Cancers 2023, 15(6), 1659; https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061659 - 8 Mar 2023
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 1883
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) represents a relevant disease burden in cirrhotic patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). We aimed to investigate the prognostic value of simple non-invasive tests (NITs) (AAR, APRI, BARD, FIB-4) for the stratification of HCC risk development in a cohort
[...] Read more.
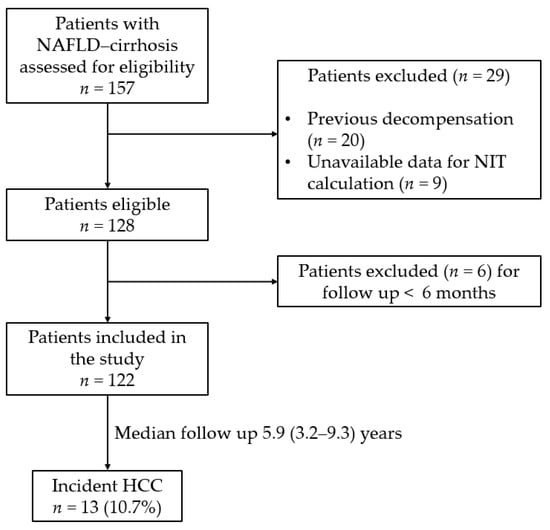
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) represents a relevant disease burden in cirrhotic patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). We aimed to investigate the prognostic value of simple non-invasive tests (NITs) (AAR, APRI, BARD, FIB-4) for the stratification of HCC risk development in a cohort of 122 consecutive cirrhotic individuals with NAFLD. Over a median follow up of 5.9 (3.2–9.3) years, 13 (10.7%) developed HCC. Only FIB-4 was associated with HCC risk (HR = 1.27, 95% CI 1.03–1.58, p = 0.027). After evaluating different established FIB-4 cut-offs, the lowest cut-off of 1.45 allowed the ruling out of a greater number of patients with a minimal risk of HCC than the 1.3 cut-off (23 vs. 18 patients). Conversely, the cumulative incidence of HCC using the highest cut-off of 3.25 (rule in) was distinctly higher than the 2.67 cut-off (19.4% vs. 13.3%). After multivariate Cox regression analysis, these cut-offs were independently associated with HCC after adjusting for sex, BMI and T2DM (HR = 6.40, 95% CI 1.71–24.00, p = 0.006). In conclusion, FIB-4 values of <1.3 and >3.25 could allow for the optimal stratification of long-term HCC risk in cirrhotic individuals with NAFLD.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Advances and Challenges in Research and Treatment)
►
Show Figures