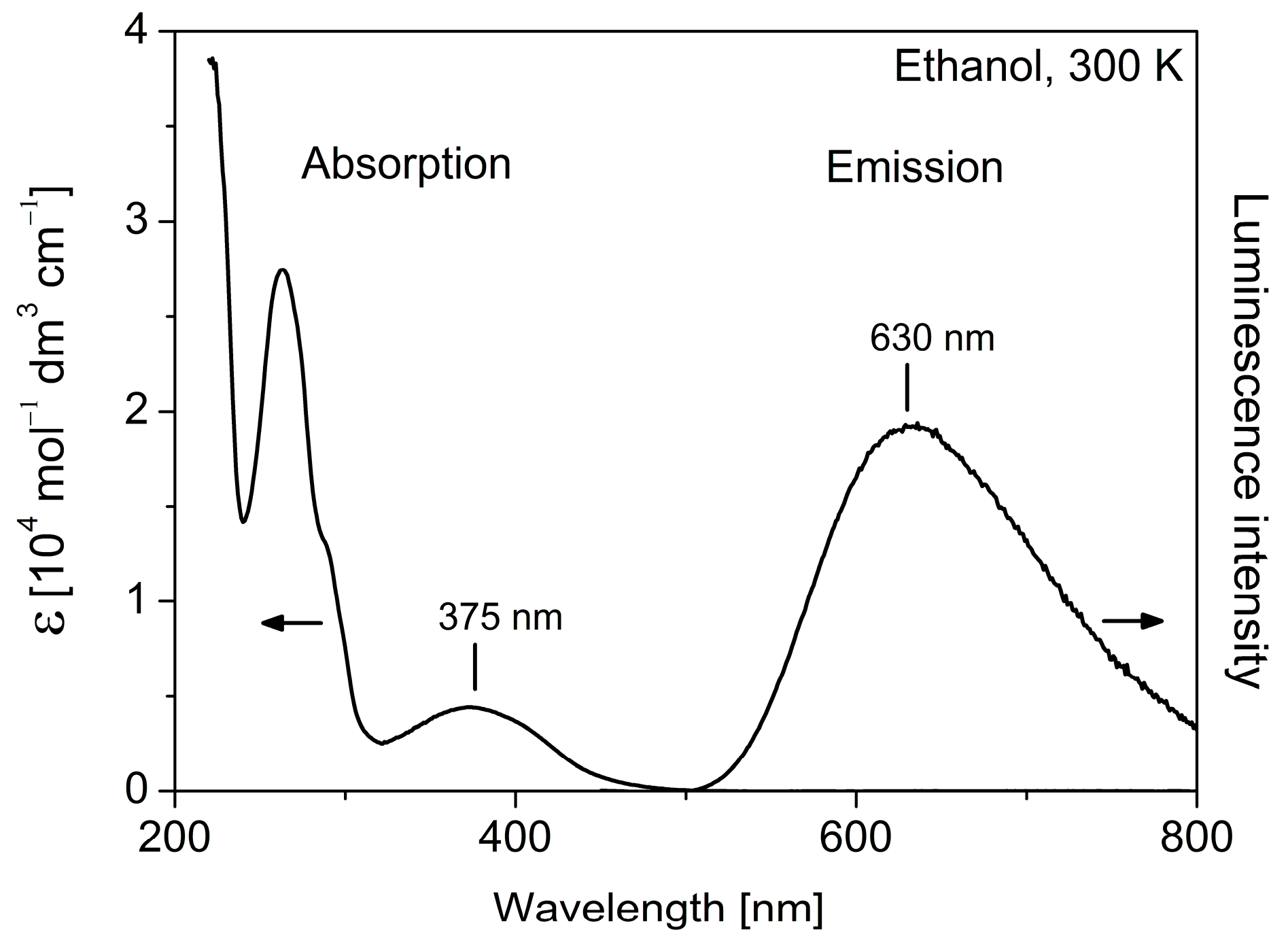
2.3. Photophysical Characterization
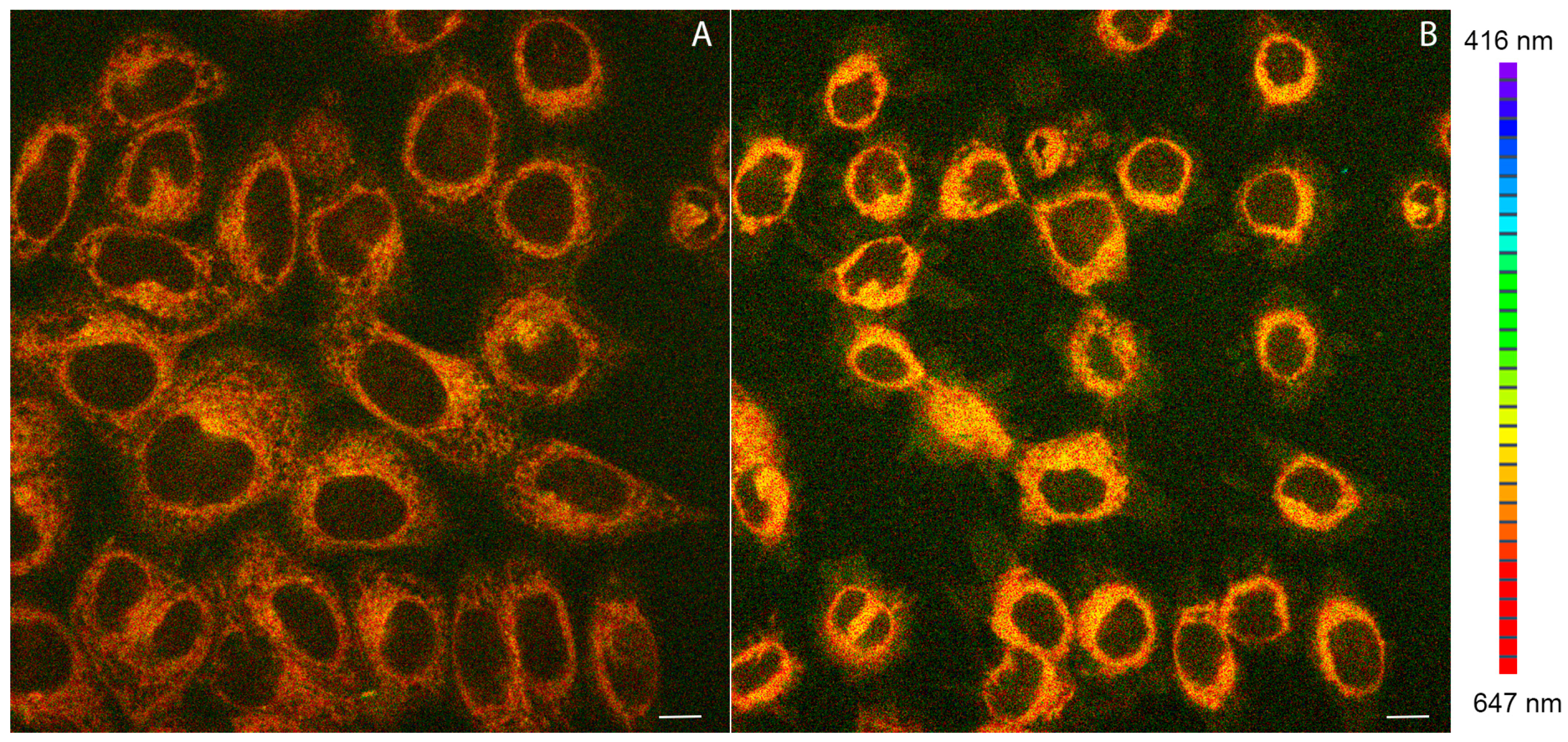
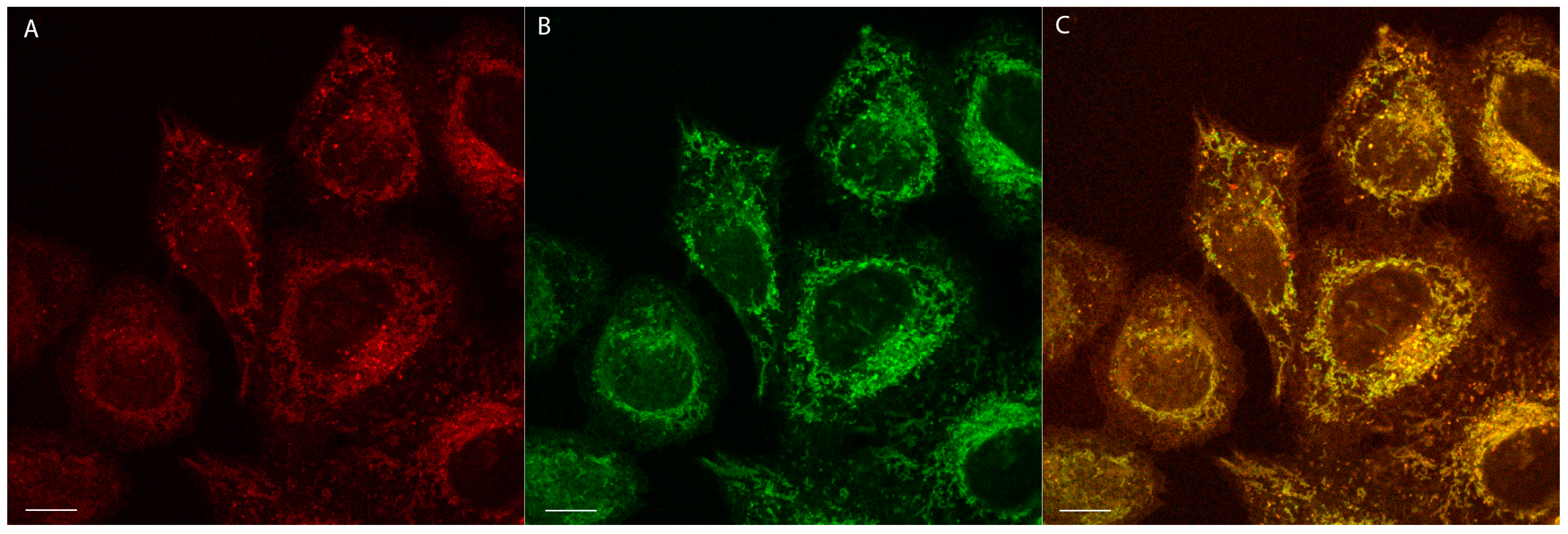
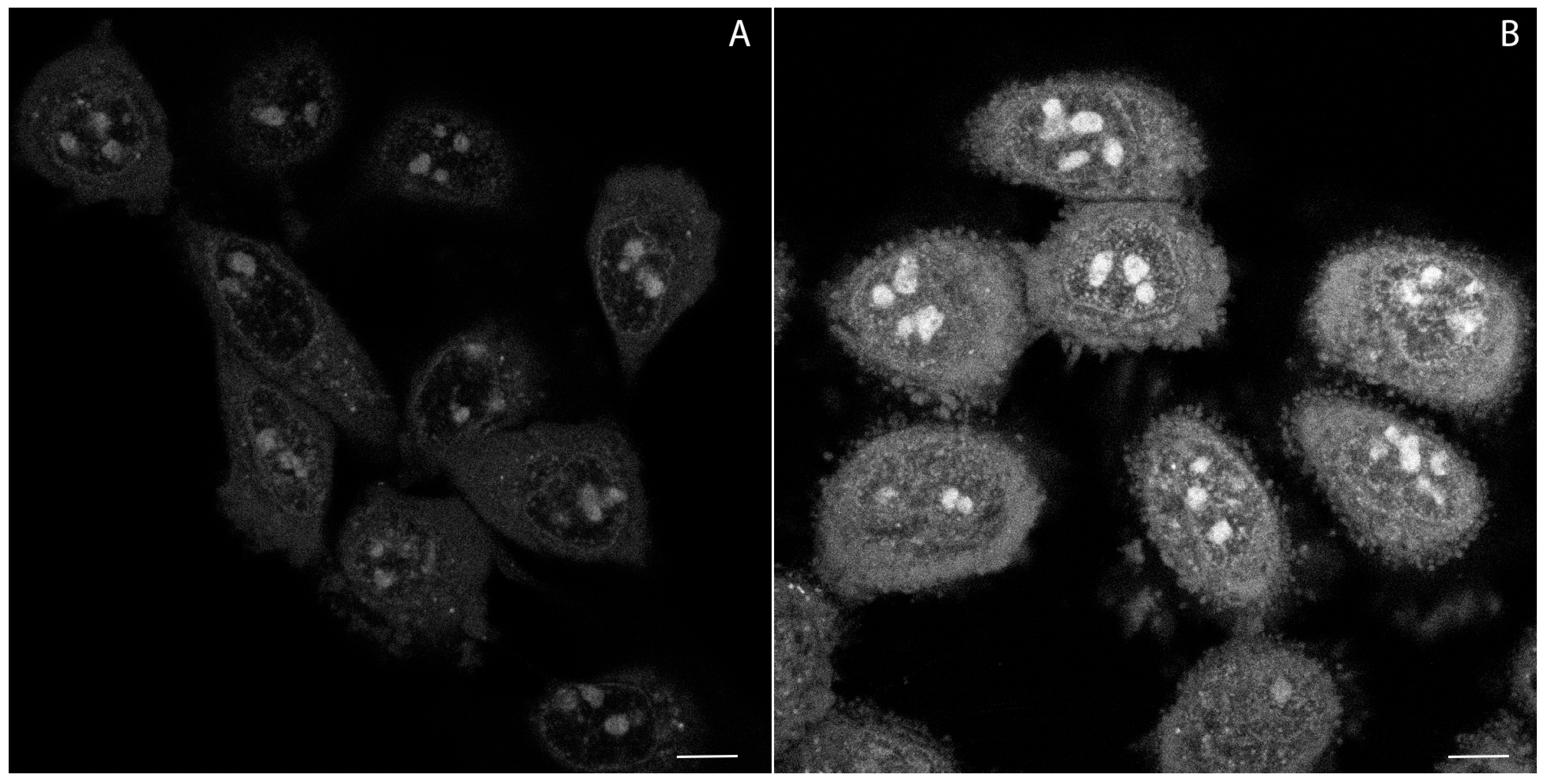
2.4. Confocal Microscopy Studies
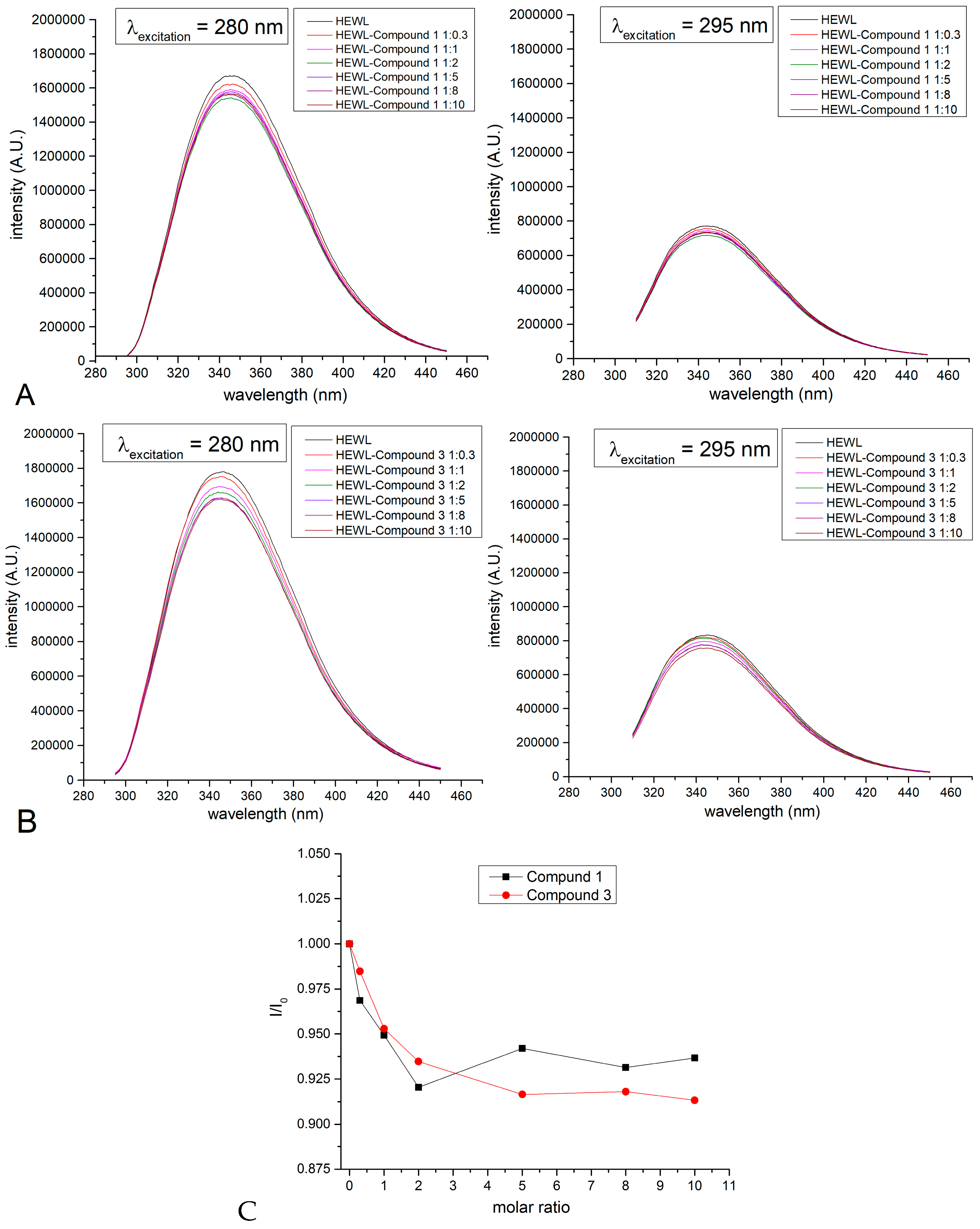
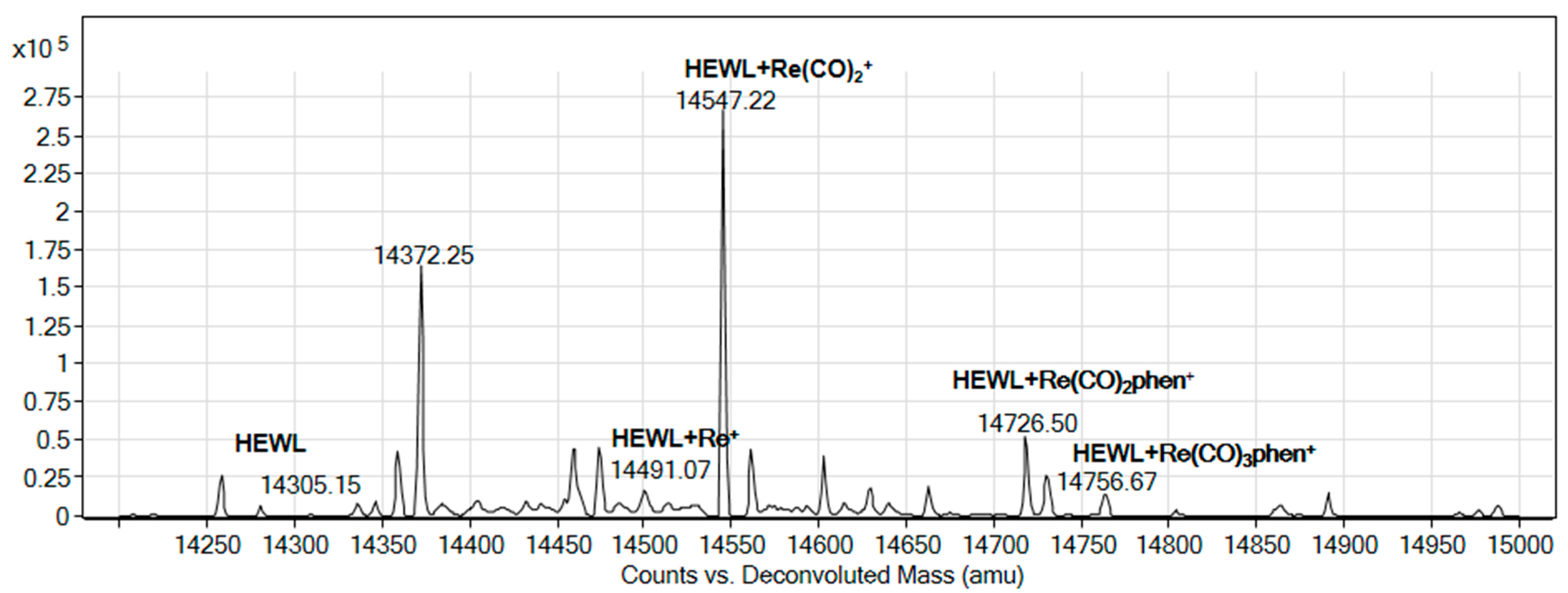
2.5. Binding to Model Proteins
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Information
3.2. Chemistry
Synthesis of Complexes 1–3
3.3. Quantum Chemical Computations
3.4. X-ray Crystallography
3.5. Luminescence Measurements
3.6. Biology
3.6.1. Biological Imaging
3.6.2. Reaction with Model Proteins
3.6.3. Deposited Data
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yersin, H.; Rausch, A.F.; Czerwieniec, R.; Hofbeck, T.; Fischer, T. The triplet state of organo-transition metal compounds. Triplet harvesting and singlet harvesting for efficient OLEDs. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 2622–2652. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, F.; Huang, C. Phosphorescent chemosensors based on heavy-metal complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3007–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashford, D.L.; Gish, M.K.; Vannucci, A.K.; Brennaman, M.K.; Templeton, J.L.; Papanikolas, J.M.; Meyer, T.J. Molecular Chromophore–Catalyst Assemblies for Solar Fuel Applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 13006–13049. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Moreira, V.; Thorp-Greenwood, F.L.; Coogan, M.P. Application of d6 transition metal complexes in fluorescence cell imaging. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 186–202. [Google Scholar]
- Baggaley, E.; Weinstein, J.A.; Williams, J.A.G. Lighting the way to see inside the live cell with luminescent transition metal complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 1762–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, K.K.-W. Luminescent Rhenium(I) and Iridium(III) Polypyridine Complexes as Biological Probes, Imaging Reagents, and Photocytotoxic Agents. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 2985–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorp-Greenwood, F.L. An Introduction to Organometallic Complexes in Fluorescence Cell Imaging: Current Applications and Future Prospects. Organometallics 2012, 31, 5686–5692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coogan, M.P.; Fernández-Moreira, V. Progress with, and prospects for, metal complexes in cell imaging. