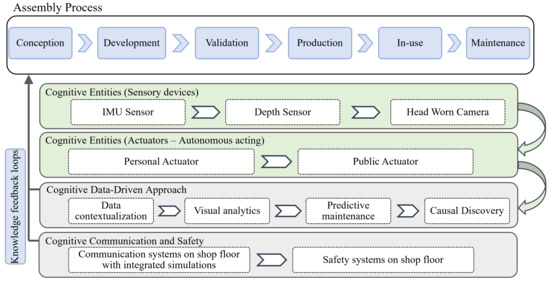
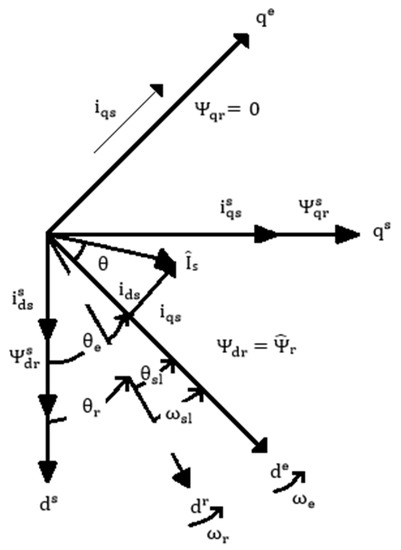
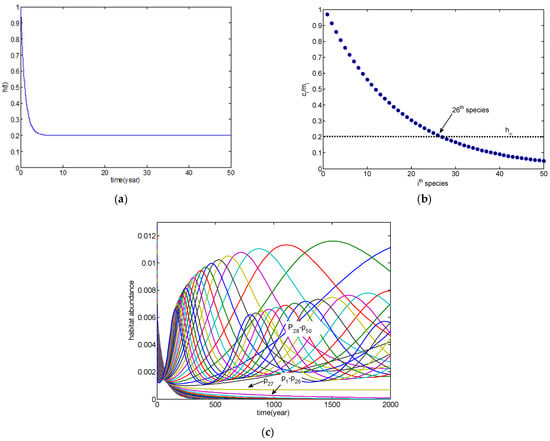
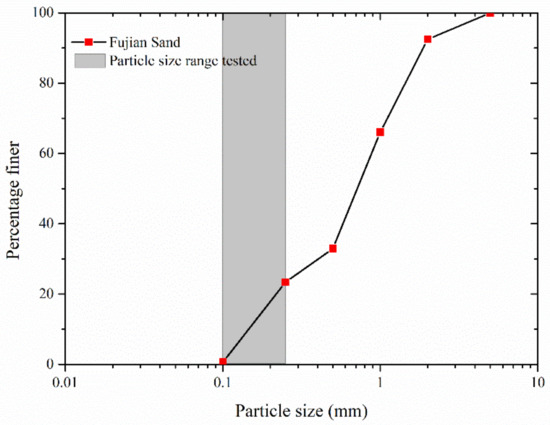
Appl. Sci. 2022, 12(17), 8699; https://doi.org/10.3390/app12178699 - 30 Aug 2022
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 2737
Abstract
The aim of this research was to evaluate the essential oils of two medicinal plants from Djibouti: Cymbopogon schoenanthus (L.) Spreng. and Nepeta azurea R.Br. ex Benth. in cytotoxic activity against thirteen (13) cancer cell lines (A2780, A549, HCT116, HEK-293, JIMT-T1, K562, MIA-Paca2,
[...] Read more.
The aim of this research was to evaluate the essential oils of two medicinal plants from Djibouti: Cymbopogon schoenanthus (L.) Spreng. and Nepeta azurea R.Br. ex Benth. in cytotoxic activity against thirteen (13) cancer cell lines (A2780, A549, HCT116, HEK-293, JIMT-T1, K562, MIA-Paca2, MRC5, NCI-N87, PC3, RT4, U2OS and U87-MG) and antibacterial activity against seven (7) Gram (−) strains (Acinetobacter baumannii, Enterobacter cloacae, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella enterica sv. Typhimurium and Shigella sonnei) and five (5) Gram (+) strains (Corynebacterium sp., Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis and Streptococcus agalactiae). The plants were extracted by hydrodistillation and were analyzed by GC-MS. The main components of Cymbopogon schoenanthus essential oil (CSEO) were 3-isopropenyl-5-methyl-1-cyclohexene (32.3%) and D-Limonene (11.3%), and the main component of Nepeta azurea essential oil (NAEO) was methyl (2E)-2-nonenoate (53.2%). The two essential oils showed inhibitory cytotoxicity activities of all the cancer cells tested; on the other hand, the antibacterial activities are only well-noticed for the CSEO oil at a concentration of 5% against Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Corynebacterium sp., Enterococcus faecalis and Staphylococcus aureus. Our results demonstrated that the two essential oils could be effective natural anticancer agents, in addition to an antibacterial character for Cymbopogon schoenanthus essential oil.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Applied Biosciences and Bioengineering)
►
Show Figures