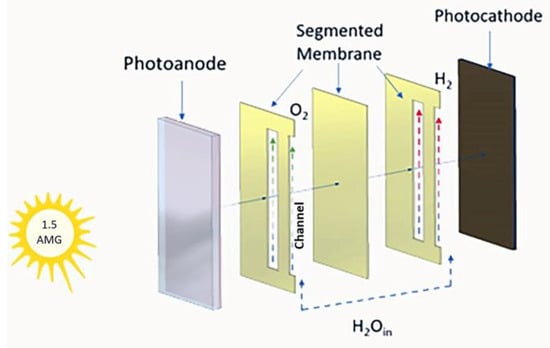
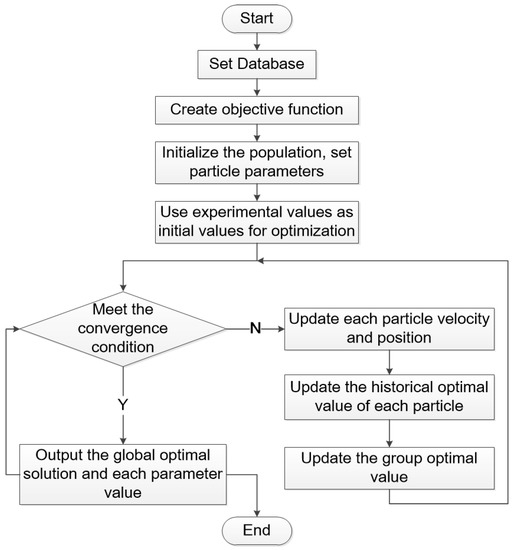
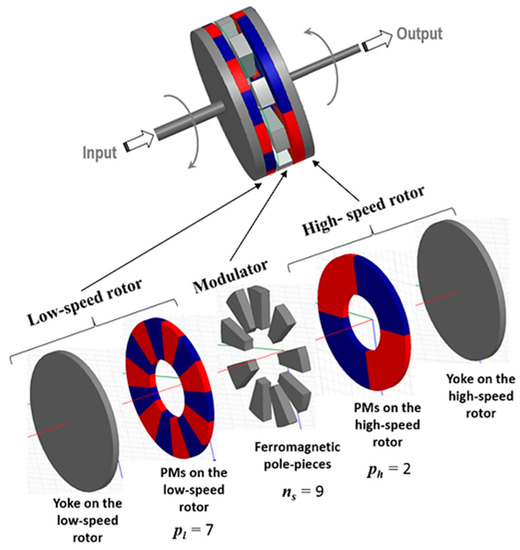
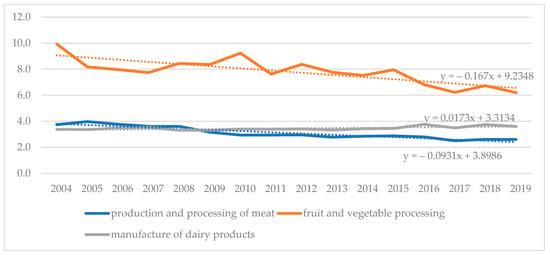
Energies 2023, 16(4), 1620; https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041620 - 6 Feb 2023
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 2195
Abstract
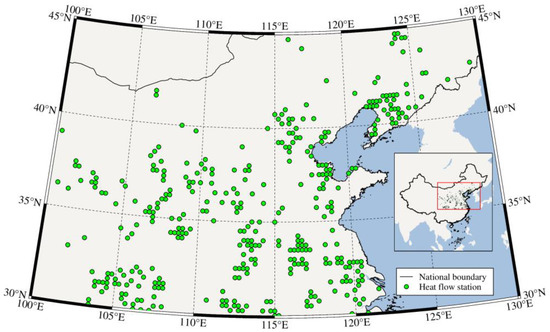
Geothermal heat flow is an essential parameter for the exploration of geothermal energy. The cost is often prohibitive if dense heat flow measurements are arranged in the study area. Regardless, an increase in the limited and sparse heat flow observation points is needed
[...] Read more.
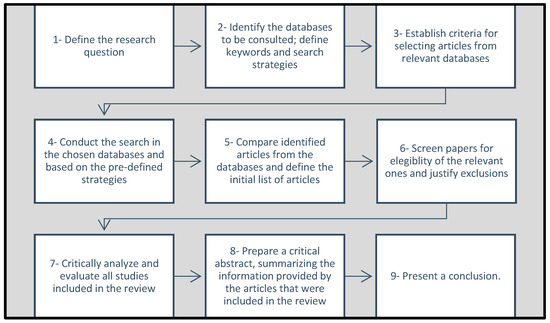
Geothermal heat flow is an essential parameter for the exploration of geothermal energy. The cost is often prohibitive if dense heat flow measurements are arranged in the study area. Regardless, an increase in the limited and sparse heat flow observation points is needed to study the regional geothermal setting. This research is significant in order to provide a new reliable map of terrestrial heat flow for the subsequent development of geothermal resources. The Gradient Boosted Regression Tree (GBRT) prediction model used in this paper is devoted to solving the problem of an insufficient number of heat flow observations in North China. It considers the geological and geophysical information in the region by training the sample data using 12 kinds of geological and geophysical features. Finally, a robust GBRT prediction model was obtained. The performance of the GBRT method was evaluated by comparing it with the kriging interpolation, the minimum curvature interpolation, and the 3D interpolation algorithm through the prediction performance analysis. Based on the GBRT prediction model, a new heat flow map with a resolution of 0.25°×0.25° was proposed, which depicted the terrestrial heat flow distribution in the study area in a more detailed and reasonable way than the interpolation results. The high heat flow values were mostly concentrated in the northeastern boundary of the Tibet Plateau, with a few scattered and small-scale high heat flow areas in the southeastern part of the North China Craton (NCC) adjacent to the Pacific Ocean. The low heat flow values were mainly resolved in the northern part of the Trans-North China Orogenic belt (TNCO) and the southmost part of the NCC. By comparing the predicted heat flow map with the plate tectonics, the olivine-Mg#, and the hot spring distribution in North China, we found that the GBRT could obtain a reliable result under the constraint of geological and geophysical information in regions with scarce and unevenly distributed heat flow observations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Artificial Intelligence and Computational Methods: Modeling, Simulations and Optimization of Complex Systems)
►
Show Figures