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 384–399. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, K.K.-W.; Choi, A.W.-T.; Law, W.H.-T. Applications of luminescent inorganic and organometallic transition metal complexes as biomolecular and cellular probes. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 6021–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.-L.; He, H.-Z.; Leung, K.-H.; Chan, D.S.-H.; Leung, C.-H. Bioactive Luminescent Transition-Metal Complexes for Biomedical Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7666–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasser, G.; Ott, I.; Metzler-Nolte, N. Organometallic anticancer compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, M.; Gasser, G. Organometallic Compounds: An Opportunity for Chemical Biology? ChemBioChem 2012, 13, 1232–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartholomä, M.; Valliant, J.; Maresca, K.P.; Babich, J.; Zubieta, J. Single amino acid chelates (SAAC): A strategy for the design of technetium and rhenium radiopharmaceuticals. Chem. Commun. 2009, 493–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clède, S.; Policar, C. Metal–Carbonyl Units for Vibrational and Luminescence Imaging: Towards Multimodality. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 942–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, P.J.; Wrighton, M.S. The nature of the lowest excited state in fac-tricarbonylhalobis(4-phenylpyridine)rhenium(I) and fac-tricarbonylhalobis(4,4′-bipyridine)rhenium(I): Emissive organometallic complexes in fluid solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1979, 101, 2888–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Záliš, S.; Milne, C.J.; El Nahhas, A.; Blanco-Rodríguez, A.M.; van der Veen, R.M.; Vlček, A., Jr. Re and Br X-ray Absorption Near-Edge Structure Study of the Ground and Excited States of [ReBr(CO)3(bpy)] Interpreted by DFT and TD-DFT Calculations. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 5775–5785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czerwieniec, R.; Kapturkiewicz, A.; Lipkowski, J.; Nowacki, J. Re(I)(tricarbonyl)+ complexes with the 2-(2-pyridyl)-N-methyl-benzimidazole, 2-(2-pyridyl)benzoxazole and 2-(2-pyridyl)benzothiazole ligands—Syntheses, structures, electrochemical and spectroscopic studies. