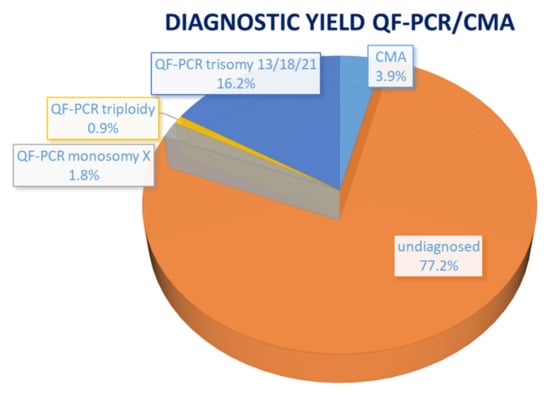
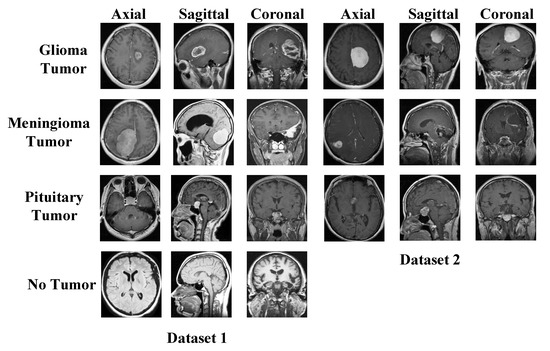
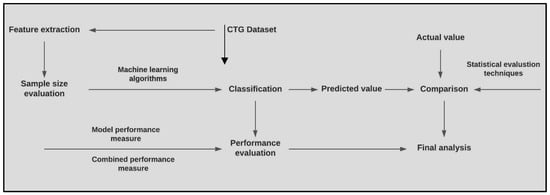
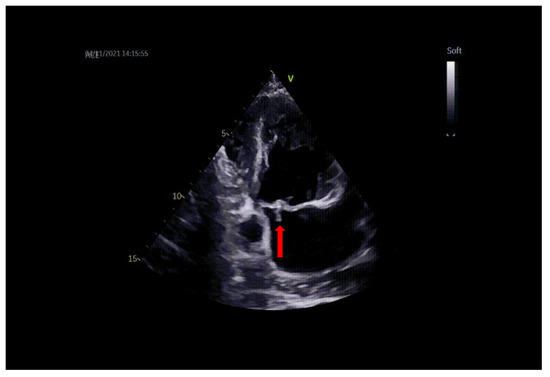
Diagnostics 2023, 13(5), 869; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13050869 - 24 Feb 2023
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2322
Abstract
This study aims to investigate hard and soft tissue asymmetry in skeletal Class III patients to elucidate how soft tissue thickness alters overall asymmetry and whether menton deviation is correlated with bilateral differences in hard and soft tissue prominence and soft tissue thickness.
[...] Read more.
This study aims to investigate hard and soft tissue asymmetry in skeletal Class III patients to elucidate how soft tissue thickness alters overall asymmetry and whether menton deviation is correlated with bilateral differences in hard and soft tissue prominence and soft tissue thickness. The cone-beam computed tomography data of 50 skeletal Class III adults were divided based on menton deviation into symmetric (n = 25; deviation ≤ 2.0 mm) and asymmetric (n = 25; deviation > 2.0 mm) groups. Forty-four corresponding hard and soft tissue points were identified. Bilateral hard and soft tissue prominence and soft tissue thickness were compared using paired t-tests. The correlations between bilateral differences in these variables and menton deviation were examined using Pearson’s correlation analysis. In the symmetric group, no significant bilateral differences in soft and hard tissue prominence and soft tissue thickness were observed. In the asymmetric group, both hard and soft tissue prominence were significantly greater on the deviated side than the non-deviated side at most of the points; however, no significant differences in soft tissue thickness were detected except at point 9 (ST9/ST’9, p = 0.011). The difference of hard and soft tissue prominence at point 8 (H8/H’8 and S8/S’8) was positively correlated with menton deviation, whereas the soft tissue thickness at point 5 (ST5/ST’5) and point 9 (ST9/ST’9) was negatively correlated with menton deviation (p = 0.05). Soft tissue thickness does not affect overall asymmetry in the presence of underlying hard tissue asymmetry. Soft tissue thickness at the centre of the ramus may be correlated with the degree of menton deviation in patients with asymmetry; however, this correlation needs to be confirmed by further studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Insights into Diagnosis of Orthodontics)
►
Show Figures