Agriculture 2023, 13(10), 1995; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13101995 - 13 Oct 2023
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 1975
Abstract
The limitation on the prophylactic use of antibiotics in animal feed in Europe has critically challenged the rabbit meat industry, which urgently needs to find solutions. A feasible alternative could be using macroalgae in the diet to improve the gut health. This research
[...] Read more.
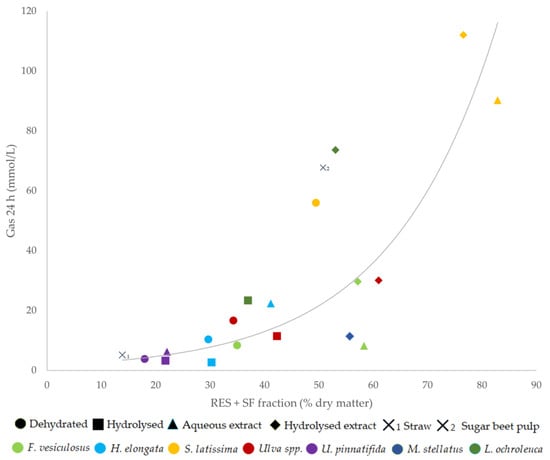
The limitation on the prophylactic use of antibiotics in animal feed in Europe has critically challenged the rabbit meat industry, which urgently needs to find solutions. A feasible alternative could be using macroalgae in the diet to improve the gut health. This research studied seven species of marine macroalgae in four formats (dehydrated, enzymatically hydrolyzed, aqueous extract, and aqueous extract of hydrolyzed macroalgae) in order to select the most promising ones for their use in rabbit feed. Chemical composition, in vitro digestibility, in vitro caecal gas, total volatile fatty acid (VFA) production, and minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC) against common pathogens were studied. All S. latissima products showed high caecal fermentability and VFA production, especially in both types of extracts. The H. elongata aqueous extract was remarkable due to its high in vitro butyrate production, which can be of great interest for improving gut health. The MIC results did not indicate any clear inhibition of the pathogens tested. The macroalgae tested appear to have a potentially prebiotic effect, rather than a direct antimicrobial activity. However, these results must be confirmed in vivo, in order to observe the real benefits of feeding macroalgae during the rabbit weaning period.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Precision Feeding and Management of Farm Animals)
►
Show Figures