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2005, 358, 2701–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirgan, R.A.; Sullivan, B.P.; Rillema, D.P. Photochemistry and photophysics of coordination compounds: Rhenium. Top. Curr. Chem. 2007, 281, 45–100. [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson, K.A.; Banerjee, S.R.; Besanger, T.; Sogbein, O.O.; Levadala, M.K.; McFarlane, N.; Lemon, J.A.; Boreham, D.R.; Maresca, K.P.; Brennan, J.D. Bridging the Gap between in Vitro and in Vivo Imaging: Isostructural Re and 99mTc Complexes for Correlating Fluorescence and Radioimaging Studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 8598–8599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoroso, A.J.; Arthur, R.J.; Coogan, M.P.; Court, J.B.; Fernández-Moreira, V.; Hayes, A.J.; Lioyd, D.; Millet, C.; Pope, S.J.A. 3-Chloromethylpyridyl bipyridine fac-tricarbonyl rhenium: A thiol-reactive luminophore for fluorescence microscopy accumulates in mitochondria. New. J. Chem. 2008, 32, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Moreira, V.; Thorp-Greenwood, F.L.; Amoroso, A.J.; Cable, J.; Court, J.B.; Gray, V.; Hayes, A.J.; Jenkins, R.J.; Kariuki, B.M.; Lloyd, D. Uptake and localisation of rhenium fac-tricarbonyl polypyridyls in fluorescent cell imaging experiments. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 3888–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasingham, R.G.; Thorp-Greenwood, F.L.; Williams, C.F.; Coogan, M.P.; Pope, S.J.A. Biologically Compatible, Phosphorescent Dimetallic Rhenium Complexes Linked through Functionalized Alkyl Chains: Syntheses, Spectroscopic Properties, and Applications in Imaging Microscopy. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langdon-Jones, E.E.; Symonds, N.O.; Yates, S.E.; Hayes, A.J.; Lloyd, D.; Williams, R.; Coles, S.J.; Horton, P.N.; Pope, S.J.A. Fluorescent Rhenium-Naphthalimide Conjugates as Cellular Imaging Agents. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 3788–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clède, S.; Lambert, F.; Saint-Fort, R.; Plamont, M.