Sustainability 2022, 14(9), 5652; https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095652 - 7 May 2022
Cited by 24 | Viewed by 6646
Abstract
Carwash wastewater (CWW) contains grease, oil, hydrocarbon residues, heavy metals, and surfactants, posing severe impacts to the environment and human health. Accordingly, various physical, chemical, and biological processes for CWW treatment have been demonstrated in recent research. In this study, a bibliometric approach
[...] Read more.
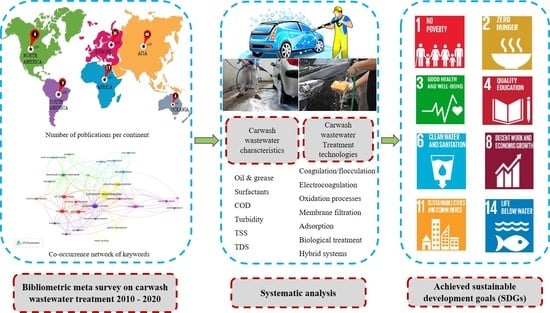
Carwash wastewater (CWW) contains grease, oil, hydrocarbon residues, heavy metals, and surfactants, posing severe impacts to the environment and human health. Accordingly, various physical, chemical, and biological processes for CWW treatment have been demonstrated in recent research. In this study, a bibliometric approach was performed to comprehensively illustrate the recent progress, current direction, and future perspectives of CWW-related research. A keyword co-occurrence network was used to represent the results of the bibliometric analysis and to show the major pollutants in CWW effluents and the common systems for treating CWW via coagulation/flocculation, electrochemical, oxidation, membrane, adsorption, biological, and hybrid methods. An integrated anaerobic digestion/oxidation process has been reported to degrade CWW-associated pollutants and help develop an energy-efficient approach for waste management. The results demonstrated that the treatment of CWW has several benefits relevant to sustainable development, viz., good health and well-being, protection of life below water, bioenergy generation, and community awareness and acceptance towards wastewater reuse. Hence, these benefits could assist in meeting the environmental, economic, and social sustainable development goals (SDGs). These study outputs can encourage policymakers and stakeholders in implementing sensible regulations that control water usage and treatment in car sharing and personal vehicle services to either directly or indirectly adopt the agenda 2030 with its seventeen SDGs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Use and Management of Nonconventional Water Resources for Agricultural Development)
►
Show Figures