Asperpyrone-Type Bis-Naphtho-γ-Pyrones with COX-2–Inhibitory Activities from Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus niger
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
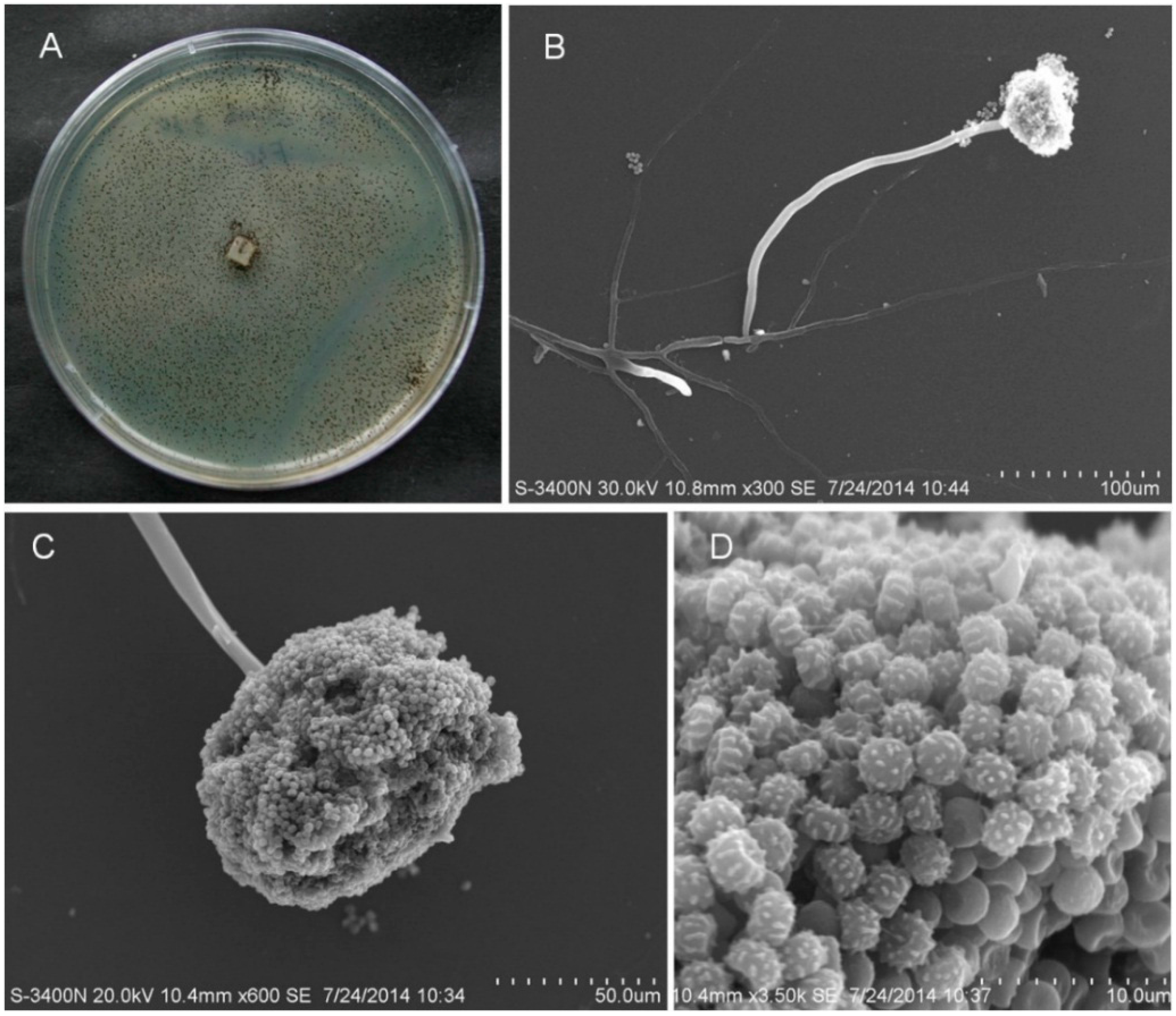
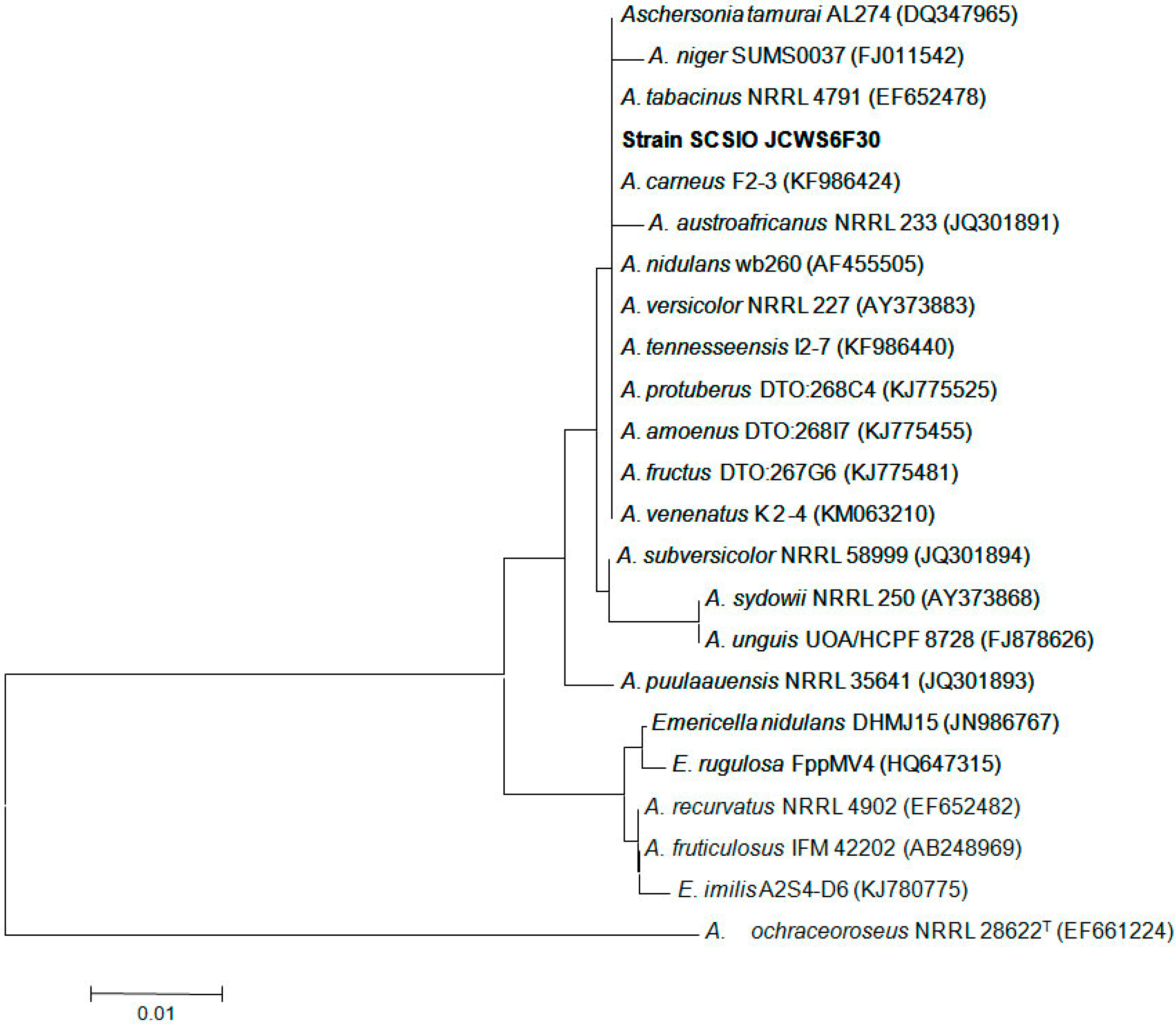
2.1. Characterization and Identification of Isolated Strain SCSIO Jcsw6F30
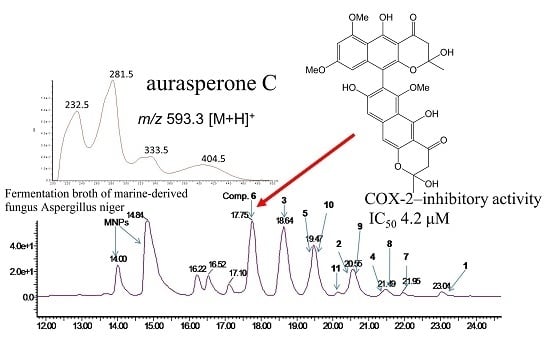
2.2. HPLC/MS Analysis of Crude Extract of the Fermentation Broth
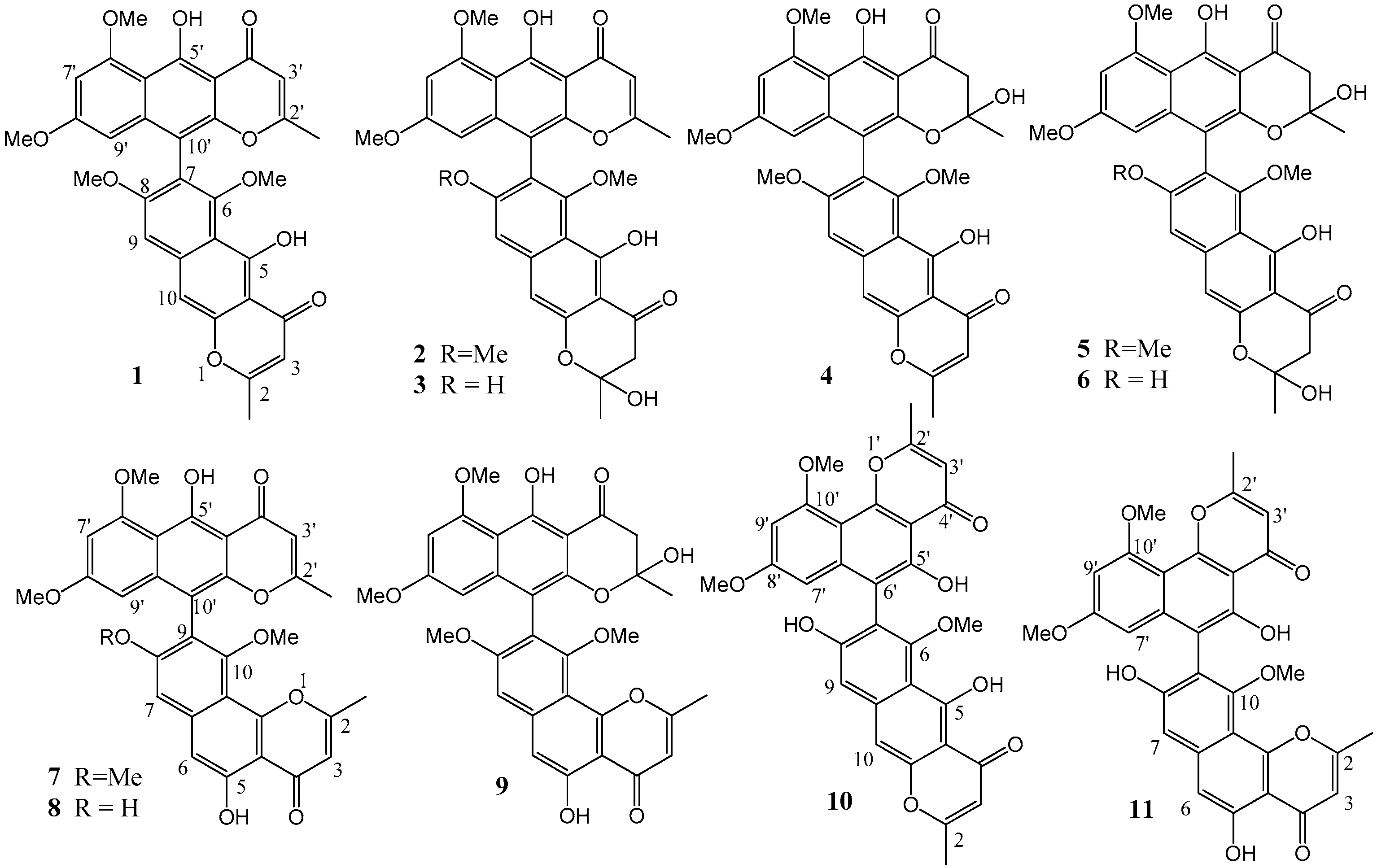
2.3. Structural Elucidation
2.4. Bioactivities
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cultural and Morphological Properties of Strain SCSIO Jcsw6F30
4.2. ITS Region Sequence and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.3. Fermentation and Extraction
4.4. HPLC/MS Analysis and Isolation of the Compounds
4.5. Bioassays
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BNPs | bis-naphtho-γ-pyrones |
| COX | cyclooxygenase |
| CC | column chromatography |
| NSAIDs | nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
| HPLC/MS | high performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometer |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance |
References
- Flewelling, A.J.; Currie, J.; Gray, C.A.; Johnson, J.A. Endophytes from marine macroalgae: Promising sources of novel natural products. Curr. Sci. India 2015, 109, 88–111. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, K.F.; Mogensen, J.M.; Johansen, M.; Larsen, T.O.; Frisvad, J.C. Review of secondary metabolites and mycotoxins from the Aspergillus niger group. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 1225–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choque, E.; El Rayess, Y.; Raynal, J.; Mathieu, F. Fungal naphtho-gamma-pyronessecondary metabolites of industrial interest. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2015, 99, 1081–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.Q.; Tian, J.; Sun, W.B.; Meng, J.J.; Wang, X.H.; Fu, X.X.; Wang, A.L.; Lai, D.W.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.G. Bis-naphtho-gamma-pyrones from fungi and their bioactivities. Molecules 2014, 19, 7169–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blobaum, A.L.; Uddin, M.J.; Felts, A.S.; Crews, B.C.; Rouzer, C.A.; Marnett, L.J. The 2’-trifluoromethyl analogue of indomethacin is a potent and selective COX-2 inhibitor. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onions, A.H.S. Aspergillus niger. CMI Descr. Pathog. Fungi Bact. 1966, 94, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, F.R.; Barison, A.; Daolio, C.; Ferreira, A.G.; Rodrigues-Fo, E. Spectral assignments and reference data—Complete H-1 and C-13 NMR assignments of aurasperone A and fonsecinone A, two bis-naphthopyrones produced by Aspergillus aculeatus. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2005, 43, 962–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, J.X.; Gunaherath, G.M.K.B.; Wijeratne, E.M.K.; Gunatilaka, A.A.L. Asperpyrone D and other metabolites of the plant-associated fungal strain Aspergillus tubingensis. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.M.; Wang, B.G. Nigerasperones A-C, new monomeric and dimeric naphtho-gamma-pyrones from a marine alga-derived endophytic fungus Aspergillus niger EN-13. J. Antibiot. 2007, 60, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siriwardane, A.M.D.A.; Kumar, N.S.; Jayasinghe, L.; Fujimoto, Y. Chemical investigation of metabolites produced by an endophytic Aspergillus sp. isolated from Limonia acidissima. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 1384–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouras, N.; Mathieu, F.; Coppel, Y.; Lebrihi, A. Aurasperone F—A new member of the naphtho-gamma-pyrone class isolated from a cultured microfungus, Aspergillus niger C-433. Nat. Prod. Res. 2005, 19, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priestap, H.A. New naphthopyrones from Aspergillus fonsecaeus. Tetrahedron 1984, 40, 3617–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, K.; Teraguchi, S.; Hamasaki, Y.; Mori, M.; Tatsumi, K.; Ohnishi, K.; Hayashi, H. New dimeric naphthopyrones from Aspergillus niger. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.B.; Xie, F.; Liu, S.S.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.C.; Liu, Y.Q.; Yuan, H.Q.; Lou, H.X. Naphtho-gamma-pyrones from endophyte Aspergillus niger occurring in the liverwort Heteroscyphus tener (STEPH.) SCHIFFN. Chem. Biodivers. 2013, 10, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjer, J.; Debbab, A.; Aly, A.H.; Proksch, P. Methods for isolation of marine-derived endophytic fungi and their bioactive secondary products. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawato, M.; Shinobu, R. On Streptomyces herbaricolor sp. nov., supplement: A single technique for microscopical observation. Mem. Osaka Unit Lib. Arts Educ. B Nat. Sci. 1959, 8, 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.H.; Liu, Z.H.; Qian, Y.D.; Kim, S.B.; Goodfellow, M. Saccharopolyspora spinosporotrichia sp. nov., a novel actinomycete from soil. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1998, 48, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.; Lin, X.; Zhou, X.; Wan, J.; Lu, X.; Yang, B.; Ai, W.; Lin, J.; Zhang, T.; Tu, Z.; Liu, Y. Cytotoxic and antiviral nitrobenzoylses quiterpenoids from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus ochraceus Jcma1F17. MedChemComm 2014, 5, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Fang, W.; Tan, S.; Lin, X.; Xun, T.; Yang, B.