-P.; Bertrand, H.; Vessières, A.; Policar, C. Influence of the Side-Chain Length on the Cellular Uptake and the Cytotoxicity of Rhenium Triscarbonyl Derivatives: A Bimodal Infrared and Luminescence Quantitative Study. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 8714–8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri, E.; Donghi, D.; Panigati, M.; Prencipe, G.; D’Alfonso, L.; Zanoni, I.; Baldoli, C.; Maiorana, S.; D’Alfonso, G.; Licandro, E. Luminescent conjugates between dinuclear rhenium(I) complexes and peptide nucleic acids (PNA) for cell imaging and DNA targeting. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 6255–6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funkhouser, J. Reintroducing pharma: Theranostic revolution. Curr. Drug Discov. 2002, 2, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Celli, J.P.; Spring, B.Q.; Rizvi, I.; Evans, C.I.; Samkoe, K.S.; Verma, S.; Pogue, B.W.; Hasan, T. Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy: Mechanisms, Monitoring, and Optimization. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2795–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juarranz, A.; Jaèn, P.; Sanz-Rodriguez, F.; Cuevas, J.; González, S. Photodynamic therapy of cancer. Basic principles and applications. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2008, 10, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taub, A.F. Photodynamic Therapy: Other Uses. Dermatol. Clin. 2007, 25, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, K.K.-W.; Louie, M.-W.; Sze, K.-S.; Lau, J.S.-Y. Rhenium(I) Polypyridine Biotin Isothiocyanate Complexes as the First Luminescent Biotinylation Reagents: Synthesis, Photophysical Properties, Biological Labeling, Cytotoxicity, and Imaging Studies. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louie, M.-W.; Liu, H.-W.; Lam, M.H.-C.; Lam, Y.-W.; Lo, K.K.-W. Luminescent Rhenium(I) Polypyridine Complexes Appended with an α-d-Glucose Moiety as Novel Biomolecular and Cellular Probes. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 8304–8308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.Y.; Tso, K.K.-S.; Louie, M.-W.; Liu, H.-W.; Lo, K.K.