Sustainability 2020, 12(15), 6156; https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156156 - 30 Jul 2020
Cited by 23 | Viewed by 6008
Abstract
Sustainable development is a priority for the future of our society. Sustainable development is of particular importance to the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry, both for new buildings and for the renovation of existing buildings. Great potential for sustainable development lies in
[...] Read more.
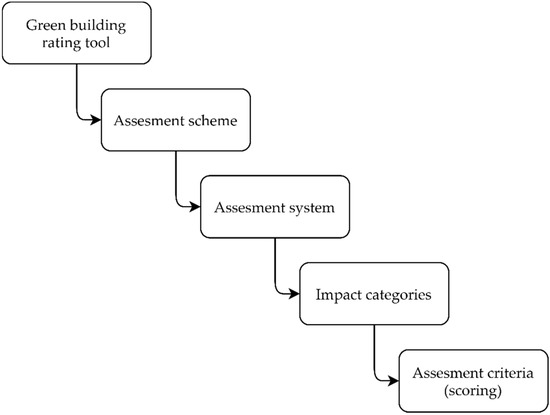
Sustainable development is a priority for the future of our society. Sustainable development is of particular importance to the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry, both for new buildings and for the renovation of existing buildings. Great potential for sustainable development lies in the renovation of existing office buildings. This paper introduces a new framework for identifying the best set of renovation strategies for existing office buildings. The framework applies selected green building rating system criteria and cost-effective sustainable renovation solutions based on cost-benefit analysis (CBA), and thus provides a novelty in decision-making support for the sustainable renovation of office buildings at an early-stage. The framework covers all necessary steps and activities including data collection, determination of the required level of renovation, selection of the green building rating system, identification of impact categories and criteria, and final evaluation and decision-making using CBA. The framework can be used in conjunction with different systems and according to different regional characteristics. The applicability of the addressing procedure is shown through a case study of a comprehensive renovation of an office building in the city of Maribor.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Sustainable Consumption and Production)
►
Show Figures