1
College of Ecology and the Environment, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361102, China
2
Advanced Membrane Technology Research Centre (AMTEC), School of Chemical and Energy Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Skudai, Johor Baru 81310, Malaysia
3
School of Electrical Engineering, Guangxi University, Nanning 530004, China
4
Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Diponegoro University, Semarang 50275, Indonesia
5
Department Chemistry, School of Science, University of Management and Technology, Lahore 54770, Pakistan
6
School of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 637459, Singapore
Sustainability 2022, 14(24), 16847; https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416847 - 15 Dec 2022
Cited by 70 | Viewed by 12381
Abstract
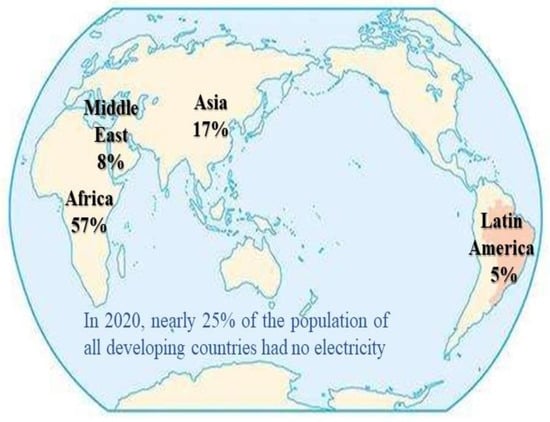
Currently, access to electricity in the cities of the Global South is so limited that electrification remains low in rural areas. Unless properly tackled, one-third of the world’s cities will suffer from energy scarcity. The emergence of microbial fuel cell (MFC) technology accelerates
[...] Read more.
Currently, access to electricity in the cities of the Global South is so limited that electrification remains low in rural areas. Unless properly tackled, one-third of the world’s cities will suffer from energy scarcity. The emergence of microbial fuel cell (MFC) technology accelerates the deployment of decentralized and sustainable energy solutions that can address the looming energy shortage. This review consolidates scattered knowledge into one article about the performance of MFC in optimizing electricity generation from phosphorus (P)-laden wastewater, while removing the target nutrient from wastewater simultaneously. It is obvious from a literature survey of 108 published articles (1999–2022) that the applications of MFC for building a self-powered municipal water treatment system represents an important breakthrough, as this enables water treatment operators to generate electricity without affecting the atmospheric balance of CO2. Using a pyrite-based wetland MFC, about 91% of P was removed after operating 180 days, while generating power output of 48 A/m2. Unlike other techniques, MFCs utilize bacteria that act as micro-reactors and allow substrates to be oxidized completely. The Earth’s tiniest inhabitants can efficiently transform the chemical energy of organic matter in unused wastewater either into hydrogen gas or electricity. This facilitates wastewater treatment plants powering themselves in daily operation or selling electricity on the market. This MFC technology radically changes how to treat wastewater universally. By exploring this direction along the water–energy–food nexus, MFC technology could transform wastewater treatment plants into a key sustainability tool in the energy sector. This suggests that MFCs provide a practical solution that addresses the need of global society for clean water and electricity simultaneously.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Frontiers in Bio-Energy Production and Applications)
▼
Show Figures