-W. A Phosphorescent Rhenium(I) Tricarbonyl Polypyridine Complex Appended with a Fructose Pendant That Exhibits Photocytotoxicity and Enhanced Uptake by Breast Cancer Cells. Organometallics 2013, 32, 5098–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola-Villegas, N.; Rabideau, A.E.; Cesnavicious, J.; Zubieta, J.; Doyle, R.P. Targeting the Folate Receptor (FR): Imaging and Cytotoxicity of ReI Conjugates in FR-Overexpressing Cancer Cells. ChemMedChem 2008, 3, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viola-Villegas, N.; Rabideau, A.E.; Bartholom, M.; Zubieta, J.; Doyle, R.P. Targeting the Cubilin Receptor through the Vitamin B12 Uptake Pathway: Cytotoxicity and Mechanistic Insight through Fluorescent Re(I) Delivery. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5253–5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitanovic, I.; Can, S.; Alborzinia, H.; Kitanovic, A.; Pierroz, V.; Leonidova, A.; Pinto, A.; Spingler, B.; Ferrari, S.; Molteni, R.; et al. A Deadly Organometallic Luminescent Probe: Anticancer Activity of a ReI Bisquinoline Complex. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 2496–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonidova, A.; Pierroz, V.; Rubbiani, R.; Heier, J.; Ferrari, S.; Gasser, G. Towards cancer cell-specific phototoxic organometallic rhenium(I) complexes. Dalton. Trans. 2014, 43, 4287–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonidova, A.; Pierroz, V.; Rubbiani, R.; Lan, Y.; Schmitz, A.G.; Kaech, A.; Sigel, R.K.O.; Ferrari, S.; Gasser, G. Photo-induced uncaging of a specific Re(I) organometallic complex in living cells. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 4044–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey-Forgues, S.; Delavaux-Nicot, B. Ferrocene and ferrocenyl derivatives in luminescent systems. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2000, 132, 137–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliz, M.; Ferraudi, G. Charge-Transfer Processes in (4-Nitrobenzoate)Re(CO)3(azine)2 Complexes. Competitive Reductions of 4-Nitrobenzoate and Azine in Thermally and Photochemically Induced Redox Processes. Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 2806–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juliarena, M.P.; Ruiz, G.T.; Wolcan, E.; Lezna, R.O.; Feliz, M.R.; Ferraudi, G.; Guerrero, J. Inhibition of the fac-(RCO2)ReI(CO3)(bis-azine) Photodecarboxylation of the Carboxylate Ligand, RCO2-, When R Is a Strongly Electron Donating Group: Thermal and Photochemical Properties of