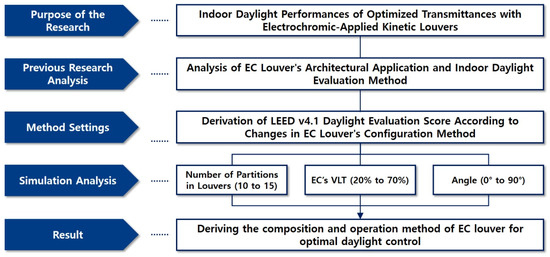
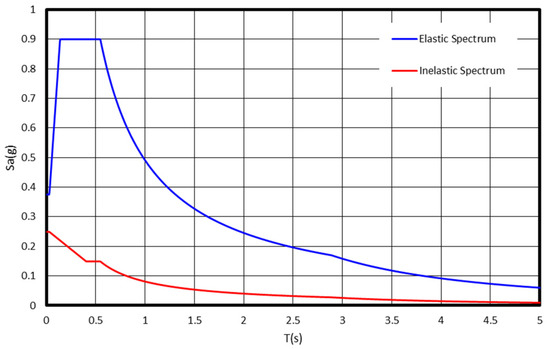
Buildings 2022, 12(3), 268; https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12030268 - 24 Feb 2022
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2709
Abstract
An analytical three-dimensional slope reliability evaluation framework was developed in this work independent of use of numerical simulations. The slope stability analysis was necessarily carried out by utilizing an extended three-dimensional Morgenstern–Price method, which was characterized by analytical formulations and competitive computational efficiency.
[...] Read more.
An analytical three-dimensional slope reliability evaluation framework was developed in this work independent of use of numerical simulations. The slope stability analysis was necessarily carried out by utilizing an extended three-dimensional Morgenstern–Price method, which was characterized by analytical formulations and competitive computational efficiency. Incorporation of the presented stability analysis method into response surface methodology led to an effective slope reliability evaluation framework. The applicability and superiority of this framework was examined and validated using a real complicated landslide case reported in practice, and a hypothetical slope example widely adopted in the literature. The impact of correlation coefficients and probability distribution patterns on the slope reliability assessment results was further addressed to derive additional benefits of this framework.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Impact of Building Materials on Construction Sustainability)
►
Show Figures