Antibiotics 2023, 12(3), 479; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12030479 - 28 Feb 2023
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3048
Abstract
Klebsiella pneumoniae is an opportunistic pathogen that frequently causes nosocomial and community-acquired (CA) infections. Until now, a limited number of studies has been focused on the analyses of changes affecting the virulence attributes. Genotypic and phenotypic methods were used to characterise the 39
[...] Read more.
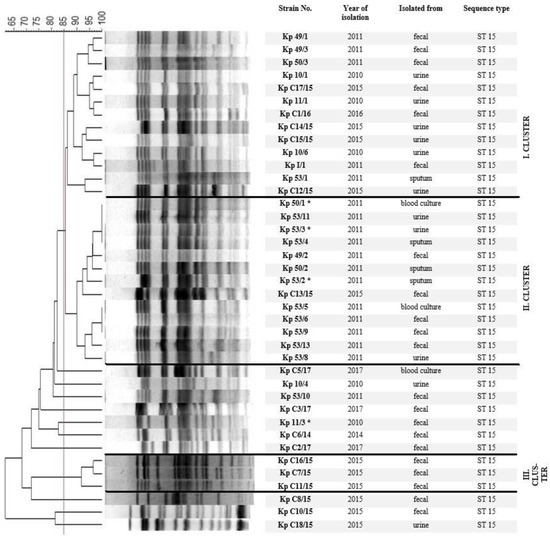
Klebsiella pneumoniae is an opportunistic pathogen that frequently causes nosocomial and community-acquired (CA) infections. Until now, a limited number of studies has been focused on the analyses of changes affecting the virulence attributes. Genotypic and phenotypic methods were used to characterise the 39 clinical K. pneumoniae isolates; all belonged to the pan-drug resistant, widespread clone ST 15 and expressed the K24 capsule. PFGE has revealed that the isolates could be divided into three distinct genomic clusters. All isolates possessed allS and uge genes, known to contribute to the virulence of K. pneumoniae and 10.25% of the isolates showed hypermucoviscosity, 94.87% produced type 1 fimbriae, 92.3% produced type 3 fimbriae, and 92.3% were able to produce biofilm. In vivo persistence could be supported by serum resistance 46.15%, enterobactin (94.87%) and aerobactin (5.12%) production and invasion of the INT407 and T24 cell lines. Sequence analysis of the whole genomes of the four representative strains 11/3, 50/1, 53/2 and 53/3 has revealed high sequence homology to the reference K. pneumoniae strain HS11286. Our results represent the divergence of virulence attributes among the isolates derived from a common ancestor clone ST 15, in an evolutionary process that occurred both in the hospital and in the community.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mechanism of Carbapenem Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae, Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas aeruginosa)
►
Show Figures