Complexes Where R = Ferrocene, 4-(Dimethylamino)benzyl. Organometallics 2007, 26, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliarena, M.P.; Lezna, R.O.; Ruiz, G.T.; Féliz, M.R.; Ferraudi, G.; Wolcan, E. On the nature of the redox products of 4-((CH3)2N)C6H4–CO2−and 4-((CH3)2N)C6H4–CO2–Re(CO)3(1,10-phenanthroline): A spectroelectrochemical, pulse radiolysis and flash photochemical study. Polyhedron 2008, 27, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, L.; Hevia, E.; Morales, D.; Pérez, J.; Riera, L.; Miguel, D. Reactivity of Molybdenum and Rhenium Hydroxo Complexes toward Organic Electrophiles: Reactions that Afford Carboxylato Products. Organometallics 2006, 25, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioni, D.; Fenili, F.; D’Alfonso, L.; Donghi, D.; Panigati, M.; Zanoni, I.; Marzi, R.; Manfredi, A.; Ferruti, P.; D’Alfonso, G.; et al. Luminescent Rhenium and Ruthenium Complexes of an Amphoteric Poly(amidoamine) Functionalized with 1,10-Phenanthroline. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 12776–12788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, W.-K.; Ko, C.-C.; Chan, K.-C.; Yiu, S.-M.; Wong, F.-L.; Lee, C.-S.; Roy, V.A.L. A Simple Design for Strongly Emissive Sky-Blue Phosphorescent Neutral Rhenium Complexes: Synthesis, Photophysics, and Electroluminescent Devices. Chem. Mat. 2014, 26, 2544–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, L.; Huertos, M.A.; Morales, D.; Pérez, J.; Riera, L.; Riera, V.; Miguel, D.; Menéndez-Velázquez, A.; Garcia-Granda, S. Synthesis, Structure, and Reactivity of Mononuclear Re(I) Oximato Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 2836–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalski, K.; Szczupak, Ł.; Bernaś, T.; Czerwieniec, R. Luminescent rhenium(I)–chromone bioconjugate: Synthesis, photophysical properties, and confocal luminescence microscopy investigation. J. Organomet. Chem. 2015, 782, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Ding, W.; Sanderson, C.T.; Borden, M.L.; Morgan, M.J.; Kutal, C. Electronic structure, spectroscopy, and photochemistry of group 8 metallocenes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2007, 251, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.K.; Kamocka, M.M.; McDonald, H.J. A practical guide to evaluating colocalization in biological microscopy. