Processes 2023, 11(3), 736; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11030736 - 1 Mar 2023
Cited by 25 | Viewed by 5900
Abstract
Jasmonates (JAs) are phospholipid-derived hormones that regulate plant development and responses to environmental stress. The synthesis of JAs and the transduction of their signaling pathways are precisely regulated at multiple levels within and outside the nucleus as a result of a combination of
[...] Read more.
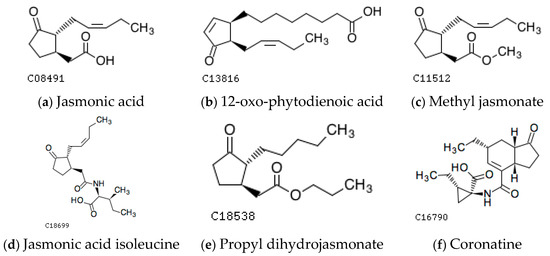
Jasmonates (JAs) are phospholipid-derived hormones that regulate plant development and responses to environmental stress. The synthesis of JAs and the transduction of their signaling pathways are precisely regulated at multiple levels within and outside the nucleus as a result of a combination of genetic and epigenetic regulation. In this review, we focus on recent advances in the regulation of JA biosynthesis and their signaling pathways. The biosynthesis of JAs was found to be regulated with an autocatalytic amplification mechanism via the MYC2 regulation pathway and inhibited by an autonomous braking mechanism via the MYC2-targeting bHLH1 protein to terminate JA signals in a highly ordered manner. The biological functions of JAs mainly include the promotion of fruit ripening at the initial stage via ethylene-dependent and independent ways, the regulation of mature coloring via regulating the degradation of chlorophyll and the metabolism of anthocyanin, and the improvement of aroma components via the regulation of fatty acid and aldehyde alcohol metabolism in agricultural crops. JA signaling pathways also function in the enhancement of biotic and abiotic stress resistance via the regulation of secondary metabolism and the redox system, and they relieve cold damage to crops through improving the stability of the cell membrane. These recently published findings indicate that JAs are an important class of plant hormones necessary for regulating plant growth and development, ripening, and the resistance to stress in agricultural crops and products.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Agriculture Products Processing and Storage)
►
Show Figures