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y. Aspernigrins with anti-HIV-1 activities from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus niger SCSIO Jcsw6F30. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, W.; Lin, X.P.; Tu, Z.; Tian, X.P.; Lu, X.; Mangaladoss, F.; Zhong, Z.L.; Liu, Y. Axinelline A, a new COX-2 inhibitor from Streptomyces axinellae SCSIO02208. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1–11 are available from the authors.

© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, W.; Lin, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Tao, H.; Zhou, X. Asperpyrone-Type Bis-Naphtho-γ-Pyrones with COX-2–Inhibitory Activities from Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus niger. Molecules 2016, 21, 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070941
Fang W, Lin X, Wang J, Liu Y, Tao H, Zhou X. Asperpyrone-Type Bis-Naphtho-γ-Pyrones with COX-2–Inhibitory Activities from Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus niger. Molecules. 2016; 21(7):941. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070941
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Wei, Xiuping Lin, Jianjiao Wang, Yonghong Liu, Huaming Tao, and Xuefeng Zhou. 2016. "Asperpyrone-Type Bis-Naphtho-γ-Pyrones with COX-2–Inhibitory Activities from Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus niger" Molecules 21, no. 7: 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070941
APA StyleFang, W., Lin, X., Wang, J., Liu, Y., Tao, H., & Zhou, X. (2016). Asperpyrone-Type Bis-Naphtho-γ-Pyrones with COX-2–Inhibitory Activities from Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus niger. Molecules, 21(7), 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070941