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 300, C723–C742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benz, R.; McLaughlin, S. The molecular mechanism of action of the proton ionophore FCCP (carbonylcyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone). Biophys. J. 1983, 41, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernaś, T.; Dobrucki, J. Backscattered light confocal imaging of intracellular MTT-formazan crystals. Micro Res. Technol. 2004, 64, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messori, L.; Marzo, T.; Gabbiani, C.; Valdes, A.A.; Quiroga, A.G.; Merlino, A. Peculiar Features in the Crystal Structure of the Adduct Formed between cis-PtI2(NH3)2 and Hen Egg White Lysozyme. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 13827–13829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messori, L.; Merlino, A. Cisplatin Binding to Proteins: Molecular Structure of the Ribonuclease A Adduct. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 3929–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messori, L.; Merlino, A. Ruthenium metalation of proteins: The X-ray structure of the complex formed between NAMI-A and hen egg white lysozyme. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 6128–6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, A.; Horn, H.; Ahlrichs, R. Fully optimized contracted Gaussian basis sets for atoms Li to Kr. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 97, 2571–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigend, F.; Ahlrichs, R. Balanced basis sets of split valence, triple zeta valence and quadruple zeta valence quality for H to Rn: Design and assessment of accuracy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, P.J.; Wadt, W.R. Ab initio effective core potentials for molecular calculations. Potentials for the transition metal atoms Sc to Hg. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 82, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian09W, V. 8.0. Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, R.C.; Reid, J.S. The analytical calculation of absorption in multifaceted crystals. Acta Cryst. Sect. A 1995, 51, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CrysAlis CCD; CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction Ltd.: Yarnton, UK, 2008.
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst. Sect. A 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L.J. ORTEP-3 for Windows—A version of ORTEP-III with a Graphical User Interface (GUI). J. Appl. Cryst. 1997, 30, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, M.-S.; Aromataris, E.C.; Castro, J.; Roberts, M.L.; Barritt, G.J.; Rychkov, G.Y. Mitochondrial uncoupler FCCP activates proton conductance but does not block store-operated Ca2+ current in liver cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 495, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1–3 are available from the authors. |


| 1 | 2 | 3A | 3B | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bond distances | ||||
| C1-O1 | 1.154(2) | 1.151(5) | 1.164(4) | 1.174(5) |
| C2-O2 | 1.155(2) | 1.152(4) | 1.160(4) | 1.167(5) |
| C3-O3 | 1.164(2) | 1.165(4) | 1.157(4) | 1.152(4) |
| Re1-C1 | 1.922(2) | 1.924(4) | 1.903(4) | 1.901(4) |
| Re1-C2 | 1.923(2) | 1.926(3) | 1.917(3) | 1.911(4) |
| Re1-C3 | 1.900(2) | 1.903(3) | 1.910(3) | 1.919(4) |
| Re1-N1 | 2.176(2) | 2.173(3) | 2.177(3) | 2.181(3) |
| Re1-N2 | 2.184(2) | 2.185(3) | 2.175(3) | 2.180(3) |
| Re1-O4 | 2.142(2) | 2.146(2) | 2.125(2) | 2.129(2) |
| Fe-mid point (Cpsub) | - | - | 1.654(2) | 1.649(2) |
| Fe-mid point (Cp) | - | - | 1.651(2) | 1.651(2) |
| bond angles | ||||
| O4-C16-O5 | 125.33(16) | 125.0(3) | 125.7(3) | 125.5(3) |
| O4-Re1-N1 | 81.42(5) | 80.83(9) | 82.33(9) | 79.74(10) |
| O4-Re1-C1 | 95.58(7) | 94.89(13) | 96.39(12) | 98.50(13) |
| O4-Re1-C3 | 174.96(6) | 174.70(12) | 174.35(12) | 173.61(12) |
| Complex | Absorption Maximum λabs (nm) (Molar Absorptivity ε (M−1 cm−1)) | Emission Maximum λem (nm) | Emission Decay Time Τ (ns) a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 375 (4600), 262 (27,600) | 630 | 60 |
| 2 | 375 (3600), 262 (24,100) | 630 | 60 |
| 3 | 375 (4400), 262 (29,000) | - | - |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skiba, J.; Bernaś, T.; Trzybiński, D.; Woźniak, K.; Ferraro, G.; Marasco, D.; Merlino, A.; Shafikov, M.Z.; Czerwieniec, R.; Kowalski, K. Mitochondria Targeting with Luminescent Rhenium(I) Complexes. Molecules 2017, 22, 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050809
Skiba J, Bernaś T, Trzybiński D, Woźniak K, Ferraro G, Marasco D, Merlino A, Shafikov MZ, Czerwieniec R, Kowalski K. Mitochondria Targeting with Luminescent Rhenium(I) Complexes. Molecules. 2017; 22(5):809. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050809
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkiba, Joanna, Tytus Bernaś, Damian Trzybiński, Krzysztof Woźniak, Giarita Ferraro, Daniela Marasco, Antonello Merlino, Marsel Z. Shafikov, Rafał Czerwieniec, and Konrad Kowalski. 2017. "Mitochondria Targeting with Luminescent Rhenium(I) Complexes" Molecules 22, no. 5: 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050809
APA StyleSkiba, J., Bernaś, T., Trzybiński, D., Woźniak, K., Ferraro, G., Marasco, D., Merlino, A., Shafikov, M. Z., Czerwieniec, R., & Kowalski, K. (2017). Mitochondria Targeting with Luminescent Rhenium(I) Complexes. Molecules, 22(